PHY 662 - Quantum Mechanics II Spring 2016 syllabus General information Class meetings
... When necessary I will supplement in lecture and homeworks from other sources. You are encouraged to look through other treatments of the same topic such as in J.J. Sakurai’s Modern Quantum Mechanics, or other appropriate text. ...
... When necessary I will supplement in lecture and homeworks from other sources. You are encouraged to look through other treatments of the same topic such as in J.J. Sakurai’s Modern Quantum Mechanics, or other appropriate text. ...
Document
... Reduction of Dirac equation to two equations: Assuming solution Dirac eq can be written as (using 1st Eq of 17) ...
... Reduction of Dirac equation to two equations: Assuming solution Dirac eq can be written as (using 1st Eq of 17) ...
Lectures - University of Toronto Physics
... Physics Colloquium: every Thursday 4:10-5pm in MP102 -international researchers give talks about their work -cookies & coffee available beforehand (3:45-4) in MP110 -first colloquium this year: Prof. Wolfgang Ketterle MIT (22 Sept) -many other talks/seminars offered every week. See posters near elev ...
... Physics Colloquium: every Thursday 4:10-5pm in MP102 -international researchers give talks about their work -cookies & coffee available beforehand (3:45-4) in MP110 -first colloquium this year: Prof. Wolfgang Ketterle MIT (22 Sept) -many other talks/seminars offered every week. See posters near elev ...
1 Lecture 10 Summary Phys 404 Statistical
... An ideal gas of N identical non-interacting particles has the partition function The energy is given by ...
... An ideal gas of N identical non-interacting particles has the partition function The energy is given by ...
Isra University Faculty of Arts and science Course Calendar 2016
... To understand the concepts that led to the transition from classical to quantum physics such as the particle properties of radiation, the wave properties of matter and the quantization of physical quantities. To understand symmetries and conservation laws. ...
... To understand the concepts that led to the transition from classical to quantum physics such as the particle properties of radiation, the wave properties of matter and the quantization of physical quantities. To understand symmetries and conservation laws. ...
Physics
... thermodynamics, waves, electricity, magnetism, and optics. Demonstrations, exercises, and experiments will be used to construct the fundamental concepts. Emphasis will be placed on verbal interpretation,arithmetical reasoning, functional reasoning, and graphical interpretation. There will be some qu ...
... thermodynamics, waves, electricity, magnetism, and optics. Demonstrations, exercises, and experiments will be used to construct the fundamental concepts. Emphasis will be placed on verbal interpretation,arithmetical reasoning, functional reasoning, and graphical interpretation. There will be some qu ...
Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules
... An introduction to quantum mechanics. The time dependent and time independent 1-d Schrödinger equation, the wavefunction and its physical interpretation, normalisation. Particle in free space, waveparticle duality and de Broglie relationship. Boundary conditions; particle-in-a-box, energy levels, wa ...
... An introduction to quantum mechanics. The time dependent and time independent 1-d Schrödinger equation, the wavefunction and its physical interpretation, normalisation. Particle in free space, waveparticle duality and de Broglie relationship. Boundary conditions; particle-in-a-box, energy levels, wa ...
Many Worlds Theory/ `Relative State` formation of Quantum Mechanics
... ~ method sums up the different conceivable paths through time and space of a particle (the measurement problem) - even those that disobey our laws - figured out that the ones that disobeyed the laws and forces that govern our life had amplitudes that summed to zero. - Only ways that abide by physica ...
... ~ method sums up the different conceivable paths through time and space of a particle (the measurement problem) - even those that disobey our laws - figured out that the ones that disobeyed the laws and forces that govern our life had amplitudes that summed to zero. - Only ways that abide by physica ...
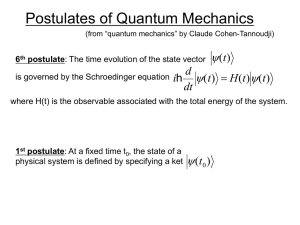
chem6V19_postulates
... where H(t) is the observable associated with the total energy of the system. ...
... where H(t) is the observable associated with the total energy of the system. ...
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... MODEL OF THE ATOM ESSENTIAL QUESTION: WHAT IS THE CURRENT MODEL OF THE ATOM? ...
... MODEL OF THE ATOM ESSENTIAL QUESTION: WHAT IS THE CURRENT MODEL OF THE ATOM? ...
Quantum Mechanical Energy and You!
... Classically we have the fundamental quantites x and t which govern the dynamics of the system. For waves, x loses some of its meaning, so instead we talk of things such as the wave number, frequency, wavelength, etc… ...
... Classically we have the fundamental quantites x and t which govern the dynamics of the system. For waves, x loses some of its meaning, so instead we talk of things such as the wave number, frequency, wavelength, etc… ...
Max Born

Max Born (German: [bɔɐ̯n]; 11 December 1882 – 5 January 1970) was a German physicist and mathematician who was instrumental in the development of quantum mechanics. He also made contributions to solid-state physics and optics and supervised the work of a number of notable physicists in the 1920s and 30s. Born won the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for his ""fundamental research in Quantum Mechanics, especially in the statistical interpretation of the wave function"".Born was born in 1882 in Breslau, then in Germany, now in Poland and known as Wrocław. He entered the University of Göttingen in 1904, where he found the three renowned mathematicians, Felix Klein, David Hilbert and Hermann Minkowski. He wrote his Ph.D. thesis on the subject of ""Stability of Elastica in a Plane and Space"", winning the University's Philosophy Faculty Prize. In 1905, he began researching special relativity with Minkowski, and subsequently wrote his habilitation thesis on the Thomson model of the atom. A chance meeting with Fritz Haber in Berlin in 1918 led to discussion of the manner in which an ionic compound is formed when a metal reacts with a halogen, which is today known as the Born–Haber cycle.In the First World War after originally being placed as a radio operator, due to his specialist knowledge he was moved to research duties regarding sound ranging. In 1921, Born returned to Göttingen, arranging another chair for his long-time friend and colleague James Franck. Under Born, Göttingen became one of the world's foremost centres for physics. In 1925, Born and Werner Heisenberg formulated the matrix mechanics representation of quantum mechanics. The following year, he formulated the now-standard interpretation of the probability density function for ψ*ψ in the Schrödinger equation, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1954. His influence extended far beyond his own research. Max Delbrück, Siegfried Flügge, Friedrich Hund, Pascual Jordan, Maria Goeppert-Mayer, Lothar Wolfgang Nordheim, Robert Oppenheimer, and Victor Weisskopf all received their Ph.D. degrees under Born at Göttingen, and his assistants included Enrico Fermi, Werner Heisenberg, Gerhard Herzberg, Friedrich Hund, Pascual Jordan, Wolfgang Pauli, Léon Rosenfeld, Edward Teller, and Eugene Wigner.In January 1933, the Nazi Party came to power in Germany, and Born, who was Jewish, was suspended. He emigrated to Britain, where he took a job at St John's College, Cambridge, and wrote a popular science book, The Restless Universe, as well as Atomic Physics, which soon became a standard text book. In October 1936, he became the Tait Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Edinburgh, where, working with German-born assistants E. Walter Kellermann and Klaus Fuchs, he continued his research into physics. Max Born became a naturalised British subject on 31 August 1939, one day before World War II broke out in Europe. He remained at Edinburgh until 1952. He retired to Bad Pyrmont, in West Germany. He died in hospital in Göttingen on 5 January 1970.