Control of Hepatic Gluconeogenesis During the Transition Period
... The importance of gluconeogenesis, a metabolic pathway that results in formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates, is underscored in dairy cattle by to the lack of intestinal glucose absorption that occurs as a consequence of the extensive fermentation of free dietary carbohydrate ...
... The importance of gluconeogenesis, a metabolic pathway that results in formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates, is underscored in dairy cattle by to the lack of intestinal glucose absorption that occurs as a consequence of the extensive fermentation of free dietary carbohydrate ...
4.6 Fermentation
... when oxygen is unavailable. • Fermentation is an anaerobic process. – occurs when oxygen is not available for cellular respiration – does not produce ATP ...
... when oxygen is unavailable. • Fermentation is an anaerobic process. – occurs when oxygen is not available for cellular respiration – does not produce ATP ...
- Wiley Online Library
... LevU) into glucose and fructose (or levan). The two hexoses can enter the cell via the common uniport system (GLF) or are converted by the periplasmic GFOR into sorbitol and gluconolactone. Sorbitol is transported into the cell by an accumulative system (sorbitol carrier [24]), gluconate uptake is n ...
... LevU) into glucose and fructose (or levan). The two hexoses can enter the cell via the common uniport system (GLF) or are converted by the periplasmic GFOR into sorbitol and gluconolactone. Sorbitol is transported into the cell by an accumulative system (sorbitol carrier [24]), gluconate uptake is n ...
University: Suez Canal University Faculty of Medicine Course
... dialysis, electrophoresis, chromatography and sequencing. 8. Describe how are the proteins digested and absorbed and describe defects in these processes may lead to disease. 9. Explain how insulin and glucocorticoids contribute to protein and nitrogen balance. 10. Describe in details and with formul ...
... dialysis, electrophoresis, chromatography and sequencing. 8. Describe how are the proteins digested and absorbed and describe defects in these processes may lead to disease. 9. Explain how insulin and glucocorticoids contribute to protein and nitrogen balance. 10. Describe in details and with formul ...
Albumin from bovine serum (A4919) - Product - Sigma
... 40 mg/mL and obtains clear to very slightly hazy, faint yellow solutions. The solution stability of BSA is very good (especially if the solutions are stored as frozen aliquots). In fact, albumins are frequently used as stabilizers for other solubilized proteins (e.g., labile enzymes). However, album ...
... 40 mg/mL and obtains clear to very slightly hazy, faint yellow solutions. The solution stability of BSA is very good (especially if the solutions are stored as frozen aliquots). In fact, albumins are frequently used as stabilizers for other solubilized proteins (e.g., labile enzymes). However, album ...
Nitrogenous Wastes
... form a white paste or powder; it is excreted by birds, insects, and reptiles. Conversion of ammonia to uric acid requires more energy and is much more complex than conversion of ammonia to urea Figure 2. ...
... form a white paste or powder; it is excreted by birds, insects, and reptiles. Conversion of ammonia to uric acid requires more energy and is much more complex than conversion of ammonia to urea Figure 2. ...
Biology
... Factors Affecting Photosynthesis Many factors affect the rate of photosynthesis, including: ...
... Factors Affecting Photosynthesis Many factors affect the rate of photosynthesis, including: ...
C274/SQP363 NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS Biology
... 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of this information is wrong, tell the Invigilator immediately. 5 If this information is correct, print ...
... 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of this information is wrong, tell the Invigilator immediately. 5 If this information is correct, print ...
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes
... The energy source for muscle contractions is ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Energy is released by the reaction ATP -----> ADP + P + energy. This reaction is reversible. ATP is available from several sources as the muscle begins to work: 1) ATP is available in the cell. This supply is very limited and ...
... The energy source for muscle contractions is ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Energy is released by the reaction ATP -----> ADP + P + energy. This reaction is reversible. ATP is available from several sources as the muscle begins to work: 1) ATP is available in the cell. This supply is very limited and ...
Sites of enzyme activity along the nephron
... [4]. Thus, knowledge of the intrarenal localization of metabolic pathways providing ATP would give more insight into the linkage between metabolism and transport processes. Fatty acids, ketone bodies, intermediates of the ...
... [4]. Thus, knowledge of the intrarenal localization of metabolic pathways providing ATP would give more insight into the linkage between metabolism and transport processes. Fatty acids, ketone bodies, intermediates of the ...
19-6-SA-V1-S1__mcq_a..
... hydrolytic cleavage of C-O, C-N, C-C and some other.: 51. biocatalyst which alters the rate of reaction without undergoing any permanent change in themselves 71. A non protein organic substance loosely attached to the enzyme and can be separated by dialysis and is essential for enzyme action. 79. __ ...
... hydrolytic cleavage of C-O, C-N, C-C and some other.: 51. biocatalyst which alters the rate of reaction without undergoing any permanent change in themselves 71. A non protein organic substance loosely attached to the enzyme and can be separated by dialysis and is essential for enzyme action. 79. __ ...
OMNI kit - EnzyPep
... Chemo-enzymatic peptide synthesis (CEPS), the enzymatic ligation of chemically synthesized peptide fragments, is potentially one of the most cost-efficient technologies for the synthesis of medium-sized and long peptides (e.g. 20-100 amino acids) and peptide-to-protein couplings. When compared to ch ...
... Chemo-enzymatic peptide synthesis (CEPS), the enzymatic ligation of chemically synthesized peptide fragments, is potentially one of the most cost-efficient technologies for the synthesis of medium-sized and long peptides (e.g. 20-100 amino acids) and peptide-to-protein couplings. When compared to ch ...
Carotenoids Biosynthesis – a review
... IPP is the fundamental C5 biosynthetic unit from which the carotenoids, and indeed all terpenoids, are constructed. However, an isomerization of IPP into dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) must occur before chain elongation can begin. ...
... IPP is the fundamental C5 biosynthetic unit from which the carotenoids, and indeed all terpenoids, are constructed. However, an isomerization of IPP into dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) must occur before chain elongation can begin. ...
(Enzymes Lecture Notes).
... 2. Others will accept a variety of substrates that have certain types of chemical similarity; will work better on some, poorer on others ...
... 2. Others will accept a variety of substrates that have certain types of chemical similarity; will work better on some, poorer on others ...
Biological Molecules Ch 2: Chemistry Comes to Life
... Triglycerides are so named because they are formed by a reaction between three fatty acid molecules and one ___________. ...
... Triglycerides are so named because they are formed by a reaction between three fatty acid molecules and one ___________. ...
Enzymes | Principles of Biology from Nature Education
... Enzymes lower activation energy of biochemical reactions, but the substrates still need to have enough kinetic energy to reach their transition state, allowing the reaction to occur. The temperature at which the enzyme works best is called the enzyme's optimum temperature. Lowering the temperature d ...
... Enzymes lower activation energy of biochemical reactions, but the substrates still need to have enough kinetic energy to reach their transition state, allowing the reaction to occur. The temperature at which the enzyme works best is called the enzyme's optimum temperature. Lowering the temperature d ...
Stoking the Brightest Fires of Life Among Vertebrates
... glycolytic pathway, the malate-aspartate shuttle for maintenance of high cytoplasmic [NAD+ ]/[NADH+ ] ratios during high rates of glycolytic flux, a carnitinedependent pathway for long-chain fatty acid oxidation, and high mitochondrial capacities for flux through the Krebs cycle, electron transport, ...
... glycolytic pathway, the malate-aspartate shuttle for maintenance of high cytoplasmic [NAD+ ]/[NADH+ ] ratios during high rates of glycolytic flux, a carnitinedependent pathway for long-chain fatty acid oxidation, and high mitochondrial capacities for flux through the Krebs cycle, electron transport, ...
Nucleus-Encoded Genes for Plastid
... Plastids are the organelles of plants and algae that house photosynthesis and many other biochemical pathways. Plastids contain a small genome, but most of their proteins are encoded in the nucleus and posttranslationally targeted to the organelle. When plants and algae lose photosynthesis, they vir ...
... Plastids are the organelles of plants and algae that house photosynthesis and many other biochemical pathways. Plastids contain a small genome, but most of their proteins are encoded in the nucleus and posttranslationally targeted to the organelle. When plants and algae lose photosynthesis, they vir ...
Transition
... 3. General acid-base catalysis • Specific acid-base catalysis involves H+ or OH- that diffuses into the catalytic center • General acid-base catalysis involves acids and bases other than H+ and OH• These other acids and bases facilitate transfer of H+ in the transition state • Histidine is often th ...
... 3. General acid-base catalysis • Specific acid-base catalysis involves H+ or OH- that diffuses into the catalytic center • General acid-base catalysis involves acids and bases other than H+ and OH• These other acids and bases facilitate transfer of H+ in the transition state • Histidine is often th ...
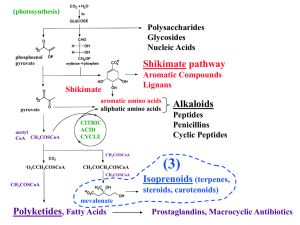
Lecture 03, NEW - terpenes + polyketides
... - provides a huge number of potential 3D structures - high degree of biological activity (3) Pathways can be elucidated using labeled precursors, such as mevalonate with a 13C at position 2 - carbon NMR experiments reveal where the label ends up in the completed molecule ...
... - provides a huge number of potential 3D structures - high degree of biological activity (3) Pathways can be elucidated using labeled precursors, such as mevalonate with a 13C at position 2 - carbon NMR experiments reveal where the label ends up in the completed molecule ...
Experimental illumination of a fitness landscape
... contacts remains an unmet challenge. EMPIRIC fitness measurements provide a high-throughput approach to identify these important interactions experimentally and, hence, a route to develop and train predictive algorithms with improved accuracy. Most of the other positions analyzed exhibit a preference ...
... contacts remains an unmet challenge. EMPIRIC fitness measurements provide a high-throughput approach to identify these important interactions experimentally and, hence, a route to develop and train predictive algorithms with improved accuracy. Most of the other positions analyzed exhibit a preference ...
S13DobrzanskiPoland
... Bakery yeasts (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) were incubated in the laboratory and pilot-plant-scale, in the presence of salts of Cr, Se and Zn according to the method described by Ryszka et al. (2002). The proposed method of yeasts production was characterized with the lack (or low amount) of liquid and ...
... Bakery yeasts (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) were incubated in the laboratory and pilot-plant-scale, in the presence of salts of Cr, Se and Zn according to the method described by Ryszka et al. (2002). The proposed method of yeasts production was characterized with the lack (or low amount) of liquid and ...
Essential Cell Biology (3rd ed.)
... by simple diffusion. But for cells to take up nutrients and release wastes, membranes must also allow the passage of many other molecules, such as ions, sugars, amino acids, nucleotides, and many cell metabolites. These molecules cross lipid bilayers far too slowly by simple diffusion; thus, special ...
... by simple diffusion. But for cells to take up nutrients and release wastes, membranes must also allow the passage of many other molecules, such as ions, sugars, amino acids, nucleotides, and many cell metabolites. These molecules cross lipid bilayers far too slowly by simple diffusion; thus, special ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.