Mutation screening of phenylketonuria in the Far East of
... newborns are investigated at the laboratory of Motherhood and Childhood Protection every year. In the period 1992 to 1997, PKU cards from 79,411 newborns were screened for the disorder in Khabarovsk, and 13 were diagnosed as having PKU. The estimated frequency of PKU in the region was 1 : 6,100, whi ...
... newborns are investigated at the laboratory of Motherhood and Childhood Protection every year. In the period 1992 to 1997, PKU cards from 79,411 newborns were screened for the disorder in Khabarovsk, and 13 were diagnosed as having PKU. The estimated frequency of PKU in the region was 1 : 6,100, whi ...
Standard Genetic Nomenclature - Iowa State University Digital
... respectively. In terms of traits, an example that would benefit from consistent nomenclature is the longissimus dorsi muscle area, which is also referred to as the loin eye area (LEA), loin muscle area (LMA), meat area (MLD), ribeye area (REA), etc. Each of these is known to certain researchers as t ...
... respectively. In terms of traits, an example that would benefit from consistent nomenclature is the longissimus dorsi muscle area, which is also referred to as the loin eye area (LEA), loin muscle area (LMA), meat area (MLD), ribeye area (REA), etc. Each of these is known to certain researchers as t ...
Caspary T, Anderson KV. Dev Dyn. 2006 Sep;235(9):2412-23. Uncovering the uncharacterized and unexpected: unbiased phenotype-driven screens in the mouse. (Review)
... the most mutations with the least lethality) creates one mutation every 0.1–1 MB, based on direct sequencing data (Beier, 2000; Concepcion et al., 2004; Sakuraba et al., 2005), or roughly 3,000 nucleotide changes per genome. The vast majority of these mutations lie in non-coding DNA and do not affec ...
... the most mutations with the least lethality) creates one mutation every 0.1–1 MB, based on direct sequencing data (Beier, 2000; Concepcion et al., 2004; Sakuraba et al., 2005), or roughly 3,000 nucleotide changes per genome. The vast majority of these mutations lie in non-coding DNA and do not affec ...
PROBLEM SET 1 - EVOLUTIONARY BIOLOGY
... What is the expected H-W ratio of PKU carriers (heterozygotes) to affected individuals (PKU homozygotes)? (1 pts) 2pq / q2 = 2(0.006)(0.994) / 0.00004 = 314; For every homozygous affected individual there will be more than 300 carriers. ...
... What is the expected H-W ratio of PKU carriers (heterozygotes) to affected individuals (PKU homozygotes)? (1 pts) 2pq / q2 = 2(0.006)(0.994) / 0.00004 = 314; For every homozygous affected individual there will be more than 300 carriers. ...
Tumour necrosis factor family genes in a phenotype of COPD
... Caucasians of Italian descent, were investigated. The first group of subjects consisted of 63 consecutive male patients with history of COPD, diagnosed according to the American Thoracic Society (ATS) guidelines [22] and characterised by significant impairment in diffusing capacity for carbon monoxi ...
... Caucasians of Italian descent, were investigated. The first group of subjects consisted of 63 consecutive male patients with history of COPD, diagnosed according to the American Thoracic Society (ATS) guidelines [22] and characterised by significant impairment in diffusing capacity for carbon monoxi ...
Evolution and Extinction in a Changing Environment
... possible that by chance the population will experience a long sequence of particularly extreme environments. This can cause the population rate of growth to be negative for a long enough time to cause extinction, and even if extinction does not result immediately, the loss of genetic variance result ...
... possible that by chance the population will experience a long sequence of particularly extreme environments. This can cause the population rate of growth to be negative for a long enough time to cause extinction, and even if extinction does not result immediately, the loss of genetic variance result ...
How to order genetic testing for Hemophilia A and B
... Most mutations that cause hemophilia B are little alterations in genetic code, which is why sequencing will detect pathogenic mutations in 97% to100% of individuals with a clinical diagnosis of hemophilia B. However, while this method allows us to see small mutations in the DNA sequence, it is too f ...
... Most mutations that cause hemophilia B are little alterations in genetic code, which is why sequencing will detect pathogenic mutations in 97% to100% of individuals with a clinical diagnosis of hemophilia B. However, while this method allows us to see small mutations in the DNA sequence, it is too f ...
Dominant vs. Recessive Traits
... of the two or more alternative forms of the same gene or segment of DNA on a chromosome. Each allele carries the genetic information that codes for specific traits (for instance, the neck length gene for our dragon). Each allele from one parent will pair with an allele from the other parent, to crea ...
... of the two or more alternative forms of the same gene or segment of DNA on a chromosome. Each allele carries the genetic information that codes for specific traits (for instance, the neck length gene for our dragon). Each allele from one parent will pair with an allele from the other parent, to crea ...
Forensic Statistics
... Takes into account the assumption that the person contributing the evidence and the suspect are from the same subgroup What it gives us is a conditional probability of the suspect genotype given that we have already seen that genotype in the perpetrator. Example… use if the suspect and all po ...
... Takes into account the assumption that the person contributing the evidence and the suspect are from the same subgroup What it gives us is a conditional probability of the suspect genotype given that we have already seen that genotype in the perpetrator. Example… use if the suspect and all po ...
Masters_Thesis_Final - JScholarship
... To demonstrate the software, we focused on the NOS1AP locus, whose effect on sudden cardiac death has been shown previously [19]. Data from all the above sources were plotted for 30kb region around NOS1AP locus on chromosome 1 as shown in figure 2.1. As can be seen in the figure, there are only a fe ...
... To demonstrate the software, we focused on the NOS1AP locus, whose effect on sudden cardiac death has been shown previously [19]. Data from all the above sources were plotted for 30kb region around NOS1AP locus on chromosome 1 as shown in figure 2.1. As can be seen in the figure, there are only a fe ...
Part-5A - UTK-EECS
... 2. Repeat for t = 0, …, tmax or until converges: a) create empty population P(t + 1) b) repeat until P(t + 1) is full: ...
... 2. Repeat for t = 0, …, tmax or until converges: a) create empty population P(t + 1) b) repeat until P(t + 1) is full: ...
Open access article
... plants were chosen that did not exhibit any severe phenotypic impairment. This selection was to maximize the number of plants for which seeds could be obtained, since seed availability is the prerequisite for phenotypic analysis of lines carrying mutations of interest. The size of GENPOP was increas ...
... plants were chosen that did not exhibit any severe phenotypic impairment. This selection was to maximize the number of plants for which seeds could be obtained, since seed availability is the prerequisite for phenotypic analysis of lines carrying mutations of interest. The size of GENPOP was increas ...
Chapter 14
... • The addition rule states that the probability that any one of two or more exclusive events will occur is calculated by adding together their individual probabilities • The rule of addition can be used to figure out the probability that an F2 plant from a monohybrid cross will be heterozygous rath ...
... • The addition rule states that the probability that any one of two or more exclusive events will occur is calculated by adding together their individual probabilities • The rule of addition can be used to figure out the probability that an F2 plant from a monohybrid cross will be heterozygous rath ...
Tree Improvement
... Allopatric: Genetically isolated species or races inhabiting separate geographic areas or adjacent but radically different habitats. See Geographical race, Race, Sympatric. Allozyme (alloenzyme): An isozyme which differs from other variants of the enzyme as a result of allelic difference, i.e differ ...
... Allopatric: Genetically isolated species or races inhabiting separate geographic areas or adjacent but radically different habitats. See Geographical race, Race, Sympatric. Allozyme (alloenzyme): An isozyme which differs from other variants of the enzyme as a result of allelic difference, i.e differ ...
univERsity oF copEnhAGEn
... Allopatric: Genetically isolated species or races inhabiting separate geographic areas or adjacent but radically different habitats. See Geographical race, Race, Sympatric. Allozyme (alloenzyme): An isozyme which differs from other variants of the enzyme as a result of allelic difference, i.e differ ...
... Allopatric: Genetically isolated species or races inhabiting separate geographic areas or adjacent but radically different habitats. See Geographical race, Race, Sympatric. Allozyme (alloenzyme): An isozyme which differs from other variants of the enzyme as a result of allelic difference, i.e differ ...
A satellite-like sequence, representing a “clone gap” in the human
... Abstract Although the human genome sequence is generally considered “finished”, the latest assembly (NCBI Build 36.1) still presents a number of gaps. Some of them are defined as “clone gaps” because they separate neighboring contigs. Evolutionary new centromeres are centromeres that repositioned al ...
... Abstract Although the human genome sequence is generally considered “finished”, the latest assembly (NCBI Build 36.1) still presents a number of gaps. Some of them are defined as “clone gaps” because they separate neighboring contigs. Evolutionary new centromeres are centromeres that repositioned al ...
Human Cloning: An African Perspective
... can be designed and manufactured to possess some specific characteristics. It is no different than buying any other commodity or merchandise in an ordinary market. “Expecting a big payoff from the child, the parent would be willing to pay top dollar for the cloned embryo of an outstanding figure suc ...
... can be designed and manufactured to possess some specific characteristics. It is no different than buying any other commodity or merchandise in an ordinary market. “Expecting a big payoff from the child, the parent would be willing to pay top dollar for the cloned embryo of an outstanding figure suc ...
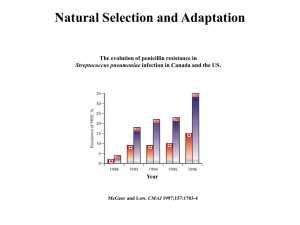
Natural Selection and Adaptation
... • Traditional wildlife management has focused on Ecology (population sizes) • This study shows that over only 30 years, evolution has occurred • Suggests that, in some cases, management strategies must also consider evolution ...
... • Traditional wildlife management has focused on Ecology (population sizes) • This study shows that over only 30 years, evolution has occurred • Suggests that, in some cases, management strategies must also consider evolution ...
Name
... 3. Which allele is the dominant allele? Explain how you know. 4. Which allele is the recessive allele? Explain how you know. 5. What alleles do the F1 offspring have? Explain which allele was inherited from each parent. ...
... 3. Which allele is the dominant allele? Explain how you know. 4. Which allele is the recessive allele? Explain how you know. 5. What alleles do the F1 offspring have? Explain which allele was inherited from each parent. ...
2010 syllabus
... transposons, etc. Human origins and genetic diversity within humans (genetic diversity of Tues sequence and copy number, nuclear ...
... transposons, etc. Human origins and genetic diversity within humans (genetic diversity of Tues sequence and copy number, nuclear ...
"Dual-coding Regions in Alternatively Spliced Human Genes". In
... are annotated as more than one type of codon position. Not surprisingly, two key factors strongly influence the identification of dual-coding regions: the completeness of transcriptome data and the accuracy of reading frame annotation. Based on a set of high-quality and wellannotated transcripts, we o ...
... are annotated as more than one type of codon position. Not surprisingly, two key factors strongly influence the identification of dual-coding regions: the completeness of transcriptome data and the accuracy of reading frame annotation. Based on a set of high-quality and wellannotated transcripts, we o ...
Allele frequency estimation in the human ABO blood group system
... While the (complete set of) genotypic frequencies always determine the allelic frequencies, the reverse is not necessarily true, that is, we cannot always calculate the genotypic frequencies from the allelic. Given some assumptions -- random union of gametes (with or without random mating), very lar ...
... While the (complete set of) genotypic frequencies always determine the allelic frequencies, the reverse is not necessarily true, that is, we cannot always calculate the genotypic frequencies from the allelic. Given some assumptions -- random union of gametes (with or without random mating), very lar ...
The evolutionary approach to human behaviour
... same argument still persists today, although culture now replaces God as the means by which we are able to rise above the beasts. Of course, in a very real sense, this is true: the impact of culture on human behaviour is enormous and not to be underestimated. The very fact that you are sitting her ...
... same argument still persists today, although culture now replaces God as the means by which we are able to rise above the beasts. Of course, in a very real sense, this is true: the impact of culture on human behaviour is enormous and not to be underestimated. The very fact that you are sitting her ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.