CH3L2
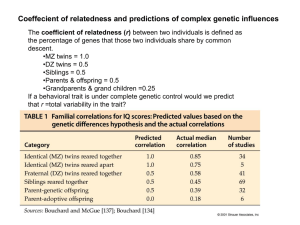
... Coeffecient of relatedness and predictions of complex genetic influences The coefficient of relatedness (r) between two individuals is defined as the percentage of genes that those two individuals share by common descent. •MZ twins = 1.0 •DZ twins = 0.5 •Siblings = 0.5 •Parents & offspring = 0.5 •Gr ...
... Coeffecient of relatedness and predictions of complex genetic influences The coefficient of relatedness (r) between two individuals is defined as the percentage of genes that those two individuals share by common descent. •MZ twins = 1.0 •DZ twins = 0.5 •Siblings = 0.5 •Parents & offspring = 0.5 •Gr ...
Meiosis and Fertilization
... Meiosis and Fertilization Meiosis is the form of cell division that produces the special haploid cells called gametes. In meiosis, chromosomes are randomly shuffled. As a result, the offspring of organisms that reproduce sexually have a mixture of both parent’s genes. In humans, over 8 million genet ...
... Meiosis and Fertilization Meiosis is the form of cell division that produces the special haploid cells called gametes. In meiosis, chromosomes are randomly shuffled. As a result, the offspring of organisms that reproduce sexually have a mixture of both parent’s genes. In humans, over 8 million genet ...
2010 PCB 5530 Class Projects
... mutant phenotypes, if available. Use the Golm Arabidopsis Expression dbase Multiple Expression Query tool to plot the expression in different organs of each Arabidopsis gene in the pathway. For ‘missing genes’, predict candidates from Arabidopsis and maize based on homology with proteins from other ...
... mutant phenotypes, if available. Use the Golm Arabidopsis Expression dbase Multiple Expression Query tool to plot the expression in different organs of each Arabidopsis gene in the pathway. For ‘missing genes’, predict candidates from Arabidopsis and maize based on homology with proteins from other ...
Supplementary Glossary 1
... Nested Genes: A nested gene is defined as any gene located wholly within another gene. Nested genes are usually located within an intron of the host gene. Nested genes are relatively common within the genome and are usually coded on the complementary strand and transcribed in an antisense direction ...
... Nested Genes: A nested gene is defined as any gene located wholly within another gene. Nested genes are usually located within an intron of the host gene. Nested genes are relatively common within the genome and are usually coded on the complementary strand and transcribed in an antisense direction ...
29 inheritance
... “Real human Y chromosome” http://www.life.uiuc.edu/bio100/lectures/s07lects/12s07-chromo.html ...
... “Real human Y chromosome” http://www.life.uiuc.edu/bio100/lectures/s07lects/12s07-chromo.html ...
Document
... • Why a mouse develops into a mouse and not a human: – Genes are expressed at different times; – In different tissues; – In different amounts; – In different combinations; – Example: cystic fibrosis gene. ...
... • Why a mouse develops into a mouse and not a human: – Genes are expressed at different times; – In different tissues; – In different amounts; – In different combinations; – Example: cystic fibrosis gene. ...
How Exercise Changes Fat and Muscle Cells
... blood pressure, cholesterol levels and similar markers of health and fitness. Then they asked the men to start working out. Under the guidance of a trainer, the volunteers began attending hourlong spinning or aerobics classes approximately twice a week for six months. By the end of that time, the me ...
... blood pressure, cholesterol levels and similar markers of health and fitness. Then they asked the men to start working out. Under the guidance of a trainer, the volunteers began attending hourlong spinning or aerobics classes approximately twice a week for six months. By the end of that time, the me ...
Vigneshwaran Mani
... factor receptor Ribosomal protein L35A Down-regulated genes in HCC mRNAs of Nip3 Decorin Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 ...
... factor receptor Ribosomal protein L35A Down-regulated genes in HCC mRNAs of Nip3 Decorin Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 ...
Biol518Lec2final-2 - Cal State LA
... Transposons – DNA elements that can hop (transpose) from one place in DNA to another Transposons are known to exist in all organisms on earth Movement by a transposon is called transposition, catalyzed by enzymes called transposases Transposons usually encode their own transposases ...
... Transposons – DNA elements that can hop (transpose) from one place in DNA to another Transposons are known to exist in all organisms on earth Movement by a transposon is called transposition, catalyzed by enzymes called transposases Transposons usually encode their own transposases ...
Human Genetics (website)
... the recessive gene cd on the same chromosome. Between these two loci is a third locus with a recessive allele e that produces ebony body color. Homozygous "kidney," cardinal females are mated to homozygous ebony males. The trihybrid F1 females are then testcrossed to produce the F2. Among 4000 F2 pr ...
... the recessive gene cd on the same chromosome. Between these two loci is a third locus with a recessive allele e that produces ebony body color. Homozygous "kidney," cardinal females are mated to homozygous ebony males. The trihybrid F1 females are then testcrossed to produce the F2. Among 4000 F2 pr ...
CH-14 Sect 14
... a. Chromosomes 21 and 22 are the largest human chromosome. b. Chromosome 22 contains long stretches of repetitive DNA that do not code for proteins. c. Biologists know everything about how the arrangements of genes on chromosomes affect gene expression. d. Human genes located close together on the s ...
... a. Chromosomes 21 and 22 are the largest human chromosome. b. Chromosome 22 contains long stretches of repetitive DNA that do not code for proteins. c. Biologists know everything about how the arrangements of genes on chromosomes affect gene expression. d. Human genes located close together on the s ...
NonMendelian Inheritance Patterns
... • Example 2 = Color blindness in humans / normal color seeing is dominant to color blindness but the gene that codes for this trait is linked (found on) to the X ...
... • Example 2 = Color blindness in humans / normal color seeing is dominant to color blindness but the gene that codes for this trait is linked (found on) to the X ...
Slide 1
... alleles will have a phenotype that’s intermediate. E.g. Serotonin transporter gene located on chromosome 17 can have alleles of different length, long allele has incomplete dominance over short. ...
... alleles will have a phenotype that’s intermediate. E.g. Serotonin transporter gene located on chromosome 17 can have alleles of different length, long allele has incomplete dominance over short. ...
Is there an alternative to MRT?
... • Two implantations with XO after CT • Possibly significant • Possibly related to cellular stress (XO can occur during formation of pb2) • Strongly recommend PGS after MRT to confirm normal chromosome set ...
... • Two implantations with XO after CT • Possibly significant • Possibly related to cellular stress (XO can occur during formation of pb2) • Strongly recommend PGS after MRT to confirm normal chromosome set ...
msb4100030-sup
... An annotation-based procedure to determine a threshold score in assigning genes to a PSSM Alternative assignments of genes to a PSSM, each corresponding to a different threshold score of the basic assignment algorithm (Elkon et al., 2003), are examined. At each assignment, that corresponds to a (typ ...
... An annotation-based procedure to determine a threshold score in assigning genes to a PSSM Alternative assignments of genes to a PSSM, each corresponding to a different threshold score of the basic assignment algorithm (Elkon et al., 2003), are examined. At each assignment, that corresponds to a (typ ...
1 Inheritance 1
... 4. How did geneticists determine which genes were closer together? Carrying out crosses and determining how frequently genes were separated by crossing over. 5. What do we mean by “cross over value”? High cross over value – genes are far away, low – genes are close and less likely to be separated at ...
... 4. How did geneticists determine which genes were closer together? Carrying out crosses and determining how frequently genes were separated by crossing over. 5. What do we mean by “cross over value”? High cross over value – genes are far away, low – genes are close and less likely to be separated at ...
How many genes are responsible for phenotypic differences
... How many genes contribute to phenotypic differences? What are the contributions of individual genes? Key question: are evolutionary changes due to many genes of small effect, or to few genes of large effect? 100 genes that contribute 1% each, or 4 genes that contribute 25% each? ...
... How many genes contribute to phenotypic differences? What are the contributions of individual genes? Key question: are evolutionary changes due to many genes of small effect, or to few genes of large effect? 100 genes that contribute 1% each, or 4 genes that contribute 25% each? ...
Lesson Overview
... They occur randomly Only heritable mutations matter for evolution Other sources of variation include: 1. Genetic recombinationcrossing over and independent assortment in meiosis 2. Lateral gene transfer- (bacteria only) Bacteria swap plasmids between members of the same generation, then pass them to ...
... They occur randomly Only heritable mutations matter for evolution Other sources of variation include: 1. Genetic recombinationcrossing over and independent assortment in meiosis 2. Lateral gene transfer- (bacteria only) Bacteria swap plasmids between members of the same generation, then pass them to ...























