Ear Infections: Facts for Parents About Otitis Media
... Medicines called antibiotics are sometimes given for ear infections. It is important to know how they work. Antibiotics only work against organisms called bacteria, which can cause illness. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses, such as those associated with a cold. In order to be effective, ...
... Medicines called antibiotics are sometimes given for ear infections. It is important to know how they work. Antibiotics only work against organisms called bacteria, which can cause illness. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses, such as those associated with a cold. In order to be effective, ...
Viktor`s Notes * Middle Ear Disorders
... 1) suppurative complication of temporal bone (e.g. mastoiditis) 2) history of repetitive attacks (tube design permits tube placement for longer than 2 years!). Prevention of recurrences: 1) conjugated heptavalent pneumococcal vaccine 2) SULFISOXAZOLE or AMOXICILLIN daily for 3-8 months (indicated if ...
... 1) suppurative complication of temporal bone (e.g. mastoiditis) 2) history of repetitive attacks (tube design permits tube placement for longer than 2 years!). Prevention of recurrences: 1) conjugated heptavalent pneumococcal vaccine 2) SULFISOXAZOLE or AMOXICILLIN daily for 3-8 months (indicated if ...
Management of otitis media with effusion in children - ORL
... degree of hearing loss is not compatible with the clinical findings, or when there is a sensorineural hearing loss, high-resolution CT and MRI scans allows identification of middle and inner ear abnormalities. Screening Programs It is important to identify children at risk for possible developmental ...
... degree of hearing loss is not compatible with the clinical findings, or when there is a sensorineural hearing loss, high-resolution CT and MRI scans allows identification of middle and inner ear abnormalities. Screening Programs It is important to identify children at risk for possible developmental ...
Meniers disease PPT Dr Javed shah
... Viral-serum IgE to herpes simples virus types I and II, EpsteinBarr virus and CMV Vascular-associated with migraines Metabolic-potassium intoxication ...
... Viral-serum IgE to herpes simples virus types I and II, EpsteinBarr virus and CMV Vascular-associated with migraines Metabolic-potassium intoxication ...
Infections of the External Ear - ANNALS Academy of Medicine
... narrow ear canals and non-atopic eczema. Pain (70%), itch (60%), deafness (32%) and fullness (22%) are the main cardinal symptoms. 8 Signs on examination include erythema, oedema, purulent otorrhoea and crusting of the canal wall skin. A gentle tug of the auricle upward and backward usually causes p ...
... narrow ear canals and non-atopic eczema. Pain (70%), itch (60%), deafness (32%) and fullness (22%) are the main cardinal symptoms. 8 Signs on examination include erythema, oedema, purulent otorrhoea and crusting of the canal wall skin. A gentle tug of the auricle upward and backward usually causes p ...
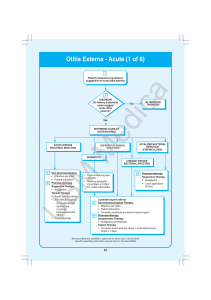
Infections of the External Ear March 2001
... Anatomy and Physiology The external ear is an area commonly subjected to acute and chronic inflammatory conditions. It consists of the auricle and external auditory meatus. The auricle is mostly composed of fibroelastic cartilage to which the skin and a small portion of subcutaneous tissue are close ...
... Anatomy and Physiology The external ear is an area commonly subjected to acute and chronic inflammatory conditions. It consists of the auricle and external auditory meatus. The auricle is mostly composed of fibroelastic cartilage to which the skin and a small portion of subcutaneous tissue are close ...
Case Study - Child 2 - National Minor Illness Centre
... of these areas was important due to the recent history of an upper respiratory tract infection and also to assess for signs of mastoiditis, a rare condition but one that can present as otalgia (NICE 2009). It was noted that Rosie had evidence of blocked nasal passages with some rhinorrhea, but all o ...
... of these areas was important due to the recent history of an upper respiratory tract infection and also to assess for signs of mastoiditis, a rare condition but one that can present as otalgia (NICE 2009). It was noted that Rosie had evidence of blocked nasal passages with some rhinorrhea, but all o ...
Guideline for - Toward Optimized Practice
... symptoms and signs of ear infection, i.e., earache, fever, irritability, poor feeding or vomiting, often associated with cough and rhinitis.18 This differentiates AOM from: ♦ Myringitis - inflammation of the tympanic membrane. This is usually associated with viral infections of the upper respirator ...
... symptoms and signs of ear infection, i.e., earache, fever, irritability, poor feeding or vomiting, often associated with cough and rhinitis.18 This differentiates AOM from: ♦ Myringitis - inflammation of the tympanic membrane. This is usually associated with viral infections of the upper respirator ...
Otitis media

Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. The two main types are acute otitis media (AOM) and otitis media with effusion (OME). AOM is an infection of abrupt onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep. Decreased eating and a fever may also be present. OME is typically not associated with symptoms. Occasionally a feeling of fullness is described. It is defined as the presence of non-infectious fluid in the middle ear for more than three months. Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is middle ear inflammation of greater than two weeks that results in episodes of discharge from the ear. It may be a complication of acute otitis media. Pain is rarely present. All three may be associated with hearing loss. The hearing loss in OME, due to its chronic nature, may affect a child's ability to learn.The cause of AOM is related to childhood anatomy and immune function. Either bacteria or viruses may be involved. Risk factors include: exposure to smoke, use of pacifiers, and attending daycare. It occurs more commonly in those who are Native American or who have Down syndrome. OME frequently occurs following AOM but may also be related to viral upper respiratory infections, irritants such as smoke, or allergies. Looking at the eardrum is important for making the correct diagnosis. Signs of AOM include bulging or a lack of movement of the tympanic membrane from a puff of air. New discharge not related to otitis externa also indicates the diagnosis.A number of measures decrease the risk of otitis media including: pneumococcal and influenza vaccination, exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life, and avoiding tobacco smoke. In those with otitis media with effusion antibiotics do not generally speed recovery. The use of pain medications for AOM is important. This may include: paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen, benzocaine ear drops, or opioids. In AOM, antibiotics may speed recovery but may result in side effects. Antibiotics are often recommended in those with severe disease or under two years old. In those with less severe disease they may only be recommended in those who do not improve after two or three days. The initial antibiotic of choice is typically amoxicillin. In those with frequent infections tympanostomy tubes may decrease recurrence.Worldwide AOM affect about 11% of people a year (about 710 million cases). Half the cases involve children less than five years of age and it is more common among males. Of those affected about 4.8% or 31 million develop chronic suppurative otitis media. Before the age of ten OME affects about 80% of children at some point in time. Otitis media resulted in 2,400 deaths in 2013 – down from 4,900 deaths in 1990.