Leukaemia Section t(9;11)(p22;p15) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Note: The gene contains at least 15 exons and 14 introns. DNA / RNA Two alternative splice variants: p75 and p52. Protein Chromatin-associated protein involved in trascriptional regulation, mRNA splicing and cell survival in vitro. Contains a PWWP domain and AT hook-like motifs. ...
... Note: The gene contains at least 15 exons and 14 introns. DNA / RNA Two alternative splice variants: p75 and p52. Protein Chromatin-associated protein involved in trascriptional regulation, mRNA splicing and cell survival in vitro. Contains a PWWP domain and AT hook-like motifs. ...
- Wiley Online Library
... nodular heterotopia or they may be the direct result of the combined deletion/duplication of genes specific to our patient’s particular chromosomal aberration. None of the reported cases with deletions or duplications similar to those constituting our patient’s set of modifications had periventricul ...
... nodular heterotopia or they may be the direct result of the combined deletion/duplication of genes specific to our patient’s particular chromosomal aberration. None of the reported cases with deletions or duplications similar to those constituting our patient’s set of modifications had periventricul ...
G 1 - University of Queensland
... McLachlan (1977) proposed w=wo where wo is chosen to minimize asymptotic bias of A(w) in the case of two homoscedastic normal groups. Value of w0 was found to range between 0.6 and 0.7, depending on the values of p, , and n1 . ...
... McLachlan (1977) proposed w=wo where wo is chosen to minimize asymptotic bias of A(w) in the case of two homoscedastic normal groups. Value of w0 was found to range between 0.6 and 0.7, depending on the values of p, , and n1 . ...
Genetics
... Who was Gregor Mendel? • Austrian monk who studied mathematics and science • As a boy he experimented with pea plants • Made careful use of scientific methods, which resulted in the first recorded study of how traits pass from one generation to the next. ...
... Who was Gregor Mendel? • Austrian monk who studied mathematics and science • As a boy he experimented with pea plants • Made careful use of scientific methods, which resulted in the first recorded study of how traits pass from one generation to the next. ...
(2013). Nothing in genetics makes sense except in light of genomic
... Next, suppose that A and B are two alleles at a single locus. If A increases because (a) it was favored by selectionSIL , (b) the forward mutation rate producing it was faster than the back-mutation rate destroying it, (c) immigration brought in the allele faster than emigration removed it, or (d ) ...
... Next, suppose that A and B are two alleles at a single locus. If A increases because (a) it was favored by selectionSIL , (b) the forward mutation rate producing it was faster than the back-mutation rate destroying it, (c) immigration brought in the allele faster than emigration removed it, or (d ) ...
Individual gene function 4A. Inferring gene function from mutations
... phenotypes, such a gene might be called long1. Indeed, genes in C. elegans named lon for long are required to limit body size. Going in the other direction, the wee1 gene in Schizzosacharomyces pombe is necessary for appropriate cell size. Because loss-of-function is the gold standard for genetic in ...
... phenotypes, such a gene might be called long1. Indeed, genes in C. elegans named lon for long are required to limit body size. Going in the other direction, the wee1 gene in Schizzosacharomyces pombe is necessary for appropriate cell size. Because loss-of-function is the gold standard for genetic in ...
Chapter12_Section05_edit-1
... The repressor protein changes shape and falls off the operator and transcription is made possible. ...
... The repressor protein changes shape and falls off the operator and transcription is made possible. ...
Natural Selection and Variation in Populations
... determined largely by selection acting on the gene fund already present in the population, the component genes of which represent mutations that have occurred many generations ago. New mutations are important chiefly as a means of replenishing the store of variability which is continuously being dep ...
... determined largely by selection acting on the gene fund already present in the population, the component genes of which represent mutations that have occurred many generations ago. New mutations are important chiefly as a means of replenishing the store of variability which is continuously being dep ...
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION
... Chromatin structure and organization fundamentally affect gene expression by changing the chromatin structure, especially its compaction state. The degree of chromatin compaction essentially relies on histone modifications and DNA methylation. Active chromatin regions usually contain high rate of ac ...
... Chromatin structure and organization fundamentally affect gene expression by changing the chromatin structure, especially its compaction state. The degree of chromatin compaction essentially relies on histone modifications and DNA methylation. Active chromatin regions usually contain high rate of ac ...
Document
... In particular, many enzymes exclusively produced by bacteria have been discovered thanks to the activity based exploration of metagenomes, espically those originating from highly polluted environments and also expose to extreme physical conditions. ...
... In particular, many enzymes exclusively produced by bacteria have been discovered thanks to the activity based exploration of metagenomes, espically those originating from highly polluted environments and also expose to extreme physical conditions. ...
marker-assisted backcrossing - Rice Knowledge Bank
... • Large amounts of donor chromosome remain even after many backcrosses • Undesirable due to other donor genes that negatively ...
... • Large amounts of donor chromosome remain even after many backcrosses • Undesirable due to other donor genes that negatively ...
1.5 - Biology Junction
... in structure and function. Hox genes control the differentiation of cells and tissues in the embryo. ...
... in structure and function. Hox genes control the differentiation of cells and tissues in the embryo. ...
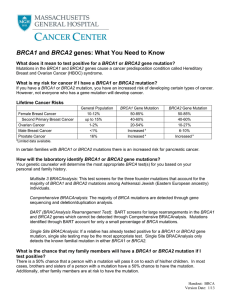
BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes: What You Need to Know
... majority of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations among Ashkenazi Jewish (Eastern European ancestry) individuals. Comprehensive BRACAnalysis: The majority of BRCA mutations are detected through gene sequencing and deletion/duplication analysis. BART (BRACAnalysis Rearrangement Test): BART screens for large rear ...
... majority of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations among Ashkenazi Jewish (Eastern European ancestry) individuals. Comprehensive BRACAnalysis: The majority of BRCA mutations are detected through gene sequencing and deletion/duplication analysis. BART (BRACAnalysis Rearrangement Test): BART screens for large rear ...
Brief Historical Sketch of Chromosomal
... was another term for chromosomal translocations (CTs) used by Belling (11). CTs, insertions, and inversions became the subject of extensive studies in the late 1920s and 1930s. Important advances in 1926–1927 were the discoveries of the mutagenic effects of X-rays in Drosophila by Herman J. Muller ( ...
... was another term for chromosomal translocations (CTs) used by Belling (11). CTs, insertions, and inversions became the subject of extensive studies in the late 1920s and 1930s. Important advances in 1926–1927 were the discoveries of the mutagenic effects of X-rays in Drosophila by Herman J. Muller ( ...
B-Cell Gene Rearrangement
... Genomic DNA is extracted from blood, lymph node, bone marrow, or other tissue types (formalin-fixed or fresh) and the rearranged immunoglobulin heavy (and/or light) chain genes are amplified by PCR using a multiplex primer method based on the BIOMED-2 strategy (1,2). Precise fragment sizing of the a ...
... Genomic DNA is extracted from blood, lymph node, bone marrow, or other tissue types (formalin-fixed or fresh) and the rearranged immunoglobulin heavy (and/or light) chain genes are amplified by PCR using a multiplex primer method based on the BIOMED-2 strategy (1,2). Precise fragment sizing of the a ...
Lec 26 - Mutation Breeding
... Mutation is a sudden heritable change in a characteristic of an organisam. This definition requires that the change in the characteristic be heritable, but it does not state the genetic basis of the heritable change. Clearly, a mutation (as defined above) may be the result of a change in a gene, a c ...
... Mutation is a sudden heritable change in a characteristic of an organisam. This definition requires that the change in the characteristic be heritable, but it does not state the genetic basis of the heritable change. Clearly, a mutation (as defined above) may be the result of a change in a gene, a c ...
Hogart A, Leung KN, Wang NJ, Wu DJ, Driscoll J
... neurodevelopmental disorder with many autistic features.4 Despite incomplete penetrance of autism in 15q11–13 duplication syndrome, this duplication is the leading cytogenetic cause of autism, occurring in 1–3% of autism cases.5 The parent of origin effect observed in 15q11–13 duplication syndromes, ...
... neurodevelopmental disorder with many autistic features.4 Despite incomplete penetrance of autism in 15q11–13 duplication syndrome, this duplication is the leading cytogenetic cause of autism, occurring in 1–3% of autism cases.5 The parent of origin effect observed in 15q11–13 duplication syndromes, ...
“Adventures in Eukaryotic Gene Expression: Transcription, Splicing, Polyadenylation, and RNAi”
... Anders Virtanen: ...
... Anders Virtanen: ...
Meiosis: Pre Test - Gulf Coast State College
... A) an abnormal amount of somatic chromosomes only B) an abnormal amount of sex chromosomes only C) an abnormal amount of either somatic or sex chromosomes D) an abnormal recombination in the genes. 11. A condition characterized by an individual having six fingers is ___________________. A) polydacty ...
... A) an abnormal amount of somatic chromosomes only B) an abnormal amount of sex chromosomes only C) an abnormal amount of either somatic or sex chromosomes D) an abnormal recombination in the genes. 11. A condition characterized by an individual having six fingers is ___________________. A) polydacty ...
Gene Regulation - Lincoln Park High School
... The repressor protein changes shape and falls off the operator and transcription is made possible. ...
... The repressor protein changes shape and falls off the operator and transcription is made possible. ...
Review Questions
... but they are also classified on whether the change produces a premature stop in the gene. Nonsense mutations are mutations that result in a premature stop. They are called “nonsense” because all the codons following the stop codon are never translated, they are nonsense. If there is no premature sto ...
... but they are also classified on whether the change produces a premature stop in the gene. Nonsense mutations are mutations that result in a premature stop. They are called “nonsense” because all the codons following the stop codon are never translated, they are nonsense. If there is no premature sto ...
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2007
... function and interact, for example during embryonic development. But the technique The technique for which this year’s Nobel is perhaps even more important in medical Prize is awarded makes it possible to modify research because it now enables us to create nearly all mouse genes. The most common alt ...
... function and interact, for example during embryonic development. But the technique The technique for which this year’s Nobel is perhaps even more important in medical Prize is awarded makes it possible to modify research because it now enables us to create nearly all mouse genes. The most common alt ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.