3. Sequence preprocessing
... – some replace Ns with random base, some with fixed base (e.g. SHAHA2 & Velvet = A) ...
... – some replace Ns with random base, some with fixed base (e.g. SHAHA2 & Velvet = A) ...
William Yin
... certain fragments of double-stranded RNA interferes with the expression of a particular gene which shares a homologous sequence with the dsRNA. The RNA interference machinery cuts up double-stranded RNA molecule with an enzyme known as Dicer which separates it into two strands (cutting dsRNA into 22 ...
... certain fragments of double-stranded RNA interferes with the expression of a particular gene which shares a homologous sequence with the dsRNA. The RNA interference machinery cuts up double-stranded RNA molecule with an enzyme known as Dicer which separates it into two strands (cutting dsRNA into 22 ...
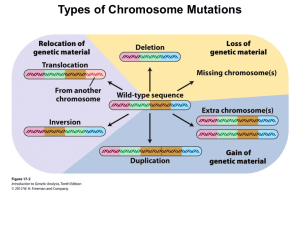
Mutations PPT
... follows the mutation to shift position • A base is inserted or removed from DNA sequence • Insertion and deletion mutations have the most effect on an organism because they affect many amino acids on the protein, not just one. ...
... follows the mutation to shift position • A base is inserted or removed from DNA sequence • Insertion and deletion mutations have the most effect on an organism because they affect many amino acids on the protein, not just one. ...
On Nature Versus And Nurture
... context-dependent such that reducing environmental sources of variation increases heritability. This means that efforts to standardize education or other aspects of the environment will magnify heritability, and we will be selecting students based mainly on genetic differences in their performance o ...
... context-dependent such that reducing environmental sources of variation increases heritability. This means that efforts to standardize education or other aspects of the environment will magnify heritability, and we will be selecting students based mainly on genetic differences in their performance o ...
Mammalian X Chromosome Inactivation
... * low-set ears * overlapping fingers * clenched fist * clubfeet ...
... * low-set ears * overlapping fingers * clenched fist * clubfeet ...
Vocabulary handout
... are stretched out very thin to allow surfaces for the various chemical reactions that involve chromosomes to take place. When the nucleus is stained and examined, it appears uniformly colored and the chromosomes collectively are termed chromatin. It is critical to remember that even though individua ...
... are stretched out very thin to allow surfaces for the various chemical reactions that involve chromosomes to take place. When the nucleus is stained and examined, it appears uniformly colored and the chromosomes collectively are termed chromatin. It is critical to remember that even though individua ...
Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... Males have only one copy of the X chromosome – They are said to be hemizygous for their X-linked genes ...
... Males have only one copy of the X chromosome – They are said to be hemizygous for their X-linked genes ...
bivarate2
... • Do the genes that influence trait B also influence trait A? • Are there genes that are unique to trait A? • Is the phenotypic correlation caused by genetic correlation? • What is the genetic correlation? (ie the genetic covariance /genetic SD(A)*genetic SD(B) • The same questions apply to environm ...
... • Do the genes that influence trait B also influence trait A? • Are there genes that are unique to trait A? • Is the phenotypic correlation caused by genetic correlation? • What is the genetic correlation? (ie the genetic covariance /genetic SD(A)*genetic SD(B) • The same questions apply to environm ...
Rice Bioinformatics. Analysis of Rice Sequence Data and
... clone, and sequence data for Arabidopsis biologists. Likewise, with the generation of a vast amount of rice genomic sequence data, the necessity to integrate rice sequence data with other information from rice genetics, breeding, physiology, and biochemistry is apparent. Several centers have develop ...
... clone, and sequence data for Arabidopsis biologists. Likewise, with the generation of a vast amount of rice genomic sequence data, the necessity to integrate rice sequence data with other information from rice genetics, breeding, physiology, and biochemistry is apparent. Several centers have develop ...
Summary 121 Summary The Hox genes form a subset of the
... homeobox encodes a DNA binding motif, called the homeodomain. In most animal species the Hox genes are organised in one or more clusters. The number of genes present in a cluster varies between animal species; the number of clusters in each species also varies. The Hox clusters are thought to have a ...
... homeobox encodes a DNA binding motif, called the homeodomain. In most animal species the Hox genes are organised in one or more clusters. The number of genes present in a cluster varies between animal species; the number of clusters in each species also varies. The Hox clusters are thought to have a ...
DESIGNER BABIES: GENETIC ENGINEERING GONE TOO FAR? INTRODUCTION: PURPOSE OF
... question was asked why not do this for humans? Because we have the human genome mapped out, we have a good sense of which genes alter what, such as a gene that alters the color of a person’s eyes or how athletic the baby will be. With this newfound idea came a slew of morally grey area. If being abl ...
... question was asked why not do this for humans? Because we have the human genome mapped out, we have a good sense of which genes alter what, such as a gene that alters the color of a person’s eyes or how athletic the baby will be. With this newfound idea came a slew of morally grey area. If being abl ...
PDF
... or extrachromosomal elements. The GC content of the chromosome is 33.96% based on the genome sequence, slightly higher than the reported value of 32.5% (Svetlichny and Svetlichnaya, 1988) and is predicted to contain 1813 proteincoding genes and 52 RNA genes (Figure 1). The completed genome sequence ...
... or extrachromosomal elements. The GC content of the chromosome is 33.96% based on the genome sequence, slightly higher than the reported value of 32.5% (Svetlichny and Svetlichnaya, 1988) and is predicted to contain 1813 proteincoding genes and 52 RNA genes (Figure 1). The completed genome sequence ...
the velocardiofacial syndrome
... located on the human chromosome 15q11-13 region [75]. Different molecular mechanisms leading to this loss of expression have been identified, including microdeletions, intragenic mutations, uniparental disomy and imprinting defects: ...
... located on the human chromosome 15q11-13 region [75]. Different molecular mechanisms leading to this loss of expression have been identified, including microdeletions, intragenic mutations, uniparental disomy and imprinting defects: ...
recessive budgies
... effect on the offspring. If the single gene has a overwhelming effect on the offspring, that is the offspring display visually the characteristic being passed on from the parent. This type of gene is said to be a dominant gene. The other basic type of gene is what we call a recessive gene, this type ...
... effect on the offspring. If the single gene has a overwhelming effect on the offspring, that is the offspring display visually the characteristic being passed on from the parent. This type of gene is said to be a dominant gene. The other basic type of gene is what we call a recessive gene, this type ...
12A.H
... As you have learned in previous units, DNA is the central molecule of the cell, encoding information that is used to make proteins essential to the cell. All of life on this planet is controlled by DNA (or in the case of some viruses, by RNA). In recent years, scientists have learned new techniques ...
... As you have learned in previous units, DNA is the central molecule of the cell, encoding information that is used to make proteins essential to the cell. All of life on this planet is controlled by DNA (or in the case of some viruses, by RNA). In recent years, scientists have learned new techniques ...
Document
... You cross one bright-eyed mutant female line to males from two different fly lines. Line 1 is pure-breeding for loss of white function (w-Y). Line 2 is pure-breeding for loss of scarlet function (st-st-). The cross to line 1 gives all wild type progeny. The cross to line 2 gives all bright-eyed mut ...
... You cross one bright-eyed mutant female line to males from two different fly lines. Line 1 is pure-breeding for loss of white function (w-Y). Line 2 is pure-breeding for loss of scarlet function (st-st-). The cross to line 1 gives all wild type progeny. The cross to line 2 gives all bright-eyed mut ...
report of the first meeting of the ad hoc technical expert group
... Transformation cassette – A transformation cassette comprises a group of genetic elements (e.g. parts of a vector and one or more of the following: a promoter, the coding sequence of a gene and a terminator), which are physically linked and often originated from different donor organisms. The transf ...
... Transformation cassette – A transformation cassette comprises a group of genetic elements (e.g. parts of a vector and one or more of the following: a promoter, the coding sequence of a gene and a terminator), which are physically linked and often originated from different donor organisms. The transf ...
b - AET
... eye allele from either parent, the offspring will have brown eyes. The offspring would have to receive a blue eye allele from each parent to have blue eyes. In cattle, the allele that causes horns to grow is recessive. The hornless, or polled, allele is dominant. There are additional genes that affe ...
... eye allele from either parent, the offspring will have brown eyes. The offspring would have to receive a blue eye allele from each parent to have blue eyes. In cattle, the allele that causes horns to grow is recessive. The hornless, or polled, allele is dominant. There are additional genes that affe ...
The Role of Mismatch Repair in Bacterial Evolution
... The spread of mutators occurs because they can create or acquire a beneficial mutation (e.g. antibiotic resistance) that gives them advantage over non-adapted bacteria. In an asexual population, the mutator may then spread with the advantageous gene, by a phenomenon called »hitch-hiking« (29) and in ...
... The spread of mutators occurs because they can create or acquire a beneficial mutation (e.g. antibiotic resistance) that gives them advantage over non-adapted bacteria. In an asexual population, the mutator may then spread with the advantageous gene, by a phenomenon called »hitch-hiking« (29) and in ...
clustering-basic
... – Class labels of training data are unknown – Given a set of measurements, observations, etc., need to establish existence of classes or clusters in data ...
... – Class labels of training data are unknown – Given a set of measurements, observations, etc., need to establish existence of classes or clusters in data ...
BINF6201/8201 Dynamics of genes in populations 2
... Ø A tree that shows the parent-child relationships of genes during evolution/history is called a genealogical tree of the gene. Ø It has been theoretically shown and experimentally demonstrated that if we go back enough number of generations, all existing descendant genes can be traced back to a s ...
... Ø A tree that shows the parent-child relationships of genes during evolution/history is called a genealogical tree of the gene. Ø It has been theoretically shown and experimentally demonstrated that if we go back enough number of generations, all existing descendant genes can be traced back to a s ...
The Genetic Code
... • DNA is transcribed to messenger RNA by RNA polymerase. – Transcription is the process by which the hereditary information in DNA is copied to RNA. • The mRNA is then translated to protein. – Translation is the process wherein the language of nucleic acids, the order of the nucleotide bases, is con ...
... • DNA is transcribed to messenger RNA by RNA polymerase. – Transcription is the process by which the hereditary information in DNA is copied to RNA. • The mRNA is then translated to protein. – Translation is the process wherein the language of nucleic acids, the order of the nucleotide bases, is con ...
Full Text - Science and Education Publishing
... for CTX-M and SHV genes by PCR. So was selected for DNA sequencing. Chromogenic agar media (Liofilchem Co. Italy) and standard biochemical tests [8], were used in the isolation and identification of bacteria. E. coli ATCC 25922 and Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 700603 were ...
... for CTX-M and SHV genes by PCR. So was selected for DNA sequencing. Chromogenic agar media (Liofilchem Co. Italy) and standard biochemical tests [8], were used in the isolation and identification of bacteria. E. coli ATCC 25922 and Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 700603 were ...
The Genetic Code
... • DNA is transcribed to messenger RNA by RNA polymerase. – Transcription is the process by which the hereditary information in DNA is copied to RNA. • The mRNA is then translated to protein. – Translation is the process wherein the language of nucleic acids, the order of the nucleotide bases, is con ...
... • DNA is transcribed to messenger RNA by RNA polymerase. – Transcription is the process by which the hereditary information in DNA is copied to RNA. • The mRNA is then translated to protein. – Translation is the process wherein the language of nucleic acids, the order of the nucleotide bases, is con ...
supervised-i
... FP: Genes newly predicted to be in a functional group that were thought to belong to another, may be coregulated with the new group. FN: Genes that were thought to belong to a functional group may not be coregulated with that group. Inspecting “errors” often leads to the most ...
... FP: Genes newly predicted to be in a functional group that were thought to belong to another, may be coregulated with the new group. FN: Genes that were thought to belong to a functional group may not be coregulated with that group. Inspecting “errors” often leads to the most ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.