Your time has expired. Submit the assessment now or you may be
... A) A 10Ω resistor in series with a j30Ω capacitor. B) A 10Ω resistor in series with a j30Ω inductor. C) A 10Ω resistor in parallel with a j30Ω inductor. D) A 10Ω resistor in parallel with a j30Ω capacitor. ...
... A) A 10Ω resistor in series with a j30Ω capacitor. B) A 10Ω resistor in series with a j30Ω inductor. C) A 10Ω resistor in parallel with a j30Ω inductor. D) A 10Ω resistor in parallel with a j30Ω capacitor. ...
Fabrication and Integration of Ultrathin, High
... high processing temperatures (>700oC) of the abovementioned ferroelectrics, they also show poor voltage response that limits their applications in power electronics. Several groups have also worked on tantalum pentoxide dielectrics (Ta2O5) for planar [13, 14] or TSV- or TPV- ...
... high processing temperatures (>700oC) of the abovementioned ferroelectrics, they also show poor voltage response that limits their applications in power electronics. Several groups have also worked on tantalum pentoxide dielectrics (Ta2O5) for planar [13, 14] or TSV- or TPV- ...
Automatic Power Factor Correction Capacitors
... Installer Qualifications: Company specializing in performing the work of this section with a minimum of five years documented experience with power factor correction systems of similar size, type, and capacity. ...
... Installer Qualifications: Company specializing in performing the work of this section with a minimum of five years documented experience with power factor correction systems of similar size, type, and capacity. ...
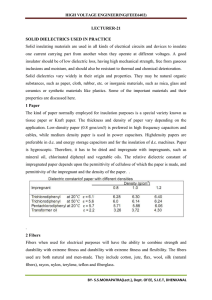
LECTURER-21 SOLID DIELECTRICS USED IN PRACTICE Solid
... Ceramics are inorganic materials produced by consolidating minerals into monolithic bodies by high temperature heat treatment. Ceramics can be divided into two groups depending on the dielectric constant. Low permittivity ceramics are used as insulators, while the high permittivity ceramics are used ...
... Ceramics are inorganic materials produced by consolidating minerals into monolithic bodies by high temperature heat treatment. Ceramics can be divided into two groups depending on the dielectric constant. Low permittivity ceramics are used as insulators, while the high permittivity ceramics are used ...
Low Inductance DC
... vCE vovershoot vDClink With low inductive DC-Link design (small Lstray) these voltage overshoots can be reduced significantly. ...
... vCE vovershoot vDClink With low inductive DC-Link design (small Lstray) these voltage overshoots can be reduced significantly. ...
B41794A5228Q000 - EPCOS AG
... As a rule, EPCOS is either unfamiliar with individual customer applications or less familiar with them than the customers themselves. For these reasons, it is always ultimately incumbent on the customer to check and decide whether an EPCOS product with the properties described in the product specifi ...
... As a rule, EPCOS is either unfamiliar with individual customer applications or less familiar with them than the customers themselves. For these reasons, it is always ultimately incumbent on the customer to check and decide whether an EPCOS product with the properties described in the product specifi ...
LA6585FA - ON Semiconductor
... ON Semiconductor and the ON logo are registered trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC (SCILLC). SCILLC owns the rights to a number of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent coverage may be accessed at www ...
... ON Semiconductor and the ON logo are registered trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC (SCILLC). SCILLC owns the rights to a number of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent coverage may be accessed at www ...
Step 5: Solve the circuit with ATP
... The Circuit: An ideal 120 Vrms, 60 Hz, single-phase voltage source drives a 200 W, pf = 0.85, lagging load. The wiring between the source and load has resistance 0.50 Ω and inductance 1 mH. A switchable power factor correction capacitor is connected across the load to correct the load power factor t ...
... The Circuit: An ideal 120 Vrms, 60 Hz, single-phase voltage source drives a 200 W, pf = 0.85, lagging load. The wiring between the source and load has resistance 0.50 Ω and inductance 1 mH. A switchable power factor correction capacitor is connected across the load to correct the load power factor t ...
It`s Electric - studentorg
... ohm is the resistance, R, that permits a current of 1 A to flow through a circuit with 1 V. The connecting wires in electric circuits have very low resistance; the copper wire used to wire houses has about 0.004 ohms per meter. ...
... ohm is the resistance, R, that permits a current of 1 A to flow through a circuit with 1 V. The connecting wires in electric circuits have very low resistance; the copper wire used to wire houses has about 0.004 ohms per meter. ...
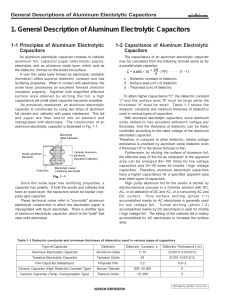
1. General Description of Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors
... rectifying properties. When in contact with electrolyte, the oxide layer possesses an excellent forward direction insulation property. Together with magnified effective surface area attained by etching the foil, a high capacitance yet small sized capacitor becomes available. As previously mentioned, ...
... rectifying properties. When in contact with electrolyte, the oxide layer possesses an excellent forward direction insulation property. Together with magnified effective surface area attained by etching the foil, a high capacitance yet small sized capacitor becomes available. As previously mentioned, ...
PWM voltage regulator
... Many microcontrollers feature a pulse-width-modulated (PWM) output that can be low-pass filtered to produce a variable dc voltage. Without additional circuitry, however, this technique is limited to controlling very low-power loads. The circuit here illustrates a scheme that lets this dc voltage con ...
... Many microcontrollers feature a pulse-width-modulated (PWM) output that can be low-pass filtered to produce a variable dc voltage. Without additional circuitry, however, this technique is limited to controlling very low-power loads. The circuit here illustrates a scheme that lets this dc voltage con ...
pptx
... Linear regulator has many vias to copper plane for heatsinking Sufficient capacitance nearby for low ripple ...
... Linear regulator has many vias to copper plane for heatsinking Sufficient capacitance nearby for low ripple ...
Capacitor Self
... a. First of all, ideally how much audio power can this system give into an 8 Ω speaker without clipping? The #2 supply can deliver a ± 24 V max. and ± 6A current max. Therefore, the output of the power amplifier can go to ± 24 V (assume no voltage drop in the output amplifier). b. Design the power s ...
... a. First of all, ideally how much audio power can this system give into an 8 Ω speaker without clipping? The #2 supply can deliver a ± 24 V max. and ± 6A current max. Therefore, the output of the power amplifier can go to ± 24 V (assume no voltage drop in the output amplifier). b. Design the power s ...
Capacitor
.jpg?width=300)
A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an insulator that can store energy by becoming polarized). The conductors can be thin films, foils or sintered beads of metal or conductive electrolyte, etc. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's charge capacity. A dielectric can be glass, ceramic, plastic film, air, vacuum, paper, mica, oxide layer etc. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. Unlike a resistor, an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy. Instead, a capacitor stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field between its plates.When there is a potential difference across the conductors (e.g., when a capacitor is attached across a battery), an electric field develops across the dielectric, causing positive charge +Q to collect on one plate and negative charge −Q to collect on the other plate. If a battery has been attached to a capacitor for a sufficient amount of time, no current can flow through the capacitor. However, if a time-varying voltage is applied across the leads of the capacitor, a displacement current can flow.An ideal capacitor is characterized by a single constant value, its capacitance. Capacitance is defined as the ratio of the electric charge Q on each conductor to the potential difference V between them. The SI unit of capacitance is the farad (F), which is equal to one coulomb per volt (1 C/V). Typical capacitance values range from about 1 pF (10−12 F) to about 1 mF (10−3 F).The larger the surface area of the ""plates"" (conductors) and the narrower the gap between them, the greater the capacitance is. In practice, the dielectric between the plates passes a small amount of leakage current and also has an electric field strength limit, known as the breakdown voltage. The conductors and leads introduce an undesired inductance and resistance.Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass. In analog filter networks, they smooth the output of power supplies. In resonant circuits they tune radios to particular frequencies. In electric power transmission systems, they stabilize voltage and power flow.