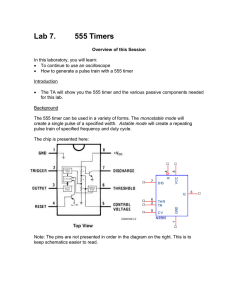
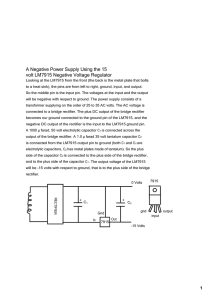
this PDF file - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... where V , I, and R are the voltage across, the current flowing through, and the resistance of the conductor respectively [2]. Szczykulska et al. show that despite current not being constant throughout the strike, an average current of 10kA is an appropriate approximation. Kirchoff’s Laws [3] state t ...
... where V , I, and R are the voltage across, the current flowing through, and the resistance of the conductor respectively [2]. Szczykulska et al. show that despite current not being constant throughout the strike, an average current of 10kA is an appropriate approximation. Kirchoff’s Laws [3] state t ...
ac voltage ratio measurement
... One note of caution for others atkmpting thew measurements. The dividers must be carefully demagnetized before measurement. Previous o v d d (removed at peak canmi) caused magnetization that resulted in changes in calibration of up to 10 ppb. Such overiods may occur in a comparison circuit if the tw ...
... One note of caution for others atkmpting thew measurements. The dividers must be carefully demagnetized before measurement. Previous o v d d (removed at peak canmi) caused magnetization that resulted in changes in calibration of up to 10 ppb. Such overiods may occur in a comparison circuit if the tw ...
EE426 Course title: High Voltage Engineering
... with high ohmic resistors and high ohmic resistor voltage dividers, generating voltmeters and field sensors, The measurement of peak voltages, The ChubbFortescue method, voltage dividers and passive rectifier circuits, active peak reading circuits, high voltage capacitors for measuring circuits, ...
... with high ohmic resistors and high ohmic resistor voltage dividers, generating voltmeters and field sensors, The measurement of peak voltages, The ChubbFortescue method, voltage dividers and passive rectifier circuits, active peak reading circuits, high voltage capacitors for measuring circuits, ...
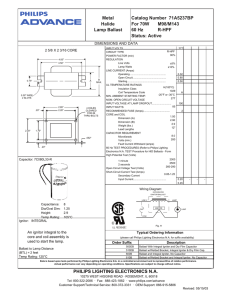
Metal Halide Lamp Ballast Catalog Number 71A5237BP For 70W
... core and coil assembly is used to start the lamp. Ballast to Lamp Distance (BTL) = 2 feet Temp Rating: 125°C ...
... core and coil assembly is used to start the lamp. Ballast to Lamp Distance (BTL) = 2 feet Temp Rating: 125°C ...
Test - Electro Tech Online
... somewhere between 10 and 100 MHz. I lined up the traces by guess based on how the RC circuit probably controls the transistor Q1. ...
... somewhere between 10 and 100 MHz. I lined up the traces by guess based on how the RC circuit probably controls the transistor Q1. ...
RCD Fuse Resistor Questionnaire
... Or just in an amount of time brief enough to prevent the PCB and adjacent components from charring? If a specific amount of time, what is the minimum blow time? Max blow time? 7. Is there a “hold-off” voltage requirement (voltage level that the part must be able to hold-off after fusing)? If yes, wh ...
... Or just in an amount of time brief enough to prevent the PCB and adjacent components from charring? If a specific amount of time, what is the minimum blow time? Max blow time? 7. Is there a “hold-off” voltage requirement (voltage level that the part must be able to hold-off after fusing)? If yes, wh ...
International Journal of Electrical, Electronics and Computer
... impact of systematic errors introduced by the binaryweighted parasitic capacitances and parasitic capacitances related to the C-array’s top-plate rail, on the INL and DNL of ADC. We provide a behavioral model of a split capacitor array, which takes into account the parasitic capacitors related to th ...
... impact of systematic errors introduced by the binaryweighted parasitic capacitances and parasitic capacitances related to the C-array’s top-plate rail, on the INL and DNL of ADC. We provide a behavioral model of a split capacitor array, which takes into account the parasitic capacitors related to th ...
2013 kcse muhoroni physics pp2
... A pin hole camera forms on the screen an image which appears upside down and magnified with the aid of a ray diagram, explain how this happens. ...
... A pin hole camera forms on the screen an image which appears upside down and magnified with the aid of a ray diagram, explain how this happens. ...
Photoelectric Effect - University of Colorado Boulder
... of the capacitor. Current will flow thus charging up the capacitor until the charge imbalance is great enough that the resulting potential difference across the capacitor prevents the buildup of additional ...
... of the capacitor. Current will flow thus charging up the capacitor until the charge imbalance is great enough that the resulting potential difference across the capacitor prevents the buildup of additional ...
Harmonic filters for high voltage - El
... Particular problems are experienced when the network contains power factor correction capacitors. The capacitor bank and the inductance of the network may form a parallel resonant circuit at the harmonic frequency, with the result that harmonics are amplified to such an extent that the voltage becom ...
... Particular problems are experienced when the network contains power factor correction capacitors. The capacitor bank and the inductance of the network may form a parallel resonant circuit at the harmonic frequency, with the result that harmonics are amplified to such an extent that the voltage becom ...
Exponential Functions and RC circuits
... Finally, note that we could use any base, not just e, the base for natural logarithms. Functions of the form 10kt or 2kt have much the same properties. We could, for example, define doubling times or halving times (“half-lives”), as we did in class. ...
... Finally, note that we could use any base, not just e, the base for natural logarithms. Functions of the form 10kt or 2kt have much the same properties. We could, for example, define doubling times or halving times (“half-lives”), as we did in class. ...
Optional Extra Credit Exercise
... C. is conserved D. increases or decreases depending on the sign of the charge My answer was C and the other students got B. 9. A point charge q sets up an electric field E at the position of another charge q; the force exerted by E on q’ is independent of the magnitude of q’ My answer was True the o ...
... C. is conserved D. increases or decreases depending on the sign of the charge My answer was C and the other students got B. 9. A point charge q sets up an electric field E at the position of another charge q; the force exerted by E on q’ is independent of the magnitude of q’ My answer was True the o ...
Capacitor
.jpg?width=300)
A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an insulator that can store energy by becoming polarized). The conductors can be thin films, foils or sintered beads of metal or conductive electrolyte, etc. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's charge capacity. A dielectric can be glass, ceramic, plastic film, air, vacuum, paper, mica, oxide layer etc. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. Unlike a resistor, an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy. Instead, a capacitor stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field between its plates.When there is a potential difference across the conductors (e.g., when a capacitor is attached across a battery), an electric field develops across the dielectric, causing positive charge +Q to collect on one plate and negative charge −Q to collect on the other plate. If a battery has been attached to a capacitor for a sufficient amount of time, no current can flow through the capacitor. However, if a time-varying voltage is applied across the leads of the capacitor, a displacement current can flow.An ideal capacitor is characterized by a single constant value, its capacitance. Capacitance is defined as the ratio of the electric charge Q on each conductor to the potential difference V between them. The SI unit of capacitance is the farad (F), which is equal to one coulomb per volt (1 C/V). Typical capacitance values range from about 1 pF (10−12 F) to about 1 mF (10−3 F).The larger the surface area of the ""plates"" (conductors) and the narrower the gap between them, the greater the capacitance is. In practice, the dielectric between the plates passes a small amount of leakage current and also has an electric field strength limit, known as the breakdown voltage. The conductors and leads introduce an undesired inductance and resistance.Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass. In analog filter networks, they smooth the output of power supplies. In resonant circuits they tune radios to particular frequencies. In electric power transmission systems, they stabilize voltage and power flow.