Chapter 3 - The Nature and Nurture of Behavior
... • Non therapeutic genetic alteration • An attempt to enhance an already healthy genetic makeup by inserting a gene for improvement (e.g. height, intelligence, eye color) ...
... • Non therapeutic genetic alteration • An attempt to enhance an already healthy genetic makeup by inserting a gene for improvement (e.g. height, intelligence, eye color) ...
Unit 4 Review Sheet Genetics and Biotechnology Vocabulary
... - Do all mutations result in a faulty protein? Why or why not? - What is trisomy 12? What is another name for this disease? Mendelian Genetics - How many copies of genes does each of us have? Where do we get each copy from? - What’s the difference between dominant and recessive alleles? *You do NOT ...
... - Do all mutations result in a faulty protein? Why or why not? - What is trisomy 12? What is another name for this disease? Mendelian Genetics - How many copies of genes does each of us have? Where do we get each copy from? - What’s the difference between dominant and recessive alleles? *You do NOT ...
Answers PDP Chapter 11.3
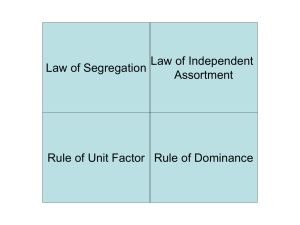
... independent assortment by performing a two factor cross. Dominance comes in different forms and environment increases genetic variation. ...
... independent assortment by performing a two factor cross. Dominance comes in different forms and environment increases genetic variation. ...
What happens to the repressor when lactose is present?
... “marking” the spot just before where transcription will take place. ...
... “marking” the spot just before where transcription will take place. ...
Document
... • The problem of identifying (annotating) human genes is considerably harder than the early success story for ßglobin might suggest (see Lesk’s “Introduction to bioinf”). • The human factor VIII gene (whose mutations cause hemophilia A) is spread over ~186,000 bp. It consists of 26 exons ranging in ...
... • The problem of identifying (annotating) human genes is considerably harder than the early success story for ßglobin might suggest (see Lesk’s “Introduction to bioinf”). • The human factor VIII gene (whose mutations cause hemophilia A) is spread over ~186,000 bp. It consists of 26 exons ranging in ...
Genetics - National Multiple Sclerosis Society
... specifying a protein can influence how, and in which cells, the DNA segment is turned on and off to make a protein. We are only beginning to appreciate the extent to which these additional changes in the architecture of our DNA influence our risk for disease. Genetic maps being developed by researchers ...
... specifying a protein can influence how, and in which cells, the DNA segment is turned on and off to make a protein. We are only beginning to appreciate the extent to which these additional changes in the architecture of our DNA influence our risk for disease. Genetic maps being developed by researchers ...
genes - Vietsciences
... anemia and cystic fibrosis, are known to be genetic and are passed on in families. ...
... anemia and cystic fibrosis, are known to be genetic and are passed on in families. ...
Human Genetics Section 5-3 Mutations • Change in order of base
... Cystic Fibrosis Mutation causes thick _______________________to build up in lungs. • Mucus causes breathing problems and lung damage. • 1 in ________ people are carriers (Rr). Sex Determination • Special chromosomes determine individual’s sex. • Two X chromosomes = _____________________ • One X, o ...
... Cystic Fibrosis Mutation causes thick _______________________to build up in lungs. • Mucus causes breathing problems and lung damage. • 1 in ________ people are carriers (Rr). Sex Determination • Special chromosomes determine individual’s sex. • Two X chromosomes = _____________________ • One X, o ...
11-1 The Work of Mendel
... 11.3 Genetics and the Environment • Genes provide a plan for development, but how the plan unfolds also depends on the environment: • Ex. Butterflies have different wing colors depending on ___________ _______________ • Ex. Hydrangea flowers are different colors depending on __________ ...
... 11.3 Genetics and the Environment • Genes provide a plan for development, but how the plan unfolds also depends on the environment: • Ex. Butterflies have different wing colors depending on ___________ _______________ • Ex. Hydrangea flowers are different colors depending on __________ ...
Set 5
... 5. You believe that the product of your antenna gene turns on other genes in the antenna. How would you test this idea? What materials would you need? What parts of the regulated genes must you identify? How would you verify a direct interaction in vitro and in vivo, between the protein and candidat ...
... 5. You believe that the product of your antenna gene turns on other genes in the antenna. How would you test this idea? What materials would you need? What parts of the regulated genes must you identify? How would you verify a direct interaction in vitro and in vivo, between the protein and candidat ...
Name________________ Where does variation come from
... Name________________ Where does variation come from? - Guided Notes _____________ are controlled by genes. Individuals within a population are not _____________, there is _______________ or differences within the populations genes. ________________________: process by which organisms with traits bes ...
... Name________________ Where does variation come from? - Guided Notes _____________ are controlled by genes. Individuals within a population are not _____________, there is _______________ or differences within the populations genes. ________________________: process by which organisms with traits bes ...
Psy 232 chapter1 v02
... Jean Piaget: Nature of the human organism is to adapt to its environment – Concepts – Stage theory of cognitive development • All children go through the same kinds of sequential discoveries about their world • Cognitively, children must progress through four distinct stages ...
... Jean Piaget: Nature of the human organism is to adapt to its environment – Concepts – Stage theory of cognitive development • All children go through the same kinds of sequential discoveries about their world • Cognitively, children must progress through four distinct stages ...
Bot3404_11_week6.2 - Ecological Evolution – E
... example that evolution primarily builds upon existing genes, instead of evolving new ones. ...
... example that evolution primarily builds upon existing genes, instead of evolving new ones. ...
Ask A Bioloigist - Darwin and Mendel`s Afternoon Tea
... study how traits are inherited. Bred pea plants and discovered heritable characteristics. A two word significant award given to living scientists for their remarkable discoveries. A trait passed from parent to offspring is ___. A bird commonly found in cities; studied by Darwin to better understand ...
... study how traits are inherited. Bred pea plants and discovered heritable characteristics. A two word significant award given to living scientists for their remarkable discoveries. A trait passed from parent to offspring is ___. A bird commonly found in cities; studied by Darwin to better understand ...
GBE 305 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY II
... The course covers advanved topics on molecules, energy, and biosynthesis, macromolecules (structure, shape, and information), how cells are studied, protein function, basic genetic mechanisms, recombinant DNA technology, and control of gene expression etc ...
... The course covers advanved topics on molecules, energy, and biosynthesis, macromolecules (structure, shape, and information), how cells are studied, protein function, basic genetic mechanisms, recombinant DNA technology, and control of gene expression etc ...
Chapter 1 Interactive Quiz
... A. Chromosomes separate at the centromeres. B. Chromosomes separate to form the egg and sperm. C. Chromosomes separate during anaphase. D. Chromosomes separate during telophase. ...
... A. Chromosomes separate at the centromeres. B. Chromosomes separate to form the egg and sperm. C. Chromosomes separate during anaphase. D. Chromosomes separate during telophase. ...
Chapter 12: Mendel and Heredity Study Guide (Pages 280 – 284
... 5. Explain how codominance & incomplete dominance differ from one another. ...
... 5. Explain how codominance & incomplete dominance differ from one another. ...
Q: What does “DNA” stand for? A: Deoxyribonucleic Acid Q: If an
... Q: What does a DNA molecule look like? A: DNA is made of two long strands of bases twisted around each other. It looks like a twisted ladder (a double helix). ...
... Q: What does a DNA molecule look like? A: DNA is made of two long strands of bases twisted around each other. It looks like a twisted ladder (a double helix). ...
Using bioinformatics for better understanding of genes amplify
... How this project using DOGMA will help me teaching my genetics course The next time I teach the part of genomes and proteomes in my genetics course, in the explanation of comparative genomics, I can show similarities between different genomes and introduce them the evolutionary relationships betwee ...
... How this project using DOGMA will help me teaching my genetics course The next time I teach the part of genomes and proteomes in my genetics course, in the explanation of comparative genomics, I can show similarities between different genomes and introduce them the evolutionary relationships betwee ...
A Statistical Approach to Literature
... • It is well known that the distribution of LRS converges to chi-square, with degree of freedom equal to the difference between the number of free parameters of null and alternative hypothesis • However, this does not apply in mixture models because the regularity condition is violated • Analyticall ...
... • It is well known that the distribution of LRS converges to chi-square, with degree of freedom equal to the difference between the number of free parameters of null and alternative hypothesis • However, this does not apply in mixture models because the regularity condition is violated • Analyticall ...