of genome-wide association studies
... Introduction to statistics for geneticists - Dr. Krista Fischer Basics of probability theory, binomial and normal distribution, polygenic inheritance and complex traits, allele frequencies in population, Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, linear and logistic regression, additive genetic model, test signifi ...
... Introduction to statistics for geneticists - Dr. Krista Fischer Basics of probability theory, binomial and normal distribution, polygenic inheritance and complex traits, allele frequencies in population, Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, linear and logistic regression, additive genetic model, test signifi ...
Biology Chapter 10 Review
... 17. Be familiar with the “Exceptions” to Mendel’s Rules. (Why are they exception?) 18. Be able to conduct Punnett Square crosses involving exceptions to Mendel’s Rules. 19. Why are some alleles written as a letter/symbol as an exponent on a base letter? 20. What is unique about a heterozygous indivi ...
... 17. Be familiar with the “Exceptions” to Mendel’s Rules. (Why are they exception?) 18. Be able to conduct Punnett Square crosses involving exceptions to Mendel’s Rules. 19. Why are some alleles written as a letter/symbol as an exponent on a base letter? 20. What is unique about a heterozygous indivi ...
That Come Close to the Bone - Max-Planck
... this category. According to research carried out by the Network for Rare Diseases, five new ones are described every week in the specialist medical literature. Rare diseases take very different forms, but are usually caused by mutations in certain genes and can thus be passed on from one generation ...
... this category. According to research carried out by the Network for Rare Diseases, five new ones are described every week in the specialist medical literature. Rare diseases take very different forms, but are usually caused by mutations in certain genes and can thus be passed on from one generation ...
... Calculate the probability that an individual heterozygous for a cleft chin (Cc) and an individual homozygous for a cleft chin (cc) will produce offspring that are homozygous for a cleft chin When analyzing a pedigree, how can you determine if an individual is a carrier (heterozygous) for a trait ...
Chance and risk in adaptive evolution
... volution is a quest for innovation. Organisms keep inventing new phenotypes to adapt to changing environments. Intuitively, adaptive processes are captured by Sewall Wright’s picture of a population moving up a fitness landscape (1). At the molecular level, adaptation is carried by mutations with a s ...
... volution is a quest for innovation. Organisms keep inventing new phenotypes to adapt to changing environments. Intuitively, adaptive processes are captured by Sewall Wright’s picture of a population moving up a fitness landscape (1). At the molecular level, adaptation is carried by mutations with a s ...
Acquired Traits Revisited
... in progeny. Newborn rat pups that are licked and groomed by their mothers mature to be relatively calm and brave. Newborns that receive little or no maternal licking grow up to be nervous and seek darkness. The hippocampus of the brain of a well-licked rat is better developed and releases less of th ...
... in progeny. Newborn rat pups that are licked and groomed by their mothers mature to be relatively calm and brave. Newborns that receive little or no maternal licking grow up to be nervous and seek darkness. The hippocampus of the brain of a well-licked rat is better developed and releases less of th ...
Principles of Biology Lake Tahoe Community College
... A. near each other on same chromosome, tend to be inherited together 1. Linked genes – chromosomal basis a. X linked b. Y linked 2. X inactivation in female mammals a. one chromosome in each cell of females becomes inactivated b. males and females both have one active X in their bodies c. inactive X ...
... A. near each other on same chromosome, tend to be inherited together 1. Linked genes – chromosomal basis a. X linked b. Y linked 2. X inactivation in female mammals a. one chromosome in each cell of females becomes inactivated b. males and females both have one active X in their bodies c. inactive X ...
Worksheet: The theory of natural selection
... If you have variation, differential reproduction, and heredity, you will have evolution by natural selection as an outcome. ...
... If you have variation, differential reproduction, and heredity, you will have evolution by natural selection as an outcome. ...
Basic Genetics & Background on Genetic Testing
... profiling is making it possible to assess disease risk from looking at a persons DNA. • The pattern of diagnosis and treatment of disease may be replacement by a new pattern of predicting a disease and preventing it. Meet the Gene Machine ...
... profiling is making it possible to assess disease risk from looking at a persons DNA. • The pattern of diagnosis and treatment of disease may be replacement by a new pattern of predicting a disease and preventing it. Meet the Gene Machine ...
8.5 - Allelic Frequencies & Population Genetics (AKA Hardy
... Frequencies of the 2 alleles must add up to 1.0 A recessive/dominant situation If everyone in a population was TT, then what would the frequency of the T allele be? 1.0 If everyone in a population was Tt, then what would the frequency of the T allele be? 0.5 The t allele? 0.5 However, real ...
... Frequencies of the 2 alleles must add up to 1.0 A recessive/dominant situation If everyone in a population was TT, then what would the frequency of the T allele be? 1.0 If everyone in a population was Tt, then what would the frequency of the T allele be? 0.5 The t allele? 0.5 However, real ...
Genetic Testing for Endocrine Gland Cancer Susceptibility
... The testing is being offered in a setting with adequately trained health care professionals to provide appropriate pre- and post-test counseling Other (please describe): ...
... The testing is being offered in a setting with adequately trained health care professionals to provide appropriate pre- and post-test counseling Other (please describe): ...
Realized Heritability
... To quantify any increase in number of hairs made by selecting and intermating the hairy portion of a population, students would first want to record the number of hairs on each plant in the experimental population (Generation 0) of size = n. Then calculate the average number of hairs on a represent ...
... To quantify any increase in number of hairs made by selecting and intermating the hairy portion of a population, students would first want to record the number of hairs on each plant in the experimental population (Generation 0) of size = n. Then calculate the average number of hairs on a represent ...
Genetic Testing for Endocrine Gland Cancer Susceptibility
... The testing is being offered in a setting with adequately trained health care professionals to provide appropriate pre- and post-test counseling Other (please describe): ...
... The testing is being offered in a setting with adequately trained health care professionals to provide appropriate pre- and post-test counseling Other (please describe): ...
Chapter 3 - McConnell
... Evolutionary psychology studies why we as humans are alike. In particular, it studies the evolution of behavior and mind using principles of natural selection. Natural selection is an evolutionary process through which adaptive traits are passed on to ongoing generations because these traits help an ...
... Evolutionary psychology studies why we as humans are alike. In particular, it studies the evolution of behavior and mind using principles of natural selection. Natural selection is an evolutionary process through which adaptive traits are passed on to ongoing generations because these traits help an ...
all in the genes - The Wild Trout Trust
... The complete wild trout gene pool represents the ultimate “master library” of every single version of every single trout gene that could possibly be present in any lineages (whether domestic or wild). Both domestication and local adaptation in the wild involves selecting only a subset of the total g ...
... The complete wild trout gene pool represents the ultimate “master library” of every single version of every single trout gene that could possibly be present in any lineages (whether domestic or wild). Both domestication and local adaptation in the wild involves selecting only a subset of the total g ...
Interactions between SNP Alleles at Multiple Loci Contribute to Skin
... 2σ and defined two groups in the Mongoloid cohort based on constitutive skin color (low and high melanin groups). To examine the contribution of non-random associations of SNP alleles at multiple loci to skin color variations (i.e. low/high melanin content), we examined the associations among the 20 ...
... 2σ and defined two groups in the Mongoloid cohort based on constitutive skin color (low and high melanin groups). To examine the contribution of non-random associations of SNP alleles at multiple loci to skin color variations (i.e. low/high melanin content), we examined the associations among the 20 ...
Genetic Algorithms Selection Presentation
... double rand1 = tot*rand.nextDouble(); double ttot=0.0; for (int x=l.size()-1;x>=0;x--) { Chomosone node = (Chomosone)l.get(x); ttot+=node.score; if (ttot>=rand1) { l.remove(x); return node; ...
... double rand1 = tot*rand.nextDouble(); double ttot=0.0; for (int x=l.size()-1;x>=0;x--) { Chomosone node = (Chomosone)l.get(x); ttot+=node.score; if (ttot>=rand1) { l.remove(x); return node; ...
Chapter 2 The role of chance in evolution
... Another important role that chance can play in evolution is seen when a population splits off and forms a colony. Depending on the size of the group that founds the colony, the gene frequencies of the colony will either resemble the parent population closely, or it may be quite different from the pa ...
... Another important role that chance can play in evolution is seen when a population splits off and forms a colony. Depending on the size of the group that founds the colony, the gene frequencies of the colony will either resemble the parent population closely, or it may be quite different from the pa ...
Molecular population genetics Magnus Nordborg* and Hideki Innan
... LD has received much attention recently because it may be used for fine-scale mapping [41] of genes that are responsible for naturally occurring phenotypic variation (e.g. human disease loci). The idea behind LD mapping is simply to look for marker alleles, or multi-locus haplotypes, that are associ ...
... LD has received much attention recently because it may be used for fine-scale mapping [41] of genes that are responsible for naturally occurring phenotypic variation (e.g. human disease loci). The idea behind LD mapping is simply to look for marker alleles, or multi-locus haplotypes, that are associ ...
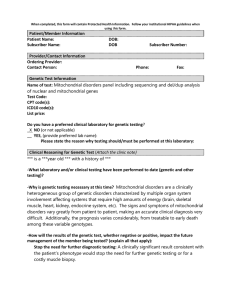
When completed, this form will contain Protected Health Information
... heterogeneous group of genetic disorders characterized by multiple organ system involvement affecting systems that require high amounts of energy (brain, skeletal muscle, heart, kidney, endocrine system, etc). The signs and symptoms of mitochondrial disorders vary greatly from patient to patient, ma ...
... heterogeneous group of genetic disorders characterized by multiple organ system involvement affecting systems that require high amounts of energy (brain, skeletal muscle, heart, kidney, endocrine system, etc). The signs and symptoms of mitochondrial disorders vary greatly from patient to patient, ma ...
Patterns of Inheritance - (www.ramsey.k12.nj.us).
... Character: heritable feature that varies among individuals (ex. seed color) Trait: possible variations for a particular character (ex. yellow seeds vs. green seeds) ...
... Character: heritable feature that varies among individuals (ex. seed color) Trait: possible variations for a particular character (ex. yellow seeds vs. green seeds) ...
Which of the following statements describe what all members of a
... If the relative frequency of a single allele for a particular trait declines over time, what would happen to the relative frequencies of some or all other alleles for that trait? ...
... If the relative frequency of a single allele for a particular trait declines over time, what would happen to the relative frequencies of some or all other alleles for that trait? ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.