DAT1 and ADHD: Family
... 1) PCR will be carried out in a 10 l volume containing 50 ng of genomic template, 0.5 M of each primer, one of which is 5' fluorescently labeled, 200 M of each dNTP (dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP), 1 x PCR buffer, 2 mM MgCl2, and 0.5 units Taq polymerase (Amplitaq Gold). Samples will be amplified on a 9700 ...
... 1) PCR will be carried out in a 10 l volume containing 50 ng of genomic template, 0.5 M of each primer, one of which is 5' fluorescently labeled, 200 M of each dNTP (dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP), 1 x PCR buffer, 2 mM MgCl2, and 0.5 units Taq polymerase (Amplitaq Gold). Samples will be amplified on a 9700 ...
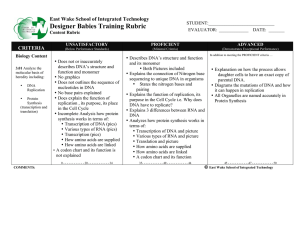
Designer Babies Training Rubric
... or not Designer babies should be placed on the market and why ...
... or not Designer babies should be placed on the market and why ...
Affected Family-based Control Association Studies
... 1) PCR will be carried out in a 10 l volume containing 50 ng of genomic template, 0.5 M of each primer, one of which is 5' fluorescently labeled, 200 M of each dNTP (dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP), 1 x PCR buffer, 2 mM MgCl2, and 0.5 units Taq polymerase (Amplitaq Gold). Samples will be amplified on a 9700 ...
... 1) PCR will be carried out in a 10 l volume containing 50 ng of genomic template, 0.5 M of each primer, one of which is 5' fluorescently labeled, 200 M of each dNTP (dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP), 1 x PCR buffer, 2 mM MgCl2, and 0.5 units Taq polymerase (Amplitaq Gold). Samples will be amplified on a 9700 ...
Employee Request for ADA Accommodation
... individual, except as specifically allowed by this law. To comply with this law, we are asking that you not provide any genetic information when responding to this request for medical information. “Genetic information,” as defined by GINA, includes an individual’s family medical history, the results ...
... individual, except as specifically allowed by this law. To comply with this law, we are asking that you not provide any genetic information when responding to this request for medical information. “Genetic information,” as defined by GINA, includes an individual’s family medical history, the results ...
Prof. Kamakaka`s Lecture 14 Notes
... Humans are genetically >99 per cent identical: it is the tiny percentage that is different Much of our genetic variation is caused by single-nucleotide differences in our DNA : these are called single nucleotide polymorphisms, or SNPs. As a result, each of us has a unique genotype that typically dif ...
... Humans are genetically >99 per cent identical: it is the tiny percentage that is different Much of our genetic variation is caused by single-nucleotide differences in our DNA : these are called single nucleotide polymorphisms, or SNPs. As a result, each of us has a unique genotype that typically dif ...
PPT
... In one of the stages of meiosis, the chromosomes line up on the midline of the cell and are separated from each other when the cell divides A ...
... In one of the stages of meiosis, the chromosomes line up on the midline of the cell and are separated from each other when the cell divides A ...
Chapter 1 The Framework of Biology
... Mendel's laws have been supported by over 100 years of evidence. Mendel discovered dominant and recessive traits. Working with true breeding pea plants as the parental or P generation, Mendel crossed these plants to produce an F1 generation followed by crossing F1 individuals for an F2 generation. L ...
... Mendel's laws have been supported by over 100 years of evidence. Mendel discovered dominant and recessive traits. Working with true breeding pea plants as the parental or P generation, Mendel crossed these plants to produce an F1 generation followed by crossing F1 individuals for an F2 generation. L ...
Parallel Evolution of Cold Tolerance within
... higher inversion frequencies. Each cold-adapted population shows lower inversion frequencies than a closely-related warm-adapted population, suggesting that inversion frequencies may decrease with altitude in addition to latitude. Using the FST-based “Population Branch Excess” statistic (PBE), we fo ...
... higher inversion frequencies. Each cold-adapted population shows lower inversion frequencies than a closely-related warm-adapted population, suggesting that inversion frequencies may decrease with altitude in addition to latitude. Using the FST-based “Population Branch Excess” statistic (PBE), we fo ...
There are a number of ways to find genes and gene information in
... sites. Look first at the homology information for the gene by clicking on Homol (homologene) and examine the mouse (M musculus) protein graphic to look for protein domain and click on the gene to look at the structure. Back at Locus Link compare the browsers. The three major browsers are the NCBI br ...
... sites. Look first at the homology information for the gene by clicking on Homol (homologene) and examine the mouse (M musculus) protein graphic to look for protein domain and click on the gene to look at the structure. Back at Locus Link compare the browsers. The three major browsers are the NCBI br ...
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) and
... • WGCNA is also useful for inter-species comparison of gene expression levels • NEO can estimate edge orientation in a weighted gene coexpression network if relevant genetic marker data is available • NEO can also perform marker selection ...
... • WGCNA is also useful for inter-species comparison of gene expression levels • NEO can estimate edge orientation in a weighted gene coexpression network if relevant genetic marker data is available • NEO can also perform marker selection ...
Pregnancy: Expecting a Child with OI
... Ultrasound can be used to examine the fetal skeleton for bowing, fractures, shortening, or other bone abnormalities consistent with OI. Ultrasound is generally most helpful for prenatal diagnosis of the more severe forms of OI. The fetal skeleton shows signs of OI as early as 16 weeks in OI Type II, ...
... Ultrasound can be used to examine the fetal skeleton for bowing, fractures, shortening, or other bone abnormalities consistent with OI. Ultrasound is generally most helpful for prenatal diagnosis of the more severe forms of OI. The fetal skeleton shows signs of OI as early as 16 weeks in OI Type II, ...
Notes for The Longevity Seekers
... Researchers clashed with evolutionary theorists who claimed that if a gene prolonged life, it would do other things that were deleterious. There was also the problem of how to prescribe a drug to “those at risk” when everyone is a risk for aging! The ethics of longevity research was discussed in Was ...
... Researchers clashed with evolutionary theorists who claimed that if a gene prolonged life, it would do other things that were deleterious. There was also the problem of how to prescribe a drug to “those at risk” when everyone is a risk for aging! The ethics of longevity research was discussed in Was ...
Human_lecture4
... Doesn’t play a large direct role in changing allele frequency because mutation rates per locus tend to be low Mutations rarely affect phenotype However, all allelic variation ultimately has a mutational origin Mutation rates differ between species and between different regions of the genome of a sin ...
... Doesn’t play a large direct role in changing allele frequency because mutation rates per locus tend to be low Mutations rarely affect phenotype However, all allelic variation ultimately has a mutational origin Mutation rates differ between species and between different regions of the genome of a sin ...
Genetic variation
... • Using your Punnett square, complete the box below to show the expected phenotype ratio for the children. • In the pedigree chart the phenotype ratio of Huntington’s disease in the children of parents 9 and 10 is not the same as the predicted ratio you have given on the previous page. Give reasons ...
... • Using your Punnett square, complete the box below to show the expected phenotype ratio for the children. • In the pedigree chart the phenotype ratio of Huntington’s disease in the children of parents 9 and 10 is not the same as the predicted ratio you have given on the previous page. Give reasons ...
Karyotyping Lab:
... b. Is the sex of each baby readily obvious? _________ Occasionally, complications exist which make it difficult to determine the sex of a baby. What do you think these complications might be, and how could they occur? Explain your answer. ...
... b. Is the sex of each baby readily obvious? _________ Occasionally, complications exist which make it difficult to determine the sex of a baby. What do you think these complications might be, and how could they occur? Explain your answer. ...
Chapter 11
... • Accidental changes in genes are called mutations mutations occur only rarely and almost always result in recessive alleles • not eliminated from the population because they are not usually expressed in most individuals (heterozygotes) • in some cases, particular mutant alleles have become more c ...
... • Accidental changes in genes are called mutations mutations occur only rarely and almost always result in recessive alleles • not eliminated from the population because they are not usually expressed in most individuals (heterozygotes) • in some cases, particular mutant alleles have become more c ...
File
... • Among females, however, colorblindness affects only about 1 in 200. In order for a recessive allele, like colorblindness, to be expressed in females, it must be present in two copies—one on each of the X chromosomes. • The recessive phenotype of a sex-linked genetic disorder tends to be much more ...
... • Among females, however, colorblindness affects only about 1 in 200. In order for a recessive allele, like colorblindness, to be expressed in females, it must be present in two copies—one on each of the X chromosomes. • The recessive phenotype of a sex-linked genetic disorder tends to be much more ...
NAME KIT # ______ Karyotyping Lab 1. a. Normally, how many
... b. Is the sex of each baby readily obvious? _________ Occasionally, complications exist which make it difficult to determine the sex of a baby. What do you think these complications might be, and how could they occur? Explain your answer. ...
... b. Is the sex of each baby readily obvious? _________ Occasionally, complications exist which make it difficult to determine the sex of a baby. What do you think these complications might be, and how could they occur? Explain your answer. ...
Slide 1
... • Accidental changes in genes are called mutations mutations occur only rarely and almost always result in recessive alleles • not eliminated from the population because they are not usually expressed in most individuals (heterozygotes) • in some cases, particular mutant alleles have become more c ...
... • Accidental changes in genes are called mutations mutations occur only rarely and almost always result in recessive alleles • not eliminated from the population because they are not usually expressed in most individuals (heterozygotes) • in some cases, particular mutant alleles have become more c ...
File - Science with Spence
... A method of creating offspring that have specific desirable traits (Such as purebred dogs) is called? What is Selective Breeding? ...
... A method of creating offspring that have specific desirable traits (Such as purebred dogs) is called? What is Selective Breeding? ...
Gene Flow - nslc.wustl.edu
... probability of two randomly chosen genes being identical, even within the same deme, is very small and therefore hard to estimate reliably. “Heterozygosity” within demes often approaches one even when the demes’ gene pools are very different, allowing little discrimination with fst . • Instead of ...
... probability of two randomly chosen genes being identical, even within the same deme, is very small and therefore hard to estimate reliably. “Heterozygosity” within demes often approaches one even when the demes’ gene pools are very different, allowing little discrimination with fst . • Instead of ...
ASA POSTER-2008
... Transposable elements have advantages over other approaches for determining gene function in large genome cereals. Different strategies have been used to exploit maize Ac/Ds for such studies in heterologous species. First, large numbers of independent Ds insertion lines (TNPs) are generated and scre ...
... Transposable elements have advantages over other approaches for determining gene function in large genome cereals. Different strategies have been used to exploit maize Ac/Ds for such studies in heterologous species. First, large numbers of independent Ds insertion lines (TNPs) are generated and scre ...
The Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
... In one of the stages of meiosis, the chromosomes line up on the midline of the cell and are separated from each other when the cell divides ...
... In one of the stages of meiosis, the chromosomes line up on the midline of the cell and are separated from each other when the cell divides ...
Patient Information: Genetic Screening What is genetic screening
... but may have mild anemia. Carriers of thalassemias can be found all over the world. We screen everybody by checking to see if they have mild anemia. We might also offer another, more specific blood test for patients of South East Asian descent or people who are mildly anemic, as they have a higher c ...
... but may have mild anemia. Carriers of thalassemias can be found all over the world. We screen everybody by checking to see if they have mild anemia. We might also offer another, more specific blood test for patients of South East Asian descent or people who are mildly anemic, as they have a higher c ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.