Quantum Mechanics OK
... • Erwin Schrödinger developed a mathematical treatment into which both the wave and particle nature of matter could be incorporated. • It is known as quantum mechanics. ...
... • Erwin Schrödinger developed a mathematical treatment into which both the wave and particle nature of matter could be incorporated. • It is known as quantum mechanics. ...
LOSS OF COHERENCE IN GATE-CONTROLLED QUBIT SYSTEMS
... We present a Monte Carlo study of irreversible, competitive deposition models, applied to single- and two-sized disks on pre-treated, patterned surfaces with short-range repulsive interactions. In particular, we study the effect of the substrate nanopatterning on coverage and particle distribution o ...
... We present a Monte Carlo study of irreversible, competitive deposition models, applied to single- and two-sized disks on pre-treated, patterned surfaces with short-range repulsive interactions. In particular, we study the effect of the substrate nanopatterning on coverage and particle distribution o ...
The concepts of an atom and chemical bond in physics and chemistry
... we assume the separation of movements of nuclei and electrons as well as the independence of the movement of each electron; we apply these assumptions to the system under consideration and in many cases the obtained results are in a quite good agreement with experiment. The calculated values are use ...
... we assume the separation of movements of nuclei and electrons as well as the independence of the movement of each electron; we apply these assumptions to the system under consideration and in many cases the obtained results are in a quite good agreement with experiment. The calculated values are use ...
1 Towards functional calculus
... and by ‘an algebra of functions’ we mean some subalgebra of this one. • The most important example of an algebra of functions is the polynomials. • The linear transformations of H form an algebra under composition. Question 1. Given a linear operator T on an infinite dimensional vector space H , and ...
... and by ‘an algebra of functions’ we mean some subalgebra of this one. • The most important example of an algebra of functions is the polynomials. • The linear transformations of H form an algebra under composition. Question 1. Given a linear operator T on an infinite dimensional vector space H , and ...
Action-Angle Variables
... Example (harmonic oscillator in two dimensions with different spring constants): total energy Hamilton-Jacobi equation for Hamilton’s characteristic function ...
... Example (harmonic oscillator in two dimensions with different spring constants): total energy Hamilton-Jacobi equation for Hamilton’s characteristic function ...
SPH4U Modern Plans
... 1. Review experiments showing light as a wave: a. Polarization b. Double slit interference & single slit diffraction c. Interferometers & thin film interference 2. What would happen in these experiments if light were a tiny particle instead of a wave? 3. Einstein history 4. www.explorelearning.com – ...
... 1. Review experiments showing light as a wave: a. Polarization b. Double slit interference & single slit diffraction c. Interferometers & thin film interference 2. What would happen in these experiments if light were a tiny particle instead of a wave? 3. Einstein history 4. www.explorelearning.com – ...
preskill-Annenberg30oct2009
... • A quantum system with two parts is entangled when its joint state is more definite and less random than the state of each part by itself. Looking at the parts one at a time, you can learn everything about a pair of socks, but not about a pair of qubits! ...
... • A quantum system with two parts is entangled when its joint state is more definite and less random than the state of each part by itself. Looking at the parts one at a time, you can learn everything about a pair of socks, but not about a pair of qubits! ...
Quantum Mechanics
... where R(λ) is called the radiancy. Physicists were interested in blackbodies because their radiancy vs. λ depends on the the temperature of the materials ...
... where R(λ) is called the radiancy. Physicists were interested in blackbodies because their radiancy vs. λ depends on the the temperature of the materials ...
s - Dl4a.org
... – Electrons passing nearby scatter some light – We see a flash near slit 1 or 2 – tells us which one it came ...
... – Electrons passing nearby scatter some light – We see a flash near slit 1 or 2 – tells us which one it came ...
full piece
... [14], a popular modern physics textbook that was consistent with our level of math and contained most topics we covered. Students complained about the text on a weekly basis, both verbally and in feedback forms, and our top students reported that they stopped reading the textbook because they couldn ...
... [14], a popular modern physics textbook that was consistent with our level of math and contained most topics we covered. Students complained about the text on a weekly basis, both verbally and in feedback forms, and our top students reported that they stopped reading the textbook because they couldn ...
SEPTEMBER 21, 2013 THESKEPTICARENA.COM QUANTUM
... Those two atoms would interact with the quantum foam around each of them. If one atom were in two different places, the virtual particles would have to be the same. How is that possible at two different locations unless the quantum foam is also in superposition? If they were really one atom, any par ...
... Those two atoms would interact with the quantum foam around each of them. If one atom were in two different places, the virtual particles would have to be the same. How is that possible at two different locations unless the quantum foam is also in superposition? If they were really one atom, any par ...
Physics - Lynchburg College
... QUANTUM MECHANICS (4) Prerequisites: MATH 211, 301 (or concurrent enrollment in MATH 301), and PHYS 211. Three hours lecture and one-hour problem session. This course introduces the methods of quantum theory. The Schrodinger approach is developed and is applied to the hydrogen atom, angular momentum ...
... QUANTUM MECHANICS (4) Prerequisites: MATH 211, 301 (or concurrent enrollment in MATH 301), and PHYS 211. Three hours lecture and one-hour problem session. This course introduces the methods of quantum theory. The Schrodinger approach is developed and is applied to the hydrogen atom, angular momentum ...
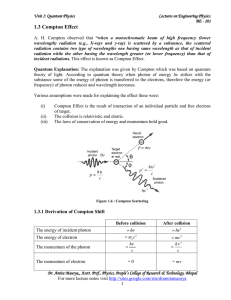
1.3 Compton Effect - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... wavelength) radiation (e.g., X-rays and γ-ray) is scattered by a substance, the scattered radiation contains two type of wavelengths one having same wavelength as that of incident radiation while the other having the wavelength greater (or lower frequency) than that of incident radiations. This effe ...
... wavelength) radiation (e.g., X-rays and γ-ray) is scattered by a substance, the scattered radiation contains two type of wavelengths one having same wavelength as that of incident radiation while the other having the wavelength greater (or lower frequency) than that of incident radiations. This effe ...
Max Born

Max Born (German: [bɔɐ̯n]; 11 December 1882 – 5 January 1970) was a German physicist and mathematician who was instrumental in the development of quantum mechanics. He also made contributions to solid-state physics and optics and supervised the work of a number of notable physicists in the 1920s and 30s. Born won the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for his ""fundamental research in Quantum Mechanics, especially in the statistical interpretation of the wave function"".Born was born in 1882 in Breslau, then in Germany, now in Poland and known as Wrocław. He entered the University of Göttingen in 1904, where he found the three renowned mathematicians, Felix Klein, David Hilbert and Hermann Minkowski. He wrote his Ph.D. thesis on the subject of ""Stability of Elastica in a Plane and Space"", winning the University's Philosophy Faculty Prize. In 1905, he began researching special relativity with Minkowski, and subsequently wrote his habilitation thesis on the Thomson model of the atom. A chance meeting with Fritz Haber in Berlin in 1918 led to discussion of the manner in which an ionic compound is formed when a metal reacts with a halogen, which is today known as the Born–Haber cycle.In the First World War after originally being placed as a radio operator, due to his specialist knowledge he was moved to research duties regarding sound ranging. In 1921, Born returned to Göttingen, arranging another chair for his long-time friend and colleague James Franck. Under Born, Göttingen became one of the world's foremost centres for physics. In 1925, Born and Werner Heisenberg formulated the matrix mechanics representation of quantum mechanics. The following year, he formulated the now-standard interpretation of the probability density function for ψ*ψ in the Schrödinger equation, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1954. His influence extended far beyond his own research. Max Delbrück, Siegfried Flügge, Friedrich Hund, Pascual Jordan, Maria Goeppert-Mayer, Lothar Wolfgang Nordheim, Robert Oppenheimer, and Victor Weisskopf all received their Ph.D. degrees under Born at Göttingen, and his assistants included Enrico Fermi, Werner Heisenberg, Gerhard Herzberg, Friedrich Hund, Pascual Jordan, Wolfgang Pauli, Léon Rosenfeld, Edward Teller, and Eugene Wigner.In January 1933, the Nazi Party came to power in Germany, and Born, who was Jewish, was suspended. He emigrated to Britain, where he took a job at St John's College, Cambridge, and wrote a popular science book, The Restless Universe, as well as Atomic Physics, which soon became a standard text book. In October 1936, he became the Tait Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Edinburgh, where, working with German-born assistants E. Walter Kellermann and Klaus Fuchs, he continued his research into physics. Max Born became a naturalised British subject on 31 August 1939, one day before World War II broke out in Europe. He remained at Edinburgh until 1952. He retired to Bad Pyrmont, in West Germany. He died in hospital in Göttingen on 5 January 1970.