Three subunits of the RNA polymerase II
... phenotypes tested (data not shown). This is in contrast to the strong synergistic interactions which are seen with migl disruptions, and suggests that all three genes function closely together in the same regulatory pathway. We also tested if any of the three genes could complement disruptions of th ...
... phenotypes tested (data not shown). This is in contrast to the strong synergistic interactions which are seen with migl disruptions, and suggests that all three genes function closely together in the same regulatory pathway. We also tested if any of the three genes could complement disruptions of th ...
Ding, Yi : Singular Value Decomposition applied to the building of class predictor
... method (eigen gene) to the commonly used marker gene method. For both data sets, higher accuracy was achieved in almost all cases by eigen gene method when using same number of features. (See figure 2 and 3). We also notice that eigen gene predictor performs much better than the marker gene in the t ...
... method (eigen gene) to the commonly used marker gene method. For both data sets, higher accuracy was achieved in almost all cases by eigen gene method when using same number of features. (See figure 2 and 3). We also notice that eigen gene predictor performs much better than the marker gene in the t ...
Copy number variants and genetic traits: closer to the resolution of
... regions of 1 kb in length or larger. For example, Goossens et al. showed that in a fraction of cases the α-globin loci are triplicated47; normally, they are present in two copies per haploid genome, although in some instances they carry deletions 48. Subsequently, the number of X-linked pigment gene ...
... regions of 1 kb in length or larger. For example, Goossens et al. showed that in a fraction of cases the α-globin loci are triplicated47; normally, they are present in two copies per haploid genome, although in some instances they carry deletions 48. Subsequently, the number of X-linked pigment gene ...
Molecular Biology Databases
... OR will locate all records containing either word not necessarily both e.g. human OR protease) NOT will locate records containing one word, but NOT the other word e.g. human NOT protease ...
... OR will locate all records containing either word not necessarily both e.g. human OR protease) NOT will locate records containing one word, but NOT the other word e.g. human NOT protease ...
Lectures 15-16 Molecular mechanisms of plant
... Molecular mechanisms of plant resistance to disease Plant disease caused by viruses, bacteria and fungi are controlled naturally by plant host resistance (R) genes and avirulence (avr) genes of the pathogen. This has been termed gene-for-gene resistance. A simple model explains these gene-for-gene i ...
... Molecular mechanisms of plant resistance to disease Plant disease caused by viruses, bacteria and fungi are controlled naturally by plant host resistance (R) genes and avirulence (avr) genes of the pathogen. This has been termed gene-for-gene resistance. A simple model explains these gene-for-gene i ...
Evidence for Evolution - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... consequence of branching evolution and common ancestry ...
... consequence of branching evolution and common ancestry ...
Imprinted green beards: a little less than kin and more than kind
... Figure 1. The mesiRNA ratchet. A population initially fixed for allele A (upper left) is successively invaded by an allele A 0 that also encodes a mesiRNA; an allele A8 that retains the mesiRNA but is insensitive to its effects and an allele A* that encodes a new mesiRNA (lower right). Subscripts m ...
... Figure 1. The mesiRNA ratchet. A population initially fixed for allele A (upper left) is successively invaded by an allele A 0 that also encodes a mesiRNA; an allele A8 that retains the mesiRNA but is insensitive to its effects and an allele A* that encodes a new mesiRNA (lower right). Subscripts m ...
Independent evolution of overlapping polymerase and surface
... The genome of hepatitis B virus (HBV) provides a striking example of gene overlapping. In particular, the surface protein gene S is overlapped completely by the polymerase gene P. Evolutionary constraints in overlapping genes have been demonstrated for many viruses, with one of the two overlapping g ...
... The genome of hepatitis B virus (HBV) provides a striking example of gene overlapping. In particular, the surface protein gene S is overlapped completely by the polymerase gene P. Evolutionary constraints in overlapping genes have been demonstrated for many viruses, with one of the two overlapping g ...
J-Clustering - Hennig
... 6. When there are no more unassigned high-affinity genes, check to see if cluster C1 contains any elements whose affinity is lower than the current threshold. If so, remove the lowest-affinity gene from C1. Update the affinities of all genes by subtracting from each gene’s affinity, its similarity t ...
... 6. When there are no more unassigned high-affinity genes, check to see if cluster C1 contains any elements whose affinity is lower than the current threshold. If so, remove the lowest-affinity gene from C1. Update the affinities of all genes by subtracting from each gene’s affinity, its similarity t ...
Chapter 9
... Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) is an uncommon inherited disorder characterized by mental retardation, decreased muscle tone, short stature, emotional lability and an insatiable appetite which can lead to life-threatening obesity. The syndrome was first described in 1956 by Drs. Prader, Labhart, and Wil ...
... Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) is an uncommon inherited disorder characterized by mental retardation, decreased muscle tone, short stature, emotional lability and an insatiable appetite which can lead to life-threatening obesity. The syndrome was first described in 1956 by Drs. Prader, Labhart, and Wil ...
EN90016_Genetics
... population genetics. To know the mechanisms that determine the transmission of hereditary traits. To know the molecular mechanisms of genetic diseases, including cancer. To provide a working knowledge of genetics of disease, including the principles of population genetics and of a broad range of inh ...
... population genetics. To know the mechanisms that determine the transmission of hereditary traits. To know the molecular mechanisms of genetic diseases, including cancer. To provide a working knowledge of genetics of disease, including the principles of population genetics and of a broad range of inh ...
Chapter 14: Patterns of Inheritance
... 3. a karyotype display reveals the composition of chromosomes for an individual a cell sample is taken (white blood cells, amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling, etc.) cells are grown in culture, and eventually treated to make chromosomes easy to photograph the chromosome images are then an ...
... 3. a karyotype display reveals the composition of chromosomes for an individual a cell sample is taken (white blood cells, amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling, etc.) cells are grown in culture, and eventually treated to make chromosomes easy to photograph the chromosome images are then an ...
Genetics, after Mendel - Missouri State University
... • Complete extra sets of chromosomes • Rare event, but important evolutionarily • Many groups of plant species and some animal species have different multiples of chromosomes than related species ...
... • Complete extra sets of chromosomes • Rare event, but important evolutionarily • Many groups of plant species and some animal species have different multiples of chromosomes than related species ...
Sigma Xi, Montreal Nov 2004 - Biology Department | UNC Chapel Hill
... location occur among individuals within populations. Additionally, we do not know the degree to which such differences in chromosomal location affect gene expression at the transposed loci. We are studying this issue using Comparative Genomic Hybridization on a Microarray (CGHM) to detect genomic se ...
... location occur among individuals within populations. Additionally, we do not know the degree to which such differences in chromosomal location affect gene expression at the transposed loci. We are studying this issue using Comparative Genomic Hybridization on a Microarray (CGHM) to detect genomic se ...
Recitation Section 16 Recombination and Pedigrees
... In 1901 a physician in London named Archibald Garrod had some new patients with an unusual condition: when their urine came into contact with air it turned black. 1. What is the wild-type phenotype? ...
... In 1901 a physician in London named Archibald Garrod had some new patients with an unusual condition: when their urine came into contact with air it turned black. 1. What is the wild-type phenotype? ...
What is life? The physicist who sparked a revolution in biology Erwin
... he introduced some of the most important concepts in the history of biology, which continue to frame how we see life. At a time when it was thought that proteins, not DNA, were the hereditary material, Schrödinger argued the genetic material had to have a non-repetitive molecular structure. He claim ...
... he introduced some of the most important concepts in the history of biology, which continue to frame how we see life. At a time when it was thought that proteins, not DNA, were the hereditary material, Schrödinger argued the genetic material had to have a non-repetitive molecular structure. He claim ...
- Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... Annotations, which provide information regarding specific locations within the Bioseq ...
... Annotations, which provide information regarding specific locations within the Bioseq ...
11-3 Exploring Mendelian Genetics
... In most sexually reproducing organisms, each adult has two copies of each gene. These genes are segregated from each other when gametes are formed. The alleles for different genes usually segregate independently of one another ...
... In most sexually reproducing organisms, each adult has two copies of each gene. These genes are segregated from each other when gametes are formed. The alleles for different genes usually segregate independently of one another ...
A-4 Notes
... This ratio of 60/40 is also true (roughly) for your personality type. • Some people feel that this will give employers an excuse to fire people if they don’t have the ‘right’ genetics. • The bottom line is that there is a lot that we do not yet know about genetics. ...
... This ratio of 60/40 is also true (roughly) for your personality type. • Some people feel that this will give employers an excuse to fire people if they don’t have the ‘right’ genetics. • The bottom line is that there is a lot that we do not yet know about genetics. ...
Biotechnology
... utilization of biological processes for obtaining maximum benefits to man and other forms of life. Biotechnology: The use of living organisms for the manufacture of useful products: It may involve algae, bacteria, fungi, yeast cells of higher animal and plants. ...
... utilization of biological processes for obtaining maximum benefits to man and other forms of life. Biotechnology: The use of living organisms for the manufacture of useful products: It may involve algae, bacteria, fungi, yeast cells of higher animal and plants. ...
1. Which of the following statements about homologous
... Boys can inherit the recessive allele (c) that causes red-green colour blindness from their mother, not from their father. The allele for normal red and green vision is C. Which of the following genotypes are possible in men? A. ...
... Boys can inherit the recessive allele (c) that causes red-green colour blindness from their mother, not from their father. The allele for normal red and green vision is C. Which of the following genotypes are possible in men? A. ...
MicroarraysExp
... help control how the coding regions are used - e.g. promoters The supercoiling of the DNA may also control how the coding regions are used. As well, there is a lot of DNA which appears to be "junk" - i.e. to date no function is known. But we keep making new discoveries e.g. some of the "junk" codes ...
... help control how the coding regions are used - e.g. promoters The supercoiling of the DNA may also control how the coding regions are used. As well, there is a lot of DNA which appears to be "junk" - i.e. to date no function is known. But we keep making new discoveries e.g. some of the "junk" codes ...
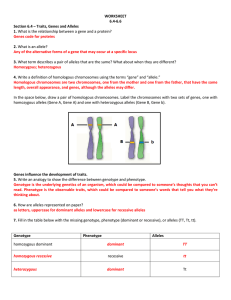
WORKSHEET 6.4-6.6 Section 6.4 – Traits, Genes and Alleles 1
... 9. The exchange of chromosome segments between homologous chromosomes is called Crossing over 10. The tendency for two genes that are located close together on a chromosome to be inherited together is called. ...
... 9. The exchange of chromosome segments between homologous chromosomes is called Crossing over 10. The tendency for two genes that are located close together on a chromosome to be inherited together is called. ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.