Preferred Basis in a Measurement Process
... hence the elements of the density matrix corresponding to these two off-diagonal peaks are negligible in magnitude. Thus, position seems to emerge as an approximate preferred basis, which works well only when one is probing length scales which are much larger than λd . ...
... hence the elements of the density matrix corresponding to these two off-diagonal peaks are negligible in magnitude. Thus, position seems to emerge as an approximate preferred basis, which works well only when one is probing length scales which are much larger than λd . ...
0051_hsm11gmtr_07EM.indd
... Are the triangles similar? If yes, write a similarity statement and explain how you know they are similar – use a shortcut if you’d like. If not, explain why not. ...
... Are the triangles similar? If yes, write a similarity statement and explain how you know they are similar – use a shortcut if you’d like. If not, explain why not. ...
SuperKEKB - grapes-3
... Quarks and leptons are basic building blocks and interact among themselves via exchange of gluons, photon, W and Z bosons ...
... Quarks and leptons are basic building blocks and interact among themselves via exchange of gluons, photon, W and Z bosons ...
Triplett Analog Panel Meter Characteristics
... ● LINEARITY applies to spacing of scale divisions only. DC types at ±2% accuracy have linear scale divisions, therefore, scales are interchangeable on all meters. AC Iron Vane Types at ±2% have non-linear scale divisions, however, scales are interchangeable on meters of a given range and type. All ± ...
... ● LINEARITY applies to spacing of scale divisions only. DC types at ±2% accuracy have linear scale divisions, therefore, scales are interchangeable on all meters. AC Iron Vane Types at ±2% have non-linear scale divisions, however, scales are interchangeable on meters of a given range and type. All ± ...
Final Review: Chapter 1- Foundations
... W h i c h formula would you use to solve the following problem?. Line segment 715 has endpoints A(2, - 3 ) and 5 ( - 4 , 6 ) . What are the coordinates of the midpoint? ...
... W h i c h formula would you use to solve the following problem?. Line segment 715 has endpoints A(2, - 3 ) and 5 ( - 4 , 6 ) . What are the coordinates of the midpoint? ...
New Features of the Relativistic Particle Scattering
... N. Bohr considered nonrelativistic orbits. The generalization to relativistic orbits was done in 1916 by Arnold Sommerfeld. In this way he obtained the shape of trajectories in the form of the well-known “rosette”. In this paper we study in some detail properties of the relativistic particle traject ...
... N. Bohr considered nonrelativistic orbits. The generalization to relativistic orbits was done in 1916 by Arnold Sommerfeld. In this way he obtained the shape of trajectories in the form of the well-known “rosette”. In this paper we study in some detail properties of the relativistic particle traject ...
4. Linear Response
... We’ve already looked at a number of situations like this earlier in the course. If you apply a shearing force to a fluid, its response is to move; how much it moves is determined by the viscosity. If you apply a temperature gradient, the response is for heat to flow; the amount of heat is determined ...
... We’ve already looked at a number of situations like this earlier in the course. If you apply a shearing force to a fluid, its response is to move; how much it moves is determined by the viscosity. If you apply a temperature gradient, the response is for heat to flow; the amount of heat is determined ...
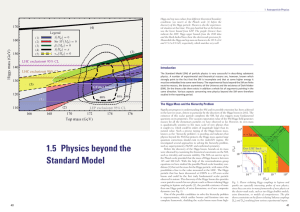
1.5 physics beyond the Standard Model
... masses around the TeV scale in order to solve the hierarchy problem and to avoid unacceptable fine-tuning. The absence of fine-tuning is often referred to as “naturalness” of a theory. But so far there is up to energies of about ~ 2 TeV absolutely no sign of new physics beyond the SM at the LHC and ...
... masses around the TeV scale in order to solve the hierarchy problem and to avoid unacceptable fine-tuning. The absence of fine-tuning is often referred to as “naturalness” of a theory. But so far there is up to energies of about ~ 2 TeV absolutely no sign of new physics beyond the SM at the LHC and ...
Why “noncommutative common causes” don`t explain anything
... be possible to avoid the consequences of Bell’s theorem by denying “commutativity”, which hasn’t been among its premises in the first place? Let me try to explain what I think the result presented in the paper actually consists in and why I think it is completely missing the point as concerning the ...
... be possible to avoid the consequences of Bell’s theorem by denying “commutativity”, which hasn’t been among its premises in the first place? Let me try to explain what I think the result presented in the paper actually consists in and why I think it is completely missing the point as concerning the ...
DOC - PBL Pathways
... To solve this problem, we first need to create the demand function p = D(x) and then use it to find the revenue function R(x). Note that in some economics application the quantity will be referenced with the variable q instead of x. ...
... To solve this problem, we first need to create the demand function p = D(x) and then use it to find the revenue function R(x). Note that in some economics application the quantity will be referenced with the variable q instead of x. ...
Buletin Stiintific - UPB - Seria A - numar 3 - 2010
... Irina MEGHEA In this paper two approach methods to obtain and characterize weak solutions or subsolutions and supersolutions for a problem of mathematical phisics equations are presented. In the first, Ekeland variational principle and a condition of Palais Smale type are both involved in order to o ...
... Irina MEGHEA In this paper two approach methods to obtain and characterize weak solutions or subsolutions and supersolutions for a problem of mathematical phisics equations are presented. In the first, Ekeland variational principle and a condition of Palais Smale type are both involved in order to o ...
Generalized Energy Variables
... Energetic interactions are mediated by the flow of power. Power flow through an interaction port may be expressed as the product of two real-valued variables, an effort and a flow, and all instantaneous interactions between systems or elements may be described in terms of these conjugate power varia ...
... Energetic interactions are mediated by the flow of power. Power flow through an interaction port may be expressed as the product of two real-valued variables, an effort and a flow, and all instantaneous interactions between systems or elements may be described in terms of these conjugate power varia ...
Colloquium on "Many Worlds Interpretation"
... Schrödinger equation) that is compatible with the way the world is perceived. However, because of quantum non-locality it requires an appropriate modification of the traditional epistemological postulate of psycho-physical parallelism. In this interpretation, the physical world is completely describ ...
... Schrödinger equation) that is compatible with the way the world is perceived. However, because of quantum non-locality it requires an appropriate modification of the traditional epistemological postulate of psycho-physical parallelism. In this interpretation, the physical world is completely describ ...
I. Waves & Particles
... B. EM Spectrum EX: Find the frequency of a photon with a wavelength of 434 nm. ...
... B. EM Spectrum EX: Find the frequency of a photon with a wavelength of 434 nm. ...
Laser–Induced Control of Condensed Phase Electron Transfer
... Given initial preparation in electronic state 1 (and assuming nuclear coordinates are equilibrated on V1(x)) ...
... Given initial preparation in electronic state 1 (and assuming nuclear coordinates are equilibrated on V1(x)) ...
quantum physics - Enggphysicsvenkat
... instability of atom. But experimental studies show that atoms are stable. Wave and particle duality - Classical physics can deal with wave or particle. Various experiment like interference, photo electric effect, electron diffraction shows that waves sometimes act as if they were stream of particles ...
... instability of atom. But experimental studies show that atoms are stable. Wave and particle duality - Classical physics can deal with wave or particle. Various experiment like interference, photo electric effect, electron diffraction shows that waves sometimes act as if they were stream of particles ...
Lieb-Robinson Bounds and the Speed of Light from
... because of the symmetry of the crystal. The understanding of the phases of matter provides an explanation for the phonon and other gapless excitations. However, one can also ask whether photons, electrons, or gravitons are emergent phenomena too, not elementary particles. Let us consider the case of ...
... because of the symmetry of the crystal. The understanding of the phases of matter provides an explanation for the phonon and other gapless excitations. However, one can also ask whether photons, electrons, or gravitons are emergent phenomena too, not elementary particles. Let us consider the case of ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.