Exact solution of the Zeeman effect in single
... known that electromagnetic radiation is produced by oscillating electric charges. The charges that produce light were however still a mystery. At the same time, it was generally believed that an electric current was made up of charged particles. Lorentz suggested that atoms might also consist of cha ...
... known that electromagnetic radiation is produced by oscillating electric charges. The charges that produce light were however still a mystery. At the same time, it was generally believed that an electric current was made up of charged particles. Lorentz suggested that atoms might also consist of cha ...
Paper
... ~BEC! is the nature of coherence in a macroscopic quantum system. Theoretically, the condensate should be described by a macroscopic wave function, behaving like a ‘‘giant matter wave’’ which is characterized by long-range order. The first experiments on BEC focused on the energetics of BoseEinstein ...
... ~BEC! is the nature of coherence in a macroscopic quantum system. Theoretically, the condensate should be described by a macroscopic wave function, behaving like a ‘‘giant matter wave’’ which is characterized by long-range order. The first experiments on BEC focused on the energetics of BoseEinstein ...
Solid-state quantum computing using spectral holes M. S. Shahriar, P. R. Hemmer,
... systems called quantum bits or qubits must be able to address and manipulate individual qubits, to effect coherent interactions between pairs of qubits, and to read out the value of qubits 关1,2兴. Current methods for addressing qubits are divided into spatial methods, as when a laser beam is focused ...
... systems called quantum bits or qubits must be able to address and manipulate individual qubits, to effect coherent interactions between pairs of qubits, and to read out the value of qubits 关1,2兴. Current methods for addressing qubits are divided into spatial methods, as when a laser beam is focused ...
Title and Abstract Shijin Deng Shanghai Jiao Tong University Title
... a one-dimensional linear radiation transport equation to a nonlinear two-dimensional grey radiative system. The newly developed scheme has the asymptotic preserving (AP) property in the optically thick regime in the capturing of diffusive solution without using a cell size being smaller than the pho ...
... a one-dimensional linear radiation transport equation to a nonlinear two-dimensional grey radiative system. The newly developed scheme has the asymptotic preserving (AP) property in the optically thick regime in the capturing of diffusive solution without using a cell size being smaller than the pho ...
S–I–S its S–I transition C.D. , Kwangmoo Kim
... the insulating regime is likely to be more than one intergrain thickness and hence three-dimensional. The film-type junctions could, in principle, be deliberately designed by having a film deposited by sputtering or chemical vapor deposition (CVD), so that the film thickness varies in a controlled way ...
... the insulating regime is likely to be more than one intergrain thickness and hence three-dimensional. The film-type junctions could, in principle, be deliberately designed by having a film deposited by sputtering or chemical vapor deposition (CVD), so that the film thickness varies in a controlled way ...
Document
... intersection, as shown in the figure. A 1300 kg minivan traveling northward is heading for the same intersection. The car and minivan collide and stick together. If the direction of the wreckage after the collision is 37.0° above the x axis, what is the initial speed of the minivan and the final spe ...
... intersection, as shown in the figure. A 1300 kg minivan traveling northward is heading for the same intersection. The car and minivan collide and stick together. If the direction of the wreckage after the collision is 37.0° above the x axis, what is the initial speed of the minivan and the final spe ...
No Slide Title
... This is an explicit example of a phenomenon already encountered in bigger systems, the symmetry of the node is higher than the symmetry of the wave function ...
... This is an explicit example of a phenomenon already encountered in bigger systems, the symmetry of the node is higher than the symmetry of the wave function ...
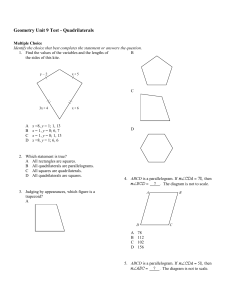
Geometry Unit 9 Test - Quadrilaterals
... 17. The isosceles trapezoid is part of an isosceles triangle with a 22° vertex angle. What is the measure of an acute base angle of the trapezoid? Of an obtuse base angle? The diagram is not to scale. ...
... 17. The isosceles trapezoid is part of an isosceles triangle with a 22° vertex angle. What is the measure of an acute base angle of the trapezoid? Of an obtuse base angle? The diagram is not to scale. ...
Kirkwood−Buff Integrals for Finite Volumes
... simulations of relatively small systems, and is therefore superior to the traditional approach of eq 4, which shows a poor convergence. Instead of calculating the upper side of eq 2 (resulting in eq 6), in principle, one could also directly compute the lower side of eq 2 from MD simulations. This re ...
... simulations of relatively small systems, and is therefore superior to the traditional approach of eq 4, which shows a poor convergence. Instead of calculating the upper side of eq 2 (resulting in eq 6), in principle, one could also directly compute the lower side of eq 2 from MD simulations. This re ...
P081
... effect for transport properties, though there are no degradation in conductance around Fermi level. As a result of research upon, metal adsorption CNTs involve the charge transfer such like our previous study using Platinum atom are also interested in the study of more complex system applying for n ...
... effect for transport properties, though there are no degradation in conductance around Fermi level. As a result of research upon, metal adsorption CNTs involve the charge transfer such like our previous study using Platinum atom are also interested in the study of more complex system applying for n ...
F1 In the Bohr model, the quantum number n gives the orbital
... (a) In the Bohr model, there is one state with orbital angular momentum of magnitude 3˙. It is the state with quantum number n = 3. Its energy is E = −13.6 eV 32 = −1.5 eV (b) In the Schrödinger model, the magnitude of the orbital angular momentum is l(l + 1) ˙ with l an integer. The magnitude is th ...
... (a) In the Bohr model, there is one state with orbital angular momentum of magnitude 3˙. It is the state with quantum number n = 3. Its energy is E = −13.6 eV 32 = −1.5 eV (b) In the Schrödinger model, the magnitude of the orbital angular momentum is l(l + 1) ˙ with l an integer. The magnitude is th ...
cond-mat/0205001 PDF
... is weakly screened by metallic plates that are separated from the electron layer by about 1 mm. It is an ideal system for testing the properties of strongly-interacting electrons. One of the interesting properties of this non-degenerate 2D electron gas is the density of states (DOS) in a magnetic fi ...
... is weakly screened by metallic plates that are separated from the electron layer by about 1 mm. It is an ideal system for testing the properties of strongly-interacting electrons. One of the interesting properties of this non-degenerate 2D electron gas is the density of states (DOS) in a magnetic fi ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.