Faster-Z Evolution Is Predominantly Due to Genetic Drift Research
... The X chromosome has several properties that distinguish it from the autosomes (Vicoso and Charlesworth 2006) and that have the potential to influence the rate and pattern of evolution of X-linked genes (Charlesworth et al. 1987). Recent genomic scans in both Drosophila (Counterman et al. 2004; Begu ...
... The X chromosome has several properties that distinguish it from the autosomes (Vicoso and Charlesworth 2006) and that have the potential to influence the rate and pattern of evolution of X-linked genes (Charlesworth et al. 1987). Recent genomic scans in both Drosophila (Counterman et al. 2004; Begu ...
PDF - Blood Journal
... region of chromosome 16 with a constitutively open chromatin structure in all cell types. The genes have methylation-free CpG islands, and the major regulatory element (␣-MRE) is a single erythroid-specific DNaseI hypersensitive site located in the intron of a ubiquitously expressed gene, some 40 kb ...
... region of chromosome 16 with a constitutively open chromatin structure in all cell types. The genes have methylation-free CpG islands, and the major regulatory element (␣-MRE) is a single erythroid-specific DNaseI hypersensitive site located in the intron of a ubiquitously expressed gene, some 40 kb ...
Document
... The assignment of a function to a gene product can be made by a human curator by assessing all of the data (similarities, protein domains, signal peptide etc) This is a labour intensive process and like gene prediction is subjective ...
... The assignment of a function to a gene product can be made by a human curator by assessing all of the data (similarities, protein domains, signal peptide etc) This is a labour intensive process and like gene prediction is subjective ...
熊本大学学術リポジトリ Kumamoto University Repository System
... processes. In the mouse, goosecoid is expressed in the developing primitive streak, more specifically in those cells that are undergoing anterior migration – one of the earliest features of gastrulation. The fate of these cells has been demonstrated to lie in the head process (Beddington, 1983). How ...
... processes. In the mouse, goosecoid is expressed in the developing primitive streak, more specifically in those cells that are undergoing anterior migration – one of the earliest features of gastrulation. The fate of these cells has been demonstrated to lie in the head process (Beddington, 1983). How ...
Reproduction and Fetal Technology
... A genome- is the totality of the genetic material of a cell or organism Vector - A vector is a small piece of DNA used to carry a gene of interest. Besides the gene being studied, a vector may contain elements which are used to help the gene integrate into a genome Recombination - The process in whi ...
... A genome- is the totality of the genetic material of a cell or organism Vector - A vector is a small piece of DNA used to carry a gene of interest. Besides the gene being studied, a vector may contain elements which are used to help the gene integrate into a genome Recombination - The process in whi ...
The linear chromosome of the plant
... [6], while most other mycoplasmas have only one. Also, in contrast to most other mycoplasmas, phytoplasmas have resisted all attempts of cultivation in cell-free media, indicating that they have a different metabolism than other mycoplasmas and/or a greater reliance on their hosts. As a consequence, ...
... [6], while most other mycoplasmas have only one. Also, in contrast to most other mycoplasmas, phytoplasmas have resisted all attempts of cultivation in cell-free media, indicating that they have a different metabolism than other mycoplasmas and/or a greater reliance on their hosts. As a consequence, ...
Introduction to GeneBreak
... the gene breakpoint frequency exceeded 15% (horizontal dashed line), the breakpoint frequency (%) follows the gene name. ...
... the gene breakpoint frequency exceeded 15% (horizontal dashed line), the breakpoint frequency (%) follows the gene name. ...
Phenotype function notes
... Genetics can be used as a tool to study problems in biology and has made important contributions to the fields of development, cell biology and neurobiology. One of the goals in this type of research is to use mutations to reveal the normal function of a gene. However, to infer the function of a gen ...
... Genetics can be used as a tool to study problems in biology and has made important contributions to the fields of development, cell biology and neurobiology. One of the goals in this type of research is to use mutations to reveal the normal function of a gene. However, to infer the function of a gen ...
Assessment Schedule 2010 AS 90459 (Biology 2.3) Describe
... describe inbreeding and its effect on one of these evolutionary process in (b). ...
... describe inbreeding and its effect on one of these evolutionary process in (b). ...
Beyond Dominant and Recessive Alleles
... said to have multiple alleles. • A common example is coat color in rabbits. • Their color is determined by a gene that has at least four different alleles. • Human blood type is also multiple allelic, meaning that there are three possible alleles, A, B, and i (ii causes O type blood) ...
... said to have multiple alleles. • A common example is coat color in rabbits. • Their color is determined by a gene that has at least four different alleles. • Human blood type is also multiple allelic, meaning that there are three possible alleles, A, B, and i (ii causes O type blood) ...
FREE Sample Here
... Answer: adenine:thymine, guanine:cytosine Section: 1.3 32) What is meant by the term genetic code? Answer: The genetic code consists of a linear series of three adjacent nucleotides present in mRNA molecules. Section: 1.3 33) Compare and contrast nonenzymatic and enzymatic proteins. Answer: Both are ...
... Answer: adenine:thymine, guanine:cytosine Section: 1.3 32) What is meant by the term genetic code? Answer: The genetic code consists of a linear series of three adjacent nucleotides present in mRNA molecules. Section: 1.3 33) Compare and contrast nonenzymatic and enzymatic proteins. Answer: Both are ...
Quiz 9 BIol203 Fall 2013ppt
... Arl is a transcription factor and thus must get into the nucleus to function. However, the nuclear localization sequence is NOT located on exon 1, exon 2, or exon 4. 4pts. Circle the portion of the above gene that you would use to make a transgene that expresses Arl in the leg only. 4pts. Mark with ...
... Arl is a transcription factor and thus must get into the nucleus to function. However, the nuclear localization sequence is NOT located on exon 1, exon 2, or exon 4. 4pts. Circle the portion of the above gene that you would use to make a transgene that expresses Arl in the leg only. 4pts. Mark with ...
Whose got Genes?
... chromosomes in the nuclei. Each organims has a fixed number of chromosomes. Humans have 23 pairs (46) chromosomes. Genetics is the study of how traits are passed on from one generation to another Baker 2003/2004 ...
... chromosomes in the nuclei. Each organims has a fixed number of chromosomes. Humans have 23 pairs (46) chromosomes. Genetics is the study of how traits are passed on from one generation to another Baker 2003/2004 ...
PowerPoint - The Science Queen
... chromosomes in the nuclei. Each organims has a fixed number of chromosomes. Humans have 23 pairs (46) chromosomes. Genetics is the study of how traits are passed on from one generation to another Baker 2003/2004 ...
... chromosomes in the nuclei. Each organims has a fixed number of chromosomes. Humans have 23 pairs (46) chromosomes. Genetics is the study of how traits are passed on from one generation to another Baker 2003/2004 ...
Gene Section MTUS1 (mitochondrial tumor suppressor 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... alternative splicing. Alternatively, this isoform 2 may be a protein product from the MTUS1 gene with a recently identified polymorphic copy number variant at DNA level (Var del Ex4 that lacking the exon 4). The existence of MTUS1 isoform 3 is not entirely certain. The expression of MTUS1 isoform 3 ...
... alternative splicing. Alternatively, this isoform 2 may be a protein product from the MTUS1 gene with a recently identified polymorphic copy number variant at DNA level (Var del Ex4 that lacking the exon 4). The existence of MTUS1 isoform 3 is not entirely certain. The expression of MTUS1 isoform 3 ...
Brooker Chapter 16
... polypeptide with a deleterious phenotype But can also be neutral of even beneficial Those that don’t cause reading frame shifts Number of base-pairs deleted or inserted is divisible by 3 (e.g. 3, 6, 9, 12…) Usually less harmful than reading frame shift mutations ...
... polypeptide with a deleterious phenotype But can also be neutral of even beneficial Those that don’t cause reading frame shifts Number of base-pairs deleted or inserted is divisible by 3 (e.g. 3, 6, 9, 12…) Usually less harmful than reading frame shift mutations ...
Gene Linkage in Fruit Flies
... Set up the fruit fly experiment so that both eye color and eye shape are analyzed in the same cross. (To select two traits, hold the control or command button as you click on both traits in the list.) Set up the alleles so that both parents are heterozygous for both traits, as in the Punnett square ...
... Set up the fruit fly experiment so that both eye color and eye shape are analyzed in the same cross. (To select two traits, hold the control or command button as you click on both traits in the list.) Set up the alleles so that both parents are heterozygous for both traits, as in the Punnett square ...
Pleiotropy and the Genomic Location of Sexually Selected Genes
... female sexual receptivity, and various accessory gland proteins transferred by males during copulation. Moreover, the associated pleiotropic effects of many genes are also known. This study provides evidence for the location and associated pleiotropic effects of genes that contribute to sexually sel ...
... female sexual receptivity, and various accessory gland proteins transferred by males during copulation. Moreover, the associated pleiotropic effects of many genes are also known. This study provides evidence for the location and associated pleiotropic effects of genes that contribute to sexually sel ...
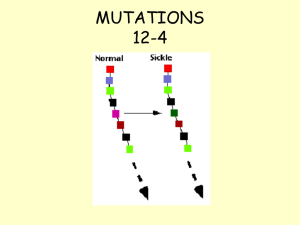
dnachap12_12
... Most mutations are ____________ neutral meaning they have little or no effect on gene ____________. function defective proteins Mutations that cause ________________ are usually ____________ HARMFUL Harmful mutations are associated with many genetic disorders and can cause ________________ _________ ...
... Most mutations are ____________ neutral meaning they have little or no effect on gene ____________. function defective proteins Mutations that cause ________________ are usually ____________ HARMFUL Harmful mutations are associated with many genetic disorders and can cause ________________ _________ ...
Analyzing ATP Synthase Gene Activity in Elizabethkingia anophelis
... The ATP synthase delta chain significantly increased under the presence of the Imipenem antibiotic (Table 1). The function of this subunit is to attach the alpha and beta subunits to the peripheral stalk and is crucial to prevent these subunits from rotating5. Thus if gene expression is increased it ...
... The ATP synthase delta chain significantly increased under the presence of the Imipenem antibiotic (Table 1). The function of this subunit is to attach the alpha and beta subunits to the peripheral stalk and is crucial to prevent these subunits from rotating5. Thus if gene expression is increased it ...
Pre – AP Biology
... • Extra copies of genes on the X chromosome interfere with male sexual development, often preventing the testes from functioning normally and reducing the levels of testosterone. • A shortage of testosterone can lead to delayed or incomplete puberty, breast enlargement (gynecomastia), reduced facial ...
... • Extra copies of genes on the X chromosome interfere with male sexual development, often preventing the testes from functioning normally and reducing the levels of testosterone. • A shortage of testosterone can lead to delayed or incomplete puberty, breast enlargement (gynecomastia), reduced facial ...
Genes, Cognition, and Communication
... to highly heritable. Neurodevelopmental disorders such as dyslexia, autism, and specific language impairment (SLI) also show strong genetic influence. Nevertheless, it has proved difficult for researchers to identify genes that would explain substantial amounts of variance in cognitive traits or dis ...
... to highly heritable. Neurodevelopmental disorders such as dyslexia, autism, and specific language impairment (SLI) also show strong genetic influence. Nevertheless, it has proved difficult for researchers to identify genes that would explain substantial amounts of variance in cognitive traits or dis ...
Olivier Pourquie. 2003. The Segmentation Clock: Converting
... lations, which are relatively easy to see in segPSM (20). However, because Wnt3A acts upsuch a mechanism in invertebrate species that mentation, where they are well coordinated in stream of fgf8 in the PSM, it could act together exhibit a progressive mode of segmentation, such all cells, might also ...
... lations, which are relatively easy to see in segPSM (20). However, because Wnt3A acts upsuch a mechanism in invertebrate species that mentation, where they are well coordinated in stream of fgf8 in the PSM, it could act together exhibit a progressive mode of segmentation, such all cells, might also ...
Slide 1
... proportional to the expression level of the gene under test. Image intensities are quantified using image analysis software. B. Raw numerical data (signal intensities). ...
... proportional to the expression level of the gene under test. Image intensities are quantified using image analysis software. B. Raw numerical data (signal intensities). ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.