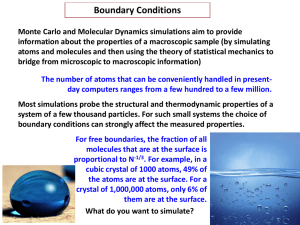
Module code SC-2242 Module Title Chemical Thermodynamics and
... Lower order: 30% - understand the concepts of enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs free energy - understand further the concepts of chemical thermodynamics with emphasis on phase equilibria and electrochemistry Middle order: 60% - define the terms and determine the change in enthalpy ...
... Lower order: 30% - understand the concepts of enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs free energy - understand further the concepts of chemical thermodynamics with emphasis on phase equilibria and electrochemistry Middle order: 60% - define the terms and determine the change in enthalpy ...
CHM 111: General Physical Chemistry 3 Units
... empirical gas laws, Ideal Gas Equation of State, qualitative treatment of kinetic theory of gases, real gases and deviations from ideal gas laws; liquid, macroscopic properties of liquids, evaporation, vapor pressure and its variation with temperature, boiling point, heat of vaporization, Clausius-C ...
... empirical gas laws, Ideal Gas Equation of State, qualitative treatment of kinetic theory of gases, real gases and deviations from ideal gas laws; liquid, macroscopic properties of liquids, evaporation, vapor pressure and its variation with temperature, boiling point, heat of vaporization, Clausius-C ...
7302 (Analytical Dynamics)
... techniques can be used to determine the behaviour of many physical systems. The mathematical framework also plays a role in the formulation of modern quantum and relativity theories. Topics studied are the kinematics of frames of reference (including rotating frames), dynamics of systems of particle ...
... techniques can be used to determine the behaviour of many physical systems. The mathematical framework also plays a role in the formulation of modern quantum and relativity theories. Topics studied are the kinematics of frames of reference (including rotating frames), dynamics of systems of particle ...
EN010 104 Engineering Mechanics
... Body – Continuum – Point force – Particle – Vector and Scalar quantities. Principles of Statics – Force Systems – Coplanar, Collinear, Concurrent and Parallel – Free body diagrams – Resolution of forces – Moment of a Force – Varignon’s Theorem – Couple – Resolution of a force into force couple syste ...
... Body – Continuum – Point force – Particle – Vector and Scalar quantities. Principles of Statics – Force Systems – Coplanar, Collinear, Concurrent and Parallel – Free body diagrams – Resolution of forces – Moment of a Force – Varignon’s Theorem – Couple – Resolution of a force into force couple syste ...
CHM 6461: Introduction to Statistical Thermodynamics, Spring 2016
... emphasis on molecular and chemical systems. We will introduce the probability and statistical laws, and derive thermodynamic relations from the statistical principles. Statistical mechanics connects the properties of the macroscopic material world to the basic constituents of matter at the deepest l ...
... emphasis on molecular and chemical systems. We will introduce the probability and statistical laws, and derive thermodynamic relations from the statistical principles. Statistical mechanics connects the properties of the macroscopic material world to the basic constituents of matter at the deepest l ...
Molecular Dynamics
... Observables, Statistics • Equilibrium temperature (in micro-canonical ensemble) by equipartition theorem. ...
... Observables, Statistics • Equilibrium temperature (in micro-canonical ensemble) by equipartition theorem. ...
Introduction to Statistical Thermodynamics - cryocourse 2011
... this work, Bernoulli positioned the argument, still used to this day, that gases consist of great numbers of molecules moving in all directions, that their impact on a surface causes the gas pressure that we feel, and that what we experience as heat is simply the kinetic energy of their motion. In 1 ...
... this work, Bernoulli positioned the argument, still used to this day, that gases consist of great numbers of molecules moving in all directions, that their impact on a surface causes the gas pressure that we feel, and that what we experience as heat is simply the kinetic energy of their motion. In 1 ...