Lesson plan - Evo-Ed
... • describe amino acid differences in the R67 and C67 variants of the MC1R protein • describe nucleotide sequence differences in mc1r alleles, and how they lead to differences in the MC1R proteins that they encode 2. Define “allele frequency” and contrast it with phenotype frequency. 3. Describe two ...
... • describe amino acid differences in the R67 and C67 variants of the MC1R protein • describe nucleotide sequence differences in mc1r alleles, and how they lead to differences in the MC1R proteins that they encode 2. Define “allele frequency” and contrast it with phenotype frequency. 3. Describe two ...
as a PDF
... genes in vertebrates and is localized close to the target residues of CK1ε-induced phosphorylation (Fig. 2) (19). It is therefore likely that the V647G variation alters CK1ε-induced phosphorylation of PER3 protein and leads to an abnormal circadian rhythm phenotype. We have also identified 4-repeat ...
... genes in vertebrates and is localized close to the target residues of CK1ε-induced phosphorylation (Fig. 2) (19). It is therefore likely that the V647G variation alters CK1ε-induced phosphorylation of PER3 protein and leads to an abnormal circadian rhythm phenotype. We have also identified 4-repeat ...
chapter 14 mendel and the gene idea
... Mendel’s laws of independent assortment and segregation explain heritable variation in terms of alternative forms of genes that are passed along according to simple rules of probability. ...
... Mendel’s laws of independent assortment and segregation explain heritable variation in terms of alternative forms of genes that are passed along according to simple rules of probability. ...
genetic and metabolic testing of children with global developmental
... mild ID is defined as having an IQ of 50 to 70 points. Moderate ID is defined as having an IQ under 50 points. ...
... mild ID is defined as having an IQ of 50 to 70 points. Moderate ID is defined as having an IQ under 50 points. ...
ASSORTATIVE MATING BY FITNESS AND SEXUALLY
... 2005; Pan et al. 2007) and Fry (2010) suggested that cases where hm + hf < 1 may be the norm for SA genetic variation because fitness functions should tend to be concave around sex-specific trait optima: whichever allele is beneficial in a given sex, this allele should be partly dominant in that sex ...
... 2005; Pan et al. 2007) and Fry (2010) suggested that cases where hm + hf < 1 may be the norm for SA genetic variation because fitness functions should tend to be concave around sex-specific trait optima: whichever allele is beneficial in a given sex, this allele should be partly dominant in that sex ...
Genome-wide association studies for complex traits: consensus
... The phenomenon whereby a single allele can affect several distinct aspects of the phenotype of an organism, often traits not previously thought to be mechanistically related. ...
... The phenomenon whereby a single allele can affect several distinct aspects of the phenotype of an organism, often traits not previously thought to be mechanistically related. ...
Internet Databases I
... references concerning specific diseases, traits and genetic mechanisms. ...
... references concerning specific diseases, traits and genetic mechanisms. ...
Population genetics and the modern synthesis of evolutionary theory
... − An individual's phenotype is the result of the interaction of both genes and environment − You can't have a phenotype without genes, and you can't have a phenotype that did not develop in some environment − both are necessarily part of the process − so the genetic processes we are looking at are n ...
... − An individual's phenotype is the result of the interaction of both genes and environment − You can't have a phenotype without genes, and you can't have a phenotype that did not develop in some environment − both are necessarily part of the process − so the genetic processes we are looking at are n ...
GApresentation
... Deme: A subset of the population that interbreeds (might be the whole population) Chromosome: A solution structure (often binary); contains one or more genes Gene: A feature or parameter Allele: A specific value for a gene Phenotype: A member of the population, a real-valued solution vector Generati ...
... Deme: A subset of the population that interbreeds (might be the whole population) Chromosome: A solution structure (often binary); contains one or more genes Gene: A feature or parameter Allele: A specific value for a gene Phenotype: A member of the population, a real-valued solution vector Generati ...
- CURRENT ZOOLOGY
... leads to reproductive isolation, a strong emphasis has been placed on distinguishing divergent ecological selection from other mechanisms of speciation (Schluter, 2009). However, traits that diverge between taxa are very unlikely to all be under divergent selection. As well as those diverging throug ...
... leads to reproductive isolation, a strong emphasis has been placed on distinguishing divergent ecological selection from other mechanisms of speciation (Schluter, 2009). However, traits that diverge between taxa are very unlikely to all be under divergent selection. As well as those diverging throug ...
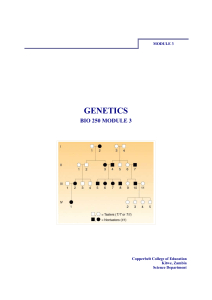
genetics bio 250 module 3
... alleles or even different genes that specify sexual morphology. In animals, this is often accompanied by chromosomal differences. Genetic determination is generally through chromosome combinations of either XY, ZW, XO, or haplodiploid. Sexual differentiation is generally started by a main gene, a se ...
... alleles or even different genes that specify sexual morphology. In animals, this is often accompanied by chromosomal differences. Genetic determination is generally through chromosome combinations of either XY, ZW, XO, or haplodiploid. Sexual differentiation is generally started by a main gene, a se ...
How the Genetics Calculator Creates Phenotype Names
... species Pterophyllum scalare is structured. ...
... species Pterophyllum scalare is structured. ...
English
... By Jakob Christensen-Dalsgaard and Morten Kanneworff, Institute of Biology, University of Southern Denmark. This practical illustrates adaptation by natural selection for a trait, in this case motility of animals with genetically specified morphology, assembled from six Lego® bricks. The animals are ...
... By Jakob Christensen-Dalsgaard and Morten Kanneworff, Institute of Biology, University of Southern Denmark. This practical illustrates adaptation by natural selection for a trait, in this case motility of animals with genetically specified morphology, assembled from six Lego® bricks. The animals are ...
The Origin of Artificial Species: Genetic Robot
... robot, Rity, as an artificial creature living in a virtual world of a PC [6-9]. Rity can be regarded as a genetic robot which has its own genetic information. Rity is developed to test the world’s first robotic “chromosomes,” which are a set of computerized DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) codes for crea ...
... robot, Rity, as an artificial creature living in a virtual world of a PC [6-9]. Rity can be regarded as a genetic robot which has its own genetic information. Rity is developed to test the world’s first robotic “chromosomes,” which are a set of computerized DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) codes for crea ...
Partnership
... efficient screening schemes should be worked out that allow identification of plants with altered recombination frequency. The outcome of this work package is knowledge of genes that control recombination frequencies, which, in addition provides molecular markers that allow „breeding‟ with alleles t ...
... efficient screening schemes should be worked out that allow identification of plants with altered recombination frequency. The outcome of this work package is knowledge of genes that control recombination frequencies, which, in addition provides molecular markers that allow „breeding‟ with alleles t ...
21 principles of genetics
... the study of heredity is ‘Genetics’. New individual develop according to the genes inherited from their parents. The transmission of characters from one generation to the next, that is from parents to offspring is known as heredity. It is further observed that siblings from same parents are unique a ...
... the study of heredity is ‘Genetics’. New individual develop according to the genes inherited from their parents. The transmission of characters from one generation to the next, that is from parents to offspring is known as heredity. It is further observed that siblings from same parents are unique a ...
GENETIC CHANGES WITH GENERATIONS OF ARTIFICIAL
... If U is small, then qP(p) is approximately normal, and E ( p ) and E ( p 2 ) can be approximated by the averages of normal-order statistics. KOJIMA(1961) calls E ( p ) the generalized selection differential, but usually it is referred to as just the intensity of selection. In the following, we shall ...
... If U is small, then qP(p) is approximately normal, and E ( p ) and E ( p 2 ) can be approximated by the averages of normal-order statistics. KOJIMA(1961) calls E ( p ) the generalized selection differential, but usually it is referred to as just the intensity of selection. In the following, we shall ...
Eiben Chapter3 Genetic Algorithms
... integer representations Selection mechanism sensitive for converging populations with close fitness values Generational population model (step 5 in SGA repr. cycle) can be improved with explicit survivor selection ...
... integer representations Selection mechanism sensitive for converging populations with close fitness values Generational population model (step 5 in SGA repr. cycle) can be improved with explicit survivor selection ...
Genetic Algorithm to find optimal GLCM features
... Algorithm (GA). The typical system performs three major tasks. The first one is texture analysis for features extraction, There are several number of texture analysis techniques that have been used in image processing area. Generally, the texture study includes: structural, transform method, and sta ...
... Algorithm (GA). The typical system performs three major tasks. The first one is texture analysis for features extraction, There are several number of texture analysis techniques that have been used in image processing area. Generally, the texture study includes: structural, transform method, and sta ...
Probability and Punnet Squares
... We can use _____________________ to predict the probability of ______________ outcomes. Dominant and Recessive Alleles _________________ alleles are expressed in _______________ ________________. Ex: T B A C X Dominant alleles can ___________ recessive alleles. This means you might have a re ...
... We can use _____________________ to predict the probability of ______________ outcomes. Dominant and Recessive Alleles _________________ alleles are expressed in _______________ ________________. Ex: T B A C X Dominant alleles can ___________ recessive alleles. This means you might have a re ...
Alzheimer`s Disease Genetics Fact Sheet
... our 23 pairs of chromosomes. A chromosome is a thread-like structure found in the cell’s nucleus, which can carry hundreds, sometimes thousands, of genes. In humans, one of each pair of 23 chromosomes is inherited from each parent. The genetic material on these chromosomes is collectively referred t ...
... our 23 pairs of chromosomes. A chromosome is a thread-like structure found in the cell’s nucleus, which can carry hundreds, sometimes thousands, of genes. In humans, one of each pair of 23 chromosomes is inherited from each parent. The genetic material on these chromosomes is collectively referred t ...
Genetic Algorithms
... integer representations Selection mechanism sensitive for converging populations with close fitness values Generational population model (step 5 in SGA repr. cycle) can be improved with explicit survivor selection ...
... integer representations Selection mechanism sensitive for converging populations with close fitness values Generational population model (step 5 in SGA repr. cycle) can be improved with explicit survivor selection ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.