BSC 350 Classical and Molecular Genetics Master Syllabus
... 2. Describe the differences between transmission genetics, molecular genetics, population genetics and evolutionary genetics. 3. Analyze genetic data to determine the modes of inheritance and predict outcomes in future generations. 4. Calculate genetics predictions using Hardy-Weinberg equations, Pu ...
... 2. Describe the differences between transmission genetics, molecular genetics, population genetics and evolutionary genetics. 3. Analyze genetic data to determine the modes of inheritance and predict outcomes in future generations. 4. Calculate genetics predictions using Hardy-Weinberg equations, Pu ...
View extract - Yale University Press
... some butterflies are stylised gestures: ‘They represent, if you like, the Expressionist style of nature.’ Then there are patterns whose meaning is established by association. Creatures which are protected by toxicity or powerful defences such as stings signal their danger with bright warning colours ...
... some butterflies are stylised gestures: ‘They represent, if you like, the Expressionist style of nature.’ Then there are patterns whose meaning is established by association. Creatures which are protected by toxicity or powerful defences such as stings signal their danger with bright warning colours ...
Prospects of genetic epidemiology in the 21st
... widely spread non-coding sequences. Thus, at one particular locus in the human genome, several forms of the same gene may exist. These are called polymorphisms. At a molecular level, the difference between mutations and polymorphisms is not clear-cut, leaving frequency and clinical penetrance as the ...
... widely spread non-coding sequences. Thus, at one particular locus in the human genome, several forms of the same gene may exist. These are called polymorphisms. At a molecular level, the difference between mutations and polymorphisms is not clear-cut, leaving frequency and clinical penetrance as the ...
Lecture # 6 Date
... appearance between the phenotypes of 2 alleles. Ex: snapdragons ■ Codominance: two alleles that affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways. Ex: sickle cell anemia ■ Multiple alleles: more than 2 possible alleles for a gene. Ex: human blood types ■ Pleiotropy: genes with multiple phenotyp ...
... appearance between the phenotypes of 2 alleles. Ex: snapdragons ■ Codominance: two alleles that affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways. Ex: sickle cell anemia ■ Multiple alleles: more than 2 possible alleles for a gene. Ex: human blood types ■ Pleiotropy: genes with multiple phenotyp ...
Populus - University of Washington
... genomics • Relatively small genome of 550Mbp (5X Arabidopsis, similar to rice, 40X smaller than pine) • 100K ESTs to be released http://www.biochem.kth.se/PopulusDB/ • Genetic linkage maps based on large progeny sets (0.05cM resolution in some cases) • 10X BAC library of a single P. balsamifera ...
... genomics • Relatively small genome of 550Mbp (5X Arabidopsis, similar to rice, 40X smaller than pine) • 100K ESTs to be released http://www.biochem.kth.se/PopulusDB/ • Genetic linkage maps based on large progeny sets (0.05cM resolution in some cases) • 10X BAC library of a single P. balsamifera ...
Short Exam Questions
... 86. What is meant by DNA profiling? 87. In DNA profiling, what are used to cut DNA strands into fragments? 88. Give two applications (uses) of DNA profiling. 89. Name the plant from which you isolated DNA in your practical studies. 90. For what precise purpose did you use freezer-cold ethanol (alcoh ...
... 86. What is meant by DNA profiling? 87. In DNA profiling, what are used to cut DNA strands into fragments? 88. Give two applications (uses) of DNA profiling. 89. Name the plant from which you isolated DNA in your practical studies. 90. For what precise purpose did you use freezer-cold ethanol (alcoh ...
Document
... Direction favored by natural selection was over 70 degrees (i.e., very close to right angles) away from this variation. Net result: very little response, although all traits have lots of genetic variation. However, little variation in the particular direction favored by selection ...
... Direction favored by natural selection was over 70 degrees (i.e., very close to right angles) away from this variation. Net result: very little response, although all traits have lots of genetic variation. However, little variation in the particular direction favored by selection ...
Genetic Algorithms: A Tutorial
... spaces our algorithm is still very simple It relies on random mutation to find a good solution It has been found that by introducing “sex” into the algorithm better results are obtained This is done by selecting two parents during reproduction and combining their genes to produce offspring ...
... spaces our algorithm is still very simple It relies on random mutation to find a good solution It has been found that by introducing “sex” into the algorithm better results are obtained This is done by selecting two parents during reproduction and combining their genes to produce offspring ...
Evolution of Functionally Diverse Alleles
... we report striking patterns of variation at TAS2R38, including a significant excess of novel rare nonsynonymous polymorphisms that recently arose only in Africa, high frequencies of haplotypes in Africa associated with intermediate bitter taste sensitivity, a remarkably similar frequency of common h ...
... we report striking patterns of variation at TAS2R38, including a significant excess of novel rare nonsynonymous polymorphisms that recently arose only in Africa, high frequencies of haplotypes in Africa associated with intermediate bitter taste sensitivity, a remarkably similar frequency of common h ...
APDC Unit XI Meiosis
... • Alternate versions of genes (alleles) account for variation in inherited traits • For each trait, an organism inherits 2 alleles (one from each parent) • Law of Segregation: Can only pass on ONE of these to gametes – why? • When in meiosis does this occur? ...
... • Alternate versions of genes (alleles) account for variation in inherited traits • For each trait, an organism inherits 2 alleles (one from each parent) • Law of Segregation: Can only pass on ONE of these to gametes – why? • When in meiosis does this occur? ...
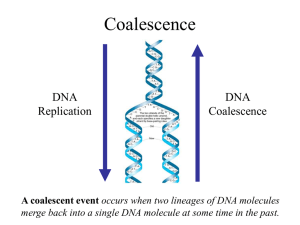
t - nslc.wustl.edu
... • In practice, real populations are not ideal, so pretend the population is ideal but with an “inbreeding effective size” of an idealized population of size Nef♀; Therefore, the prob. of coalescence in one generation is 1/(Nef♀) ...
... • In practice, real populations are not ideal, so pretend the population is ideal but with an “inbreeding effective size” of an idealized population of size Nef♀; Therefore, the prob. of coalescence in one generation is 1/(Nef♀) ...
Isochores and Genes: Who`s in the Driver`s Seat?
... functional reasons. Hence strong GO signal. In AT isochores, the genes were “never challenged”, and we see a “preisochore” mixture of the two functional ...
... functional reasons. Hence strong GO signal. In AT isochores, the genes were “never challenged”, and we see a “preisochore” mixture of the two functional ...
CG_FHIR_Obs_v3
... Attendees: Amnon Shabo, Grant Wood, Bob Milius, Mollie Ullman-Cullere, Scot Bolte, Siew Lam, Gil Alterovitz, Perry Mar, Vanderbilt: Jonathan Holt, Ari Taylor, ...
... Attendees: Amnon Shabo, Grant Wood, Bob Milius, Mollie Ullman-Cullere, Scot Bolte, Siew Lam, Gil Alterovitz, Perry Mar, Vanderbilt: Jonathan Holt, Ari Taylor, ...
V p
... • Heritability does not indicate the degree to which a characteristic is genetically determined. • Pure breed no polydactilly rabbits: still polydactilly can happen ...
... • Heritability does not indicate the degree to which a characteristic is genetically determined. • Pure breed no polydactilly rabbits: still polydactilly can happen ...
GeneticsforNursesinObstetricDisciplines
... 1Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, Texas Tech University Health Science Center at Lubbock and Private Practitioner, KinderGenome Genetics, Dallas Texas; 2Professor of Pediatrics and Obstetrics-Gynecology; Director, Cytogenetics Laboratory, Texas Tech University Health Science Center at Lubbock; 3Gen ...
... 1Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, Texas Tech University Health Science Center at Lubbock and Private Practitioner, KinderGenome Genetics, Dallas Texas; 2Professor of Pediatrics and Obstetrics-Gynecology; Director, Cytogenetics Laboratory, Texas Tech University Health Science Center at Lubbock; 3Gen ...
CILJANA MUTAGENEZA I GENETSKI MARKERI U SELEKCIJI SVINJA
... Milanko Stupar, Scientific adviser, Vitomir Vidović, PhD, professor, MSc Dragomir Lukač, MScLjuba Štrbac, Faculty of Agriculture, Department of Animal Science, Trg Dositeja Obradovića 8. 21000 Novi ...
... Milanko Stupar, Scientific adviser, Vitomir Vidović, PhD, professor, MSc Dragomir Lukač, MScLjuba Štrbac, Faculty of Agriculture, Department of Animal Science, Trg Dositeja Obradovića 8. 21000 Novi ...
Mendel**.. The Father of Genetics
... Mendel discovers each parent has 2 copies of gene Different versions of gene Mendel discovers dominant & recessive Law of segregation Law of independent Assortment Sources of variation ...
... Mendel discovers each parent has 2 copies of gene Different versions of gene Mendel discovers dominant & recessive Law of segregation Law of independent Assortment Sources of variation ...
Chapter 20
... genes near each other on a chromosome almost always end up together after crossing-over • likewise, if two genes are far apart on a chromosome, they are more likely to be affected by crossing-over • this means that genes with a cross-over value of 1% are much closer together than ones with a value o ...
... genes near each other on a chromosome almost always end up together after crossing-over • likewise, if two genes are far apart on a chromosome, they are more likely to be affected by crossing-over • this means that genes with a cross-over value of 1% are much closer together than ones with a value o ...
Genetics and Genomics of Core Short Tandem Repeat Loci
... - As of early 2005, this list contains 365 population studies based on 183 literature references. - OmniPop (Brian Burritt) permits calculation of a user inputted profile’s frequency using allele frequencies from 166 published population surveys. - Large data sets typically identify a greater number ...
... - As of early 2005, this list contains 365 population studies based on 183 literature references. - OmniPop (Brian Burritt) permits calculation of a user inputted profile’s frequency using allele frequencies from 166 published population surveys. - Large data sets typically identify a greater number ...
Reconstructing Indian population history
... may no longer exist in mainland India. However, the indigenous Andaman Islanders are unique in being ASI-related groups without ANI ancestry. Allele frequency differences between groups in India are larger than in Europe, reflecting strong founder effects whose signatures have been maintained for th ...
... may no longer exist in mainland India. However, the indigenous Andaman Islanders are unique in being ASI-related groups without ANI ancestry. Allele frequency differences between groups in India are larger than in Europe, reflecting strong founder effects whose signatures have been maintained for th ...
Mendel and Heredity
... To find the probability of two independent events that occur in sequence, find the probability of each event occurring separately, and then multiply the probabilities. This multiplication rule is defined symbolically below. Note that multiplication is represented by AND. ...
... To find the probability of two independent events that occur in sequence, find the probability of each event occurring separately, and then multiply the probabilities. This multiplication rule is defined symbolically below. Note that multiplication is represented by AND. ...
PDF
... ABSTRACT: β-Lactoglobulin (β-LG) is the dominant non-casein whey protein found in milk of bovine and of most ruminants. The amino acid sequence of β-LG along with its 3-dimensional structure illustrates linkage with the lipocalin superfamily. Preliminary studies in goats indicated that milk yield ca ...
... ABSTRACT: β-Lactoglobulin (β-LG) is the dominant non-casein whey protein found in milk of bovine and of most ruminants. The amino acid sequence of β-LG along with its 3-dimensional structure illustrates linkage with the lipocalin superfamily. Preliminary studies in goats indicated that milk yield ca ...
Chapter 13: The Five Forces Behind Human Evolution
... Because there are many more somatic than germinal cells in us humans, the overwhelming majority of detectable mutations are somatic. Somatic mutations may have no discernible effect on an organism when, for example, they take place in a unused section of DNA, or they can influence the physiology of ...
... Because there are many more somatic than germinal cells in us humans, the overwhelming majority of detectable mutations are somatic. Somatic mutations may have no discernible effect on an organism when, for example, they take place in a unused section of DNA, or they can influence the physiology of ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.