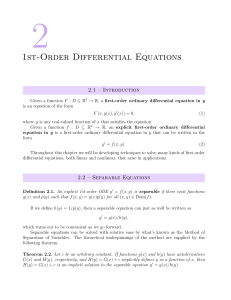
Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
... Use basic trigonometric identities to graph y = f (–x) Example 1: Sketch the graph of y = sin (–x). The graph of y = sin (–x) is the graph of y = sin x reflected in the x-axis. y = sin (–x) y Use the identity sin (–x) = – sin x y = sin x ...
... Use basic trigonometric identities to graph y = f (–x) Example 1: Sketch the graph of y = sin (–x). The graph of y = sin (–x) is the graph of y = sin x reflected in the x-axis. y = sin (–x) y Use the identity sin (–x) = – sin x y = sin x ...
Chapter 4 Continuous Random Variables
... One common question we encounter in practice is the transformation of random variables. The question is simple: Given a random variable X with PDF fX (x) and CDF FX (x), and suppose that Y = g(X) for some function g, then what are fY (y) and FY (y)? The general technique we use to tackle these probl ...
... One common question we encounter in practice is the transformation of random variables. The question is simple: Given a random variable X with PDF fX (x) and CDF FX (x), and suppose that Y = g(X) for some function g, then what are fY (y) and FY (y)? The general technique we use to tackle these probl ...
"Restricted Partition Function as Bernoulli and Eulerian Polynomials of Higher Order"
... Straightforward calculations show that the expression (46) produces exactly the same formulas for m = 1, 2, . . . , 12 which were obtained in [8]. It needs to be noted that typically the argument s in all formulas derived above is assumed to have integer values, but it is obvious that all results ca ...
... Straightforward calculations show that the expression (46) produces exactly the same formulas for m = 1, 2, . . . , 12 which were obtained in [8]. It needs to be noted that typically the argument s in all formulas derived above is assumed to have integer values, but it is obvious that all results ca ...
INTRODUCTION TO POLYNOMIAL CALCULUS 1. Straight Lines
... 2. Slope of a Curve We know about the slope of a straight line. It is the change in the y-coordinate divided by the change in the x-coordinate (rise divided by run) as we move from a given point on the line to any other point on the line. The law of similar triangles says that this ratio is independ ...
... 2. Slope of a Curve We know about the slope of a straight line. It is the change in the y-coordinate divided by the change in the x-coordinate (rise divided by run) as we move from a given point on the line to any other point on the line. The law of similar triangles says that this ratio is independ ...