PHYS 1602 Physics II - Description
... Students and faculty of Barton Community College constitute a special community engaged in the process of education. The college assumes that its students and faculty will demonstrate a code of personal honor that is based upon courtesy, integrity, common sense, and respect for others both within an ...
... Students and faculty of Barton Community College constitute a special community engaged in the process of education. The college assumes that its students and faculty will demonstrate a code of personal honor that is based upon courtesy, integrity, common sense, and respect for others both within an ...
Quantum gravity
... casting doubt on the notion of an objective reality - a concept many physicists, including Albert Einstein, have found hard to swallow. Today, scientists are grappling with these philosophical conundrums, trying to harness quantum's bizarre properties to advance technology, and struggling to weave q ...
... casting doubt on the notion of an objective reality - a concept many physicists, including Albert Einstein, have found hard to swallow. Today, scientists are grappling with these philosophical conundrums, trying to harness quantum's bizarre properties to advance technology, and struggling to weave q ...
Stephen Hawking
... systems in superposition states with observable quantum interference terms, but it does not offer any explanation of how for a given instance the system “decides” which outcome to take out of all possibilities or even why we experience just one of the possibilities. In a Stern Gerlach experiment wit ...
... systems in superposition states with observable quantum interference terms, but it does not offer any explanation of how for a given instance the system “decides” which outcome to take out of all possibilities or even why we experience just one of the possibilities. In a Stern Gerlach experiment wit ...
Toffoli gate
... It can be shown that if two observables are measured simultaneously, the uncertainty in their joint values must always obey the inequality (Heisenberg ...
... It can be shown that if two observables are measured simultaneously, the uncertainty in their joint values must always obey the inequality (Heisenberg ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 20. Obtain the ground state energy of the Hydrogen molecule using the variation method. ...
... 20. Obtain the ground state energy of the Hydrogen molecule using the variation method. ...
ECE692_1_1008
... For 2., find and read thru the math in a book, visualize results, compare to dielectric cavity or waveguide For 3., find and read thru the math in a book, visualize results; compare to the above and get some sense of how energy level spacing is related to the shape of the potential. For 4., generali ...
... For 2., find and read thru the math in a book, visualize results, compare to dielectric cavity or waveguide For 3., find and read thru the math in a book, visualize results; compare to the above and get some sense of how energy level spacing is related to the shape of the potential. For 4., generali ...
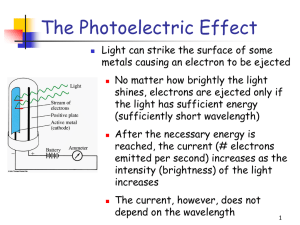
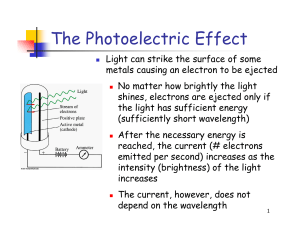
What is Light?
... • Classical Mechanics predicts that a heated body should emit an infinite amount of energy, but experiment tells us otherwise • Max Planck proposed a theory that was able to mathematically reproduce the blackbody radiation graphs : E=nhf ; n=1,2,3… • Energy of vibration could only be some whole numb ...
... • Classical Mechanics predicts that a heated body should emit an infinite amount of energy, but experiment tells us otherwise • Max Planck proposed a theory that was able to mathematically reproduce the blackbody radiation graphs : E=nhf ; n=1,2,3… • Energy of vibration could only be some whole numb ...
AIP00330WH
... email: [email protected] To understand the relationship between quantum mechanics and classical physics a crucial question to be answered is how distinct classical dynamical phase space features translate into the quantum picture. This problem becomes even more interesting if these phase sp ...
... email: [email protected] To understand the relationship between quantum mechanics and classical physics a crucial question to be answered is how distinct classical dynamical phase space features translate into the quantum picture. This problem becomes even more interesting if these phase sp ...
department of physics and engineering
... MSc (Physics) [QUALIFICATION CODE SMSC11, MODULE CODE SPHY700] This course consists of a dissertation on an approved topic, or of a dissertation plus coursework on theory on which examination papers will be written, as arranged with the supervisor appointed in consultation with the Head of Departmen ...
... MSc (Physics) [QUALIFICATION CODE SMSC11, MODULE CODE SPHY700] This course consists of a dissertation on an approved topic, or of a dissertation plus coursework on theory on which examination papers will be written, as arranged with the supervisor appointed in consultation with the Head of Departmen ...
No Slide Title
... Tutorials on-line The postulates of quantum mechanics (This is the writeup for Dry-lab-II)( This lecture has covered (briefly) postulates 1-2)(You are not expected to understand even postulates 1 and 2 fully after this lecture) The Development of Classical Mechanics Experimental Background for Quan ...
... Tutorials on-line The postulates of quantum mechanics (This is the writeup for Dry-lab-II)( This lecture has covered (briefly) postulates 1-2)(You are not expected to understand even postulates 1 and 2 fully after this lecture) The Development of Classical Mechanics Experimental Background for Quan ...
MSc Phy Int
... (qualitative idea) ,Nuclear fission and fusion. Radioactive decay law, activity, half life and average life time of a nucleus. Module -III Introduction to Quantum mechanics, Compton effect, dual nature of radiation. Wave nature of particles: De Broglie hypothesis and wave particle duality. Super pos ...
... (qualitative idea) ,Nuclear fission and fusion. Radioactive decay law, activity, half life and average life time of a nucleus. Module -III Introduction to Quantum mechanics, Compton effect, dual nature of radiation. Wave nature of particles: De Broglie hypothesis and wave particle duality. Super pos ...
Max Born

Max Born (German: [bɔɐ̯n]; 11 December 1882 – 5 January 1970) was a German physicist and mathematician who was instrumental in the development of quantum mechanics. He also made contributions to solid-state physics and optics and supervised the work of a number of notable physicists in the 1920s and 30s. Born won the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for his ""fundamental research in Quantum Mechanics, especially in the statistical interpretation of the wave function"".Born was born in 1882 in Breslau, then in Germany, now in Poland and known as Wrocław. He entered the University of Göttingen in 1904, where he found the three renowned mathematicians, Felix Klein, David Hilbert and Hermann Minkowski. He wrote his Ph.D. thesis on the subject of ""Stability of Elastica in a Plane and Space"", winning the University's Philosophy Faculty Prize. In 1905, he began researching special relativity with Minkowski, and subsequently wrote his habilitation thesis on the Thomson model of the atom. A chance meeting with Fritz Haber in Berlin in 1918 led to discussion of the manner in which an ionic compound is formed when a metal reacts with a halogen, which is today known as the Born–Haber cycle.In the First World War after originally being placed as a radio operator, due to his specialist knowledge he was moved to research duties regarding sound ranging. In 1921, Born returned to Göttingen, arranging another chair for his long-time friend and colleague James Franck. Under Born, Göttingen became one of the world's foremost centres for physics. In 1925, Born and Werner Heisenberg formulated the matrix mechanics representation of quantum mechanics. The following year, he formulated the now-standard interpretation of the probability density function for ψ*ψ in the Schrödinger equation, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1954. His influence extended far beyond his own research. Max Delbrück, Siegfried Flügge, Friedrich Hund, Pascual Jordan, Maria Goeppert-Mayer, Lothar Wolfgang Nordheim, Robert Oppenheimer, and Victor Weisskopf all received their Ph.D. degrees under Born at Göttingen, and his assistants included Enrico Fermi, Werner Heisenberg, Gerhard Herzberg, Friedrich Hund, Pascual Jordan, Wolfgang Pauli, Léon Rosenfeld, Edward Teller, and Eugene Wigner.In January 1933, the Nazi Party came to power in Germany, and Born, who was Jewish, was suspended. He emigrated to Britain, where he took a job at St John's College, Cambridge, and wrote a popular science book, The Restless Universe, as well as Atomic Physics, which soon became a standard text book. In October 1936, he became the Tait Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Edinburgh, where, working with German-born assistants E. Walter Kellermann and Klaus Fuchs, he continued his research into physics. Max Born became a naturalised British subject on 31 August 1939, one day before World War II broke out in Europe. He remained at Edinburgh until 1952. He retired to Bad Pyrmont, in West Germany. He died in hospital in Göttingen on 5 January 1970.