F. Mutation and Repair 1. Background on DNA Mutations
... • Due to proofreading and repair mechanisms this rate declines to 1 every 1,000,000,000 • Inherent in meiosis are assortment and crossover events that lead to highly significant changes in germ line DNA sequences ...
... • Due to proofreading and repair mechanisms this rate declines to 1 every 1,000,000,000 • Inherent in meiosis are assortment and crossover events that lead to highly significant changes in germ line DNA sequences ...
Ch_15
... coding SNPs and non-coding SNPs (1) coding SNPs 17.5 million have been experimentally mapped to functionally distinct regions of the genome, only 0.4M are in coding region while the rest are in non-coding region Coding SNPs are over-represented in disease associations e.g. OMIM contains 2430 non-co ...
... coding SNPs and non-coding SNPs (1) coding SNPs 17.5 million have been experimentally mapped to functionally distinct regions of the genome, only 0.4M are in coding region while the rest are in non-coding region Coding SNPs are over-represented in disease associations e.g. OMIM contains 2430 non-co ...
Chapter 5
... essential component of evolutionary change • Mutations that become part of the multicellular genome must occur in the cells of the germ line • Somatic mutations may or may not affect the individual but cannot affect the population • Low rates of mutation can result in high rates of evolution in sing ...
... essential component of evolutionary change • Mutations that become part of the multicellular genome must occur in the cells of the germ line • Somatic mutations may or may not affect the individual but cannot affect the population • Low rates of mutation can result in high rates of evolution in sing ...
The PRICE of SILENT MUTATIONS
... they found that people are rather similar to one another. These splice-associated regions lack much variation, even at sites where a mutation would be silent. The reason is not that mutations are not happening at the ends of our exons, but that when they appear, the mutations are so damaging to prot ...
... they found that people are rather similar to one another. These splice-associated regions lack much variation, even at sites where a mutation would be silent. The reason is not that mutations are not happening at the ends of our exons, but that when they appear, the mutations are so damaging to prot ...
EXTENSION OF MENDELIAN INHERITANCE: BEYOND
... Extranuclear inheritance or cytoplasmic inheritance is the transmission of genes that occur outside the nuclear chromosomes i.e. from mitochondrial DNA or chloroplast DNA. It is found in most eukaryotes and is commonly known to occur in cytoplasmic organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts. E ...
... Extranuclear inheritance or cytoplasmic inheritance is the transmission of genes that occur outside the nuclear chromosomes i.e. from mitochondrial DNA or chloroplast DNA. It is found in most eukaryotes and is commonly known to occur in cytoplasmic organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts. E ...
Genetics and Sex-Linked Inheritance Test Review
... An epigene is a chemical tag found on the DNA strand and the histone proteins within the DNA strand that modify the genes. They are what provide variation within the genes. Epigenes can also silence or inactivate a gene so it isn’t expressed. 20. What do I mean when I say that a gene has been ‘impri ...
... An epigene is a chemical tag found on the DNA strand and the histone proteins within the DNA strand that modify the genes. They are what provide variation within the genes. Epigenes can also silence or inactivate a gene so it isn’t expressed. 20. What do I mean when I say that a gene has been ‘impri ...
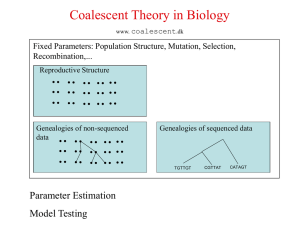
Infinite Sites Model
... or quantitative information (A) related to the observed (A,A) (B)(A) differences (B)(A) (B)(A,A) • Only keeps track of how (B)(A)(C) many of each allele type (B)(A)(C,C) • Number of mutations that (B,B)(A)(C,C) result in a variant is lost (B)(D)(A)(C,C) • Two event types, (B)(D)(A)(C,C) ...
... or quantitative information (A) related to the observed (A,A) (B)(A) differences (B)(A) (B)(A,A) • Only keeps track of how (B)(A)(C) many of each allele type (B)(A)(C,C) • Number of mutations that (B,B)(A)(C,C) result in a variant is lost (B)(D)(A)(C,C) • Two event types, (B)(D)(A)(C,C) ...
Smooth Response Surface - University of British Columbia
... These diseases may have similar synthetic effect in the yeast genetic interaction map Elements of genetic network derived from model organism, e.g. yeast, are likely to be conserved ...
... These diseases may have similar synthetic effect in the yeast genetic interaction map Elements of genetic network derived from model organism, e.g. yeast, are likely to be conserved ...
Pathway Methods - people.vcu.edu
... • Organize expression (or other) changes into meaningful ‘chunks’ (themes) • Identify crucial points in process where intervention could make a difference • Why? Biology is Redundant! Often sets of genes doing related functions are changed ...
... • Organize expression (or other) changes into meaningful ‘chunks’ (themes) • Identify crucial points in process where intervention could make a difference • Why? Biology is Redundant! Often sets of genes doing related functions are changed ...
Mendelian Genetics
... rise to a particular phenotype only in a proportion of individuals: penetrance. If the frequency of expression of a phenotype is less than 100%, then some of those who have the gene may completely fail to express it. The gene is said to show reduced penetrance. 80% penetrance: 80% of heterozygot ...
... rise to a particular phenotype only in a proportion of individuals: penetrance. If the frequency of expression of a phenotype is less than 100%, then some of those who have the gene may completely fail to express it. The gene is said to show reduced penetrance. 80% penetrance: 80% of heterozygot ...
Lecture 01. The subject and the main tasks of Medical Genetics
... unaffected males pass the condition to half their sons and daughters ...
... unaffected males pass the condition to half their sons and daughters ...
PDF - SystemsX.ch
... mice. They are particularly interested in their fitness and time of death. The initial results are striking. Despite the fact that these 60 mice strains all belong to the same “family”, the lifespan varies hugely from mouse to mouse. “Mice typically live for about two or three years”, explains the p ...
... mice. They are particularly interested in their fitness and time of death. The initial results are striking. Despite the fact that these 60 mice strains all belong to the same “family”, the lifespan varies hugely from mouse to mouse. “Mice typically live for about two or three years”, explains the p ...
Guided Notes-Genetics
... square; possible ________________________________ parent are written on the ______________ of the square. c. The genotypes are predicted by combining alleles from each parent. ...
... square; possible ________________________________ parent are written on the ______________ of the square. c. The genotypes are predicted by combining alleles from each parent. ...
alleles in gene pair are identical
... • Heterozygous means that each gene in the pair has different alleles. ...
... • Heterozygous means that each gene in the pair has different alleles. ...
Polygenic Multifactorial Inheritance
... population in a non-random manner with statistical significance • Alleles that confer only weak susceptibility to a complex disease may be more easily found through this study than linkage studies Challenges of association studies • Association of an allele with a phenotype does not prove that one ...
... population in a non-random manner with statistical significance • Alleles that confer only weak susceptibility to a complex disease may be more easily found through this study than linkage studies Challenges of association studies • Association of an allele with a phenotype does not prove that one ...
Corporate Profile
... fitness is defined in the context of the environment in which individuals live, mate, and reproduce ...
... fitness is defined in the context of the environment in which individuals live, mate, and reproduce ...
Genetics L311 exam 2
... E. Reversion or reverse mutation is the conversion of a mutation back to wild type. F. A heritable state of gene function not encoded within the DNA is referred to as epigenetics . G. Linkage is the tendency for genes located on the same chromosome to be inherited together. ...
... E. Reversion or reverse mutation is the conversion of a mutation back to wild type. F. A heritable state of gene function not encoded within the DNA is referred to as epigenetics . G. Linkage is the tendency for genes located on the same chromosome to be inherited together. ...
Lecture 1: Introduction
... phosphatases reverse the process. Adding a phosphoryl group can change a nonpolar hydrophobic protein into a polar, very hydrophilic molecule – in essence, changing its entire nature. Each phosphorylation reaction and its reverse requires ATP to power it. Tyrosine phosphorylation is not as common ...
... phosphatases reverse the process. Adding a phosphoryl group can change a nonpolar hydrophobic protein into a polar, very hydrophilic molecule – in essence, changing its entire nature. Each phosphorylation reaction and its reverse requires ATP to power it. Tyrosine phosphorylation is not as common ...
Epistasis

Epistasis is a phenomenon that consists of the effect of one gene being dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes' (genetic background). Similarly, epistatic mutations have different effects in combination than individually. It was originally a concept from genetics but is now used in biochemistry, population genetics, computational biology and evolutionary biology. It arises due to interactions, either between genes, or within them leading to non-additive effects. Epistasis has a large influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes which leads to profound consequences for evolution and evolvability of traits.