MAX3325 3V Dual RS-232 Transceiver with LCD Supply and Contrast Controller General Description
... transmitter outputs, slightly reduces power consumption, and increases the available output current from VREG and VLCD. C2, C3, and C4 can be increased without changing C1’s value. However, do not increase C1 without also increasing the values of C2, C3, C4, and C5 to maintain the proper ratios. Whe ...
... transmitter outputs, slightly reduces power consumption, and increases the available output current from VREG and VLCD. C2, C3, and C4 can be increased without changing C1’s value. However, do not increase C1 without also increasing the values of C2, C3, C4, and C5 to maintain the proper ratios. Whe ...
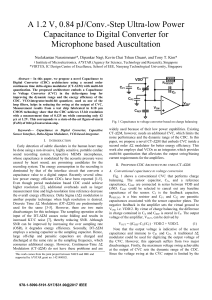
A 1.2 V, 0.84 pJ/Conv.-Step Ultra-low Power Capacitance to Digital
... dominated by that of the interface circuit that converts a capacitance value to a digital output. Recently several ultralow power energy efficient CDCs have been reported [1-5]. Even though period modulation based CDC could achieve higher resolution [2], additional overheads such as larger measureme ...
... dominated by that of the interface circuit that converts a capacitance value to a digital output. Recently several ultralow power energy efficient CDCs have been reported [1-5]. Even though period modulation based CDC could achieve higher resolution [2], additional overheads such as larger measureme ...
ICL7135 Datasheet
... cycle starting 101 clock pulses after the end of the full measurement cycle. Digit 5 (MSD) goes high at the end of the measurement cycle and stays on for 201 counts. In the center of this digit pulse (to avoid race conditions between changing BCD and digit drives) the first STROBE pulse goes negativ ...
... cycle starting 101 clock pulses after the end of the full measurement cycle. Digit 5 (MSD) goes high at the end of the measurement cycle and stays on for 201 counts. In the center of this digit pulse (to avoid race conditions between changing BCD and digit drives) the first STROBE pulse goes negativ ...
SP3232EH 数据资料DataSheet下载
... The circuit models in Figures 14 and 15 represent the typical ESD testing circuit used for all three methods. The CS is initially charged with the DC power supply when the first switch (SW1) is on. Now that the capacitor is charged, the second switch (SW2) is on while SW1 switches off. The voltage s ...
... The circuit models in Figures 14 and 15 represent the typical ESD testing circuit used for all three methods. The CS is initially charged with the DC power supply when the first switch (SW1) is on. Now that the capacitor is charged, the second switch (SW2) is on while SW1 switches off. The voltage s ...
NK2422032209
... unbalanced voltages will occur at supply side these can be eliminated by using Multi level Inverter. In this paper a closed loop Control system is designed using PI controller in order to maintain load voltage constant for under voltage and Over voltage conditions and MATLAB simulations have been ca ...
... unbalanced voltages will occur at supply side these can be eliminated by using Multi level Inverter. In this paper a closed loop Control system is designed using PI controller in order to maintain load voltage constant for under voltage and Over voltage conditions and MATLAB simulations have been ca ...
... The charge-balancing constraint has already been reported for the four-level converter [A38], in which an auxiliary circuit is proposed to achieve shared voltages among capacitors. The circuit is intended for imbalance compensation when the multilevel converter operates in inverter mode. In such con ...
FDFM2N111 Integrated N-Channel PowerTrench MOSFET and Schottky Diode
... 2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. ...
... 2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. ...
LT1373 - 250kHz Low Supply Current High Efficiency 1.5A
... directly regulate negative output voltages. The negative feedback amplifier’s 400k source resistor is brought out for negative output voltage sensing. The NFB pin regulates at – 2.45V while the amplifier output internally drives the FB pin to 1.245V. This architecture, which uses the same main error ...
... directly regulate negative output voltages. The negative feedback amplifier’s 400k source resistor is brought out for negative output voltage sensing. The NFB pin regulates at – 2.45V while the amplifier output internally drives the FB pin to 1.245V. This architecture, which uses the same main error ...
Distribution voltage regulators
... primary winding in reverse polarity, the output will read 90 V for an input of 100 V. This is a step-down autotransformer. ...
... primary winding in reverse polarity, the output will read 90 V for an input of 100 V. This is a step-down autotransformer. ...
sc2440tetrt
... input or the output of the converter. The PGOOD outputs become valid as soon as VIN rises above 1 V BE during power-up. PGOOD is actively pulled low until the corresponding FB pin rises to within 10% of the final regulation voltage. ...
... input or the output of the converter. The PGOOD outputs become valid as soon as VIN rises above 1 V BE during power-up. PGOOD is actively pulled low until the corresponding FB pin rises to within 10% of the final regulation voltage. ...
Preliminary Datasheet - MAP3702
... • Acknowledge is requested by a set RFA bit. • The transmitted device address matches with the device address of the device. • 16 bits is received correctly. If the device turns on the internal ACKN-MOSFET and pulls the CTRL pin low for the time tACKN, which is max. 616µs then the acknowledge condit ...
... • Acknowledge is requested by a set RFA bit. • The transmitted device address matches with the device address of the device. • 16 bits is received correctly. If the device turns on the internal ACKN-MOSFET and pulls the CTRL pin low for the time tACKN, which is max. 616µs then the acknowledge condit ...
LT1372/LT1377 - 500kHz and 1MHz High Efficiency 1.5A Switching
... feedback amplifier’s 100k source resistor is brought out for negative output voltage sensing. The NFB pin regulates at – 2.49V while the amplifier output internally drives the FB pin to 1.245V. This architecture, which uses the same main error amplifier, prevents duplicating functions and maintains ...
... feedback amplifier’s 100k source resistor is brought out for negative output voltage sensing. The NFB pin regulates at – 2.49V while the amplifier output internally drives the FB pin to 1.245V. This architecture, which uses the same main error amplifier, prevents duplicating functions and maintains ...
MAX14529E/MAX14530E Overvoltage Protection with USB Charger General Description
... Detection, LDO, and ESD Protection on D+/DThe MAX14529E/MAX14530E are overvoltage-protection devices with USB charger detection, a low-dropout (LDO) regulator, and ESD protection. These devices feature a low 35mΩ (typ) RON internal FET switch and protect low-voltage systems against voltage faults up ...
... Detection, LDO, and ESD Protection on D+/DThe MAX14529E/MAX14530E are overvoltage-protection devices with USB charger detection, a low-dropout (LDO) regulator, and ESD protection. These devices feature a low 35mΩ (typ) RON internal FET switch and protect low-voltage systems against voltage faults up ...
LT1372/LT1377 500kHz and 1MHz High Efficiency 1.5A Switching
... feedback amplifier’s 100k source resistor is brought out for negative output voltage sensing. The NFB pin regulates at – 2.49V while the amplifier output internally drives the FB pin to 1.245V. This architecture, which uses the same main error amplifier, prevents duplicating functions and maintains ...
... feedback amplifier’s 100k source resistor is brought out for negative output voltage sensing. The NFB pin regulates at – 2.49V while the amplifier output internally drives the FB pin to 1.245V. This architecture, which uses the same main error amplifier, prevents duplicating functions and maintains ...
TS30011/12/13 High Efficiency 1A/2A/3A Current-Mode
... Internal Current Limit The current through the high side FET is sensed on a cycle by cycle basis and if current limit is reached, it will abbreviate the cycle. In addition, the device senses the FB pin to identify hard short conditions and will direct the VSW output to skip 4 cycles if current limit ...
... Internal Current Limit The current through the high side FET is sensed on a cycle by cycle basis and if current limit is reached, it will abbreviate the cycle. In addition, the device senses the FB pin to identify hard short conditions and will direct the VSW output to skip 4 cycles if current limit ...
Evaluates: MAX1584/MAX1585 MAX1585 Evaluation Kit General Description Features
... of the MAX1585 and must reach its regulation voltage before any other output turns on. To enable OUTSU, short pins 2-3 of jumper JU1. When JU1 pins 1-2 are shorted, all outputs shut down and the IC is in low-current shutdown mode. OUTSU is configured for 5V. If a different output voltage is desired, ...
... of the MAX1585 and must reach its regulation voltage before any other output turns on. To enable OUTSU, short pins 2-3 of jumper JU1. When JU1 pins 1-2 are shorted, all outputs shut down and the IC is in low-current shutdown mode. OUTSU is configured for 5V. If a different output voltage is desired, ...
MAX221E ±15kV ESD-Protected, +5V, 1µA, Single RS-232 Transceiver with AutoShutdown General Description
... Table 1 and Figure 2c summarize the MAX221E operating modes. FORCEON and FORCEOFF override AutoShutdown. When neither control is asserted, the device selects between these states automatically, based on the receiver input level. Figures 2a, 2b, and 3a depict valid and invalid RS-232 receiver levels. ...
... Table 1 and Figure 2c summarize the MAX221E operating modes. FORCEON and FORCEOFF override AutoShutdown. When neither control is asserted, the device selects between these states automatically, based on the receiver input level. Figures 2a, 2b, and 3a depict valid and invalid RS-232 receiver levels. ...
FAN5602 — Universal (Step-Up/Step-Down) Charge Pump Regulated DC/DC Converter F AN5
... power transistors and delivers the charge to the output from the output capacitor. PFM operation is not used for Mode 1:1, even if at light load. Mode 1:1 is designed as an LDO with the oscillator off. The power transistors at LDO mode are not switching and therefore do not have the dynamic loss. ...
... power transistors and delivers the charge to the output from the output capacitor. PFM operation is not used for Mode 1:1, even if at light load. Mode 1:1 is designed as an LDO with the oscillator off. The power transistors at LDO mode are not switching and therefore do not have the dynamic loss. ...
Capacitor
.jpg?width=300)
A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an insulator that can store energy by becoming polarized). The conductors can be thin films, foils or sintered beads of metal or conductive electrolyte, etc. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's charge capacity. A dielectric can be glass, ceramic, plastic film, air, vacuum, paper, mica, oxide layer etc. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. Unlike a resistor, an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy. Instead, a capacitor stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field between its plates.When there is a potential difference across the conductors (e.g., when a capacitor is attached across a battery), an electric field develops across the dielectric, causing positive charge +Q to collect on one plate and negative charge −Q to collect on the other plate. If a battery has been attached to a capacitor for a sufficient amount of time, no current can flow through the capacitor. However, if a time-varying voltage is applied across the leads of the capacitor, a displacement current can flow.An ideal capacitor is characterized by a single constant value, its capacitance. Capacitance is defined as the ratio of the electric charge Q on each conductor to the potential difference V between them. The SI unit of capacitance is the farad (F), which is equal to one coulomb per volt (1 C/V). Typical capacitance values range from about 1 pF (10−12 F) to about 1 mF (10−3 F).The larger the surface area of the ""plates"" (conductors) and the narrower the gap between them, the greater the capacitance is. In practice, the dielectric between the plates passes a small amount of leakage current and also has an electric field strength limit, known as the breakdown voltage. The conductors and leads introduce an undesired inductance and resistance.Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass. In analog filter networks, they smooth the output of power supplies. In resonant circuits they tune radios to particular frequencies. In electric power transmission systems, they stabilize voltage and power flow.