Evolution of Populations
... • Natural selection is not the only source of evolutionary change. • The smaller a population is, the farther the results may be from what the laws of probability predict. This kind of random change in allele frequency is called genetic drift. • How does genetic drift take place? – In small populati ...
... • Natural selection is not the only source of evolutionary change. • The smaller a population is, the farther the results may be from what the laws of probability predict. This kind of random change in allele frequency is called genetic drift. • How does genetic drift take place? – In small populati ...
THEME 1: EVOLUTION OF CHEMOTAXIS
... A predictive understanding of evolutionary dynamics is a central goal of quantitative biology. In this theme we use bacterial motility as a model system for understanding evolutionary dynamics at the population and single-cell level. We study evolution in the presence of a trade-off, and how individ ...
... A predictive understanding of evolutionary dynamics is a central goal of quantitative biology. In this theme we use bacterial motility as a model system for understanding evolutionary dynamics at the population and single-cell level. We study evolution in the presence of a trade-off, and how individ ...
No Slide Title
... Law of Independent Assortment • Factors for different characteristics are distributed to gametes independently of one another • Only true for genes on separate c’somes or far apart on same c’some • Ex: white flowers and smooth pods are independent of each other OR dimples and skin color are indepen ...
... Law of Independent Assortment • Factors for different characteristics are distributed to gametes independently of one another • Only true for genes on separate c’somes or far apart on same c’some • Ex: white flowers and smooth pods are independent of each other OR dimples and skin color are indepen ...
Chapter 12 I am - Mrs Smith`s Biology
... I am the number of genes that are thought to control polygenic inherited characteristics like skin colour, hand span, foot size, weight and height Discontinuous Variation ...
... I am the number of genes that are thought to control polygenic inherited characteristics like skin colour, hand span, foot size, weight and height Discontinuous Variation ...
Document
... dispersal = movement of individuals between popns (necessary but not sufficient for gene flow) gene flow individuals leave their natal population reach new suitable habitat successfully reproduce infer dispersal from studies of movement infer gene flow from allele frequency patterns model this as ge ...
... dispersal = movement of individuals between popns (necessary but not sufficient for gene flow) gene flow individuals leave their natal population reach new suitable habitat successfully reproduce infer dispersal from studies of movement infer gene flow from allele frequency patterns model this as ge ...
Slide 1
... 3) Some individuals will reproduce more than others by random chance, which can cause allele frequency to fluctuate (genetic drift). 4) However, some individuals will reproduce more than others because their DNA makes them more fit (Natural Selection). -this genetic variation (different DNA) comes ...
... 3) Some individuals will reproduce more than others by random chance, which can cause allele frequency to fluctuate (genetic drift). 4) However, some individuals will reproduce more than others because their DNA makes them more fit (Natural Selection). -this genetic variation (different DNA) comes ...
Vocab Puzzle
... nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes. 16. Genotype of an individual with two of the same alleles for a given trait. 17. Any one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that may occur alternatively at a given site on ...
... nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes. 16. Genotype of an individual with two of the same alleles for a given trait. 17. Any one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that may occur alternatively at a given site on ...
Common Misconceptions in Genetics
... Absolutely not! Most mutations that occur in our DNA sequence are changes in single nucleotides that do not cause harm to the individual. Recent research suggests that each of us inherits approximately 60 new mutations that are not present in our parents (Conrad et al., 2011). These mutations accoun ...
... Absolutely not! Most mutations that occur in our DNA sequence are changes in single nucleotides that do not cause harm to the individual. Recent research suggests that each of us inherits approximately 60 new mutations that are not present in our parents (Conrad et al., 2011). These mutations accoun ...
to see the paper as an MS Word file
... The theory of self-organizing systems [Bak 1996] is still in its infancy, and the necessary and sufficient conditions for the process of self-organization have yet to be elucidated. However, some factors have been identified as being typical of self-organizing systems and the logical bases for their ...
... The theory of self-organizing systems [Bak 1996] is still in its infancy, and the necessary and sufficient conditions for the process of self-organization have yet to be elucidated. However, some factors have been identified as being typical of self-organizing systems and the logical bases for their ...
DO NOT USE MY WORDING in your answers!!!
... 3. Explain each step of natural selection and describe how the process of evolution is more of an “editing” process than a “creating” process? Figure this out for yourself...by reviewing and understanding the steps 4. Name and describe the different types of fossils. Which type of organism is most l ...
... 3. Explain each step of natural selection and describe how the process of evolution is more of an “editing” process than a “creating” process? Figure this out for yourself...by reviewing and understanding the steps 4. Name and describe the different types of fossils. Which type of organism is most l ...
Chapter Summary 3 - Genetics
... Every living organism inherits a blueprint for life from its parents. Genetics is the study of inheritance. Many characteristics of organisms are controlled by the genes. A gene is a heritable factor that consists of a length of DNA and that influences a specific characteristic. A gene occupies a sp ...
... Every living organism inherits a blueprint for life from its parents. Genetics is the study of inheritance. Many characteristics of organisms are controlled by the genes. A gene is a heritable factor that consists of a length of DNA and that influences a specific characteristic. A gene occupies a sp ...
Microevolution: Unique Gene Pools
... interval; if this be so, at the end of the fifth century there would be alive fifteen million elephants, descended from the first pair.” (Darwin, 1859 p.64) ...
... interval; if this be so, at the end of the fifth century there would be alive fifteen million elephants, descended from the first pair.” (Darwin, 1859 p.64) ...
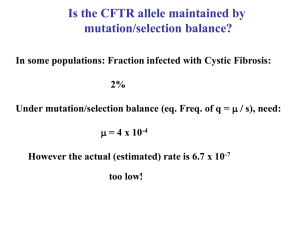
Is the CFTR allele maintained by mutation/selection balance?
... are determined by different, selective processes. ...
... are determined by different, selective processes. ...
Chapter 13
... product of the probabilities of each individual crossover therefore, the classes of offspring with the lowest numbers represent the double crossovers and allow the gene order to be determined ...
... product of the probabilities of each individual crossover therefore, the classes of offspring with the lowest numbers represent the double crossovers and allow the gene order to be determined ...
Medical Benefits from Human Genome Project
... by interplay of genetic factor and environment factor. This is also true for the colon cancer. In addition, it is known that the colon cancer may be caused by an alter gene which is inherited from parents. Although scientists have known that the hereditary colon cancer is caused by an altered gene f ...
... by interplay of genetic factor and environment factor. This is also true for the colon cancer. In addition, it is known that the colon cancer may be caused by an alter gene which is inherited from parents. Although scientists have known that the hereditary colon cancer is caused by an altered gene f ...
1 Achievements of genetic engineering
... variety of rice named Golden Rice, then Golden Rice 2. It is to give more A vitamin and iron, being so important in health prevention in Third World countries. Among other achievements in the genetic engineering relative to crop plants, one could mention beetroots with lower calorific value, and po ...
... variety of rice named Golden Rice, then Golden Rice 2. It is to give more A vitamin and iron, being so important in health prevention in Third World countries. Among other achievements in the genetic engineering relative to crop plants, one could mention beetroots with lower calorific value, and po ...
PPT - Larry Smarr - California Institute for Telecommunications and
... http://gai.nci.nih.gov/html-snp/imagemaps.html ...
... http://gai.nci.nih.gov/html-snp/imagemaps.html ...
Chapter 16 Review
... 6. Understand how Morgan’s experiments with Drosophila lead to our understanding of traits that are sex linked. 7. Why are sex linked traits more common in males? 8. What are polygenic traits, give two examples of these types of traits in humans. 9. Know how to use the product rule to predict probab ...
... 6. Understand how Morgan’s experiments with Drosophila lead to our understanding of traits that are sex linked. 7. Why are sex linked traits more common in males? 8. What are polygenic traits, give two examples of these types of traits in humans. 9. Know how to use the product rule to predict probab ...
unit 5h.1 5b.4 genetics evolution variation
... basis for evolution. May be caused by inherited genes (heritable variation) or by the environment (non-heritable variation). Heritable variation is the most significant in evolution. ...
... basis for evolution. May be caused by inherited genes (heritable variation) or by the environment (non-heritable variation). Heritable variation is the most significant in evolution. ...
Genetic Algorithms
... • Permutation encoding used to encode chromosomes. • Each chromosome is a string of numbers, which represents number of town in a entry sequence. Chromosome A Chromosome B ...
... • Permutation encoding used to encode chromosomes. • Each chromosome is a string of numbers, which represents number of town in a entry sequence. Chromosome A Chromosome B ...
ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS
... the following paragraphs. Power napping is good for the I.Q. Health professionals (11) increasingly recognize the importance of eight hours sleep ...
... the following paragraphs. Power napping is good for the I.Q. Health professionals (11) increasingly recognize the importance of eight hours sleep ...
Behavior Genetics: Predicting Individual Differences
... (deoxyribonucleic acid) that carry genetic information; located in the nucleus of every ...
... (deoxyribonucleic acid) that carry genetic information; located in the nucleus of every ...
Genetics
... 2. At least one-third of the children in pediatric hospitals are there because of hereditary disorders. ...
... 2. At least one-third of the children in pediatric hospitals are there because of hereditary disorders. ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.