SyntheticTheoryofEvo..
... Estimates of the frequency of mutations in human sex cells generally are about 1 per 10,0001,000,000 for any specific gene. Since humans have approximately 20,000-25,000 genes, it is to be expected that most sex cells contain at least one gene mutation of some sort. In other words, mutations are pro ...
... Estimates of the frequency of mutations in human sex cells generally are about 1 per 10,0001,000,000 for any specific gene. Since humans have approximately 20,000-25,000 genes, it is to be expected that most sex cells contain at least one gene mutation of some sort. In other words, mutations are pro ...
Chapter Objectives: Genetics
... 5. State the Law of Segregation 6. Use a Punnett square to predict the results of a monohybrid cross and state the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of the F2 generation 7. Distinguish between genotype and phenotype, heterozygous and homozygous, and dominant and recessive 8. Explain how a testcross ca ...
... 5. State the Law of Segregation 6. Use a Punnett square to predict the results of a monohybrid cross and state the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of the F2 generation 7. Distinguish between genotype and phenotype, heterozygous and homozygous, and dominant and recessive 8. Explain how a testcross ca ...
Lecture15
... • Comparisons of genes, proteins and non-coding sequences is not the only way to study relations between different species. • Attempts were made from 1930s to use chromosome rearrangements information for this purpose. • It has been shown that genomes consist of a relatively moderate number of “cons ...
... • Comparisons of genes, proteins and non-coding sequences is not the only way to study relations between different species. • Attempts were made from 1930s to use chromosome rearrangements information for this purpose. • It has been shown that genomes consist of a relatively moderate number of “cons ...
What to do if we think that researchers have overlooked a significant
... candidate for molecular research • Restrict attention to variation within a set of relatives • Focus on heritability as a fraction of the variation (useful in ag. & lab. breeding) • Restrict range of varieties or locations ...
... candidate for molecular research • Restrict attention to variation within a set of relatives • Focus on heritability as a fraction of the variation (useful in ag. & lab. breeding) • Restrict range of varieties or locations ...
MQ (54) LIV 2 contents
... correlation was very high and highly significant (r=0.90, N=14; p<.001). The correlation of PC1 with PISA scores was also high and significant (r=0.83; N= 11; p<0.05). PC1 also correlated highly with the frequencies of the two IQ increasing alleles (rs236330 C and rs324650 T): r= 0.838 and 0.815, re ...
... correlation was very high and highly significant (r=0.90, N=14; p<.001). The correlation of PC1 with PISA scores was also high and significant (r=0.83; N= 11; p<0.05). PC1 also correlated highly with the frequencies of the two IQ increasing alleles (rs236330 C and rs324650 T): r= 0.838 and 0.815, re ...
But what are genomic (additive) relationships?
... • Early use of markers used them to infer pedigrees or relationships • Gather markers, then reconstruct pedigrees, then construct A • In conservation genetics, molecular markers have often been used to estimate pedigree relationships • Either estimates of Axy , or estimates of « the most likely rel ...
... • Early use of markers used them to infer pedigrees or relationships • Gather markers, then reconstruct pedigrees, then construct A • In conservation genetics, molecular markers have often been used to estimate pedigree relationships • Either estimates of Axy , or estimates of « the most likely rel ...
Genetic Education for Native Americans
... regulated. They make a wide variety of claims, all of which may not be true. For example, no company can conclusively “prove” AI/AN ancestry from looking at one person’s DNA sample. However, DNA samples from two people can be compared to see if they are related (e.g., as parent and child). There is ...
... regulated. They make a wide variety of claims, all of which may not be true. For example, no company can conclusively “prove” AI/AN ancestry from looking at one person’s DNA sample. However, DNA samples from two people can be compared to see if they are related (e.g., as parent and child). There is ...
Genotype to Phenotype v2 - Avida-ED
... metabolize some sugar, say glucose. One organism that can perform this testable function—ability to metabolize glucose—is positive for the trait (Glu+) and a second that cannot is negative for it (Glu-). Some difference between these organisms’ genotypes determines which phenotypes they exhibit; per ...
... metabolize some sugar, say glucose. One organism that can perform this testable function—ability to metabolize glucose—is positive for the trait (Glu+) and a second that cannot is negative for it (Glu-). Some difference between these organisms’ genotypes determines which phenotypes they exhibit; per ...
16.1 The Canonical Genetic Algorithm
... may not be obvious when to stop, and moreover, it may be a good idea to produce as many populations as possible given the computing/time resources you have available. In this case, the termination function may be a specific time limit or a specific number of generations. It is very important to note ...
... may not be obvious when to stop, and moreover, it may be a good idea to produce as many populations as possible given the computing/time resources you have available. In this case, the termination function may be a specific time limit or a specific number of generations. It is very important to note ...
Mendel and Gen terms BIO
... 4) No blending of traits 5) Can control breeding because of access to male and female sex parts ...
... 4) No blending of traits 5) Can control breeding because of access to male and female sex parts ...
Document
... Individual genotypes might operate in ways to restrict development or constrain outcome • Range of reaction principle: • Genotype, or genetic structure, sets the limits on the range of possible phenotypes that a person might display in response to different environments: • Example: Intellectual deve ...
... Individual genotypes might operate in ways to restrict development or constrain outcome • Range of reaction principle: • Genotype, or genetic structure, sets the limits on the range of possible phenotypes that a person might display in response to different environments: • Example: Intellectual deve ...
Preimplantation Genetic Testing An Overview
... Interpretation of results. Ratio of the fluorescence intensities is proportional to the ratio of 'copy number of DNA sequences' in the test and reference genomes. Altered Cy 3 : Cy 5 ratio indicates a loss or gain of the patient DNA at that specific genomic region If Cy 3 : Cy 5 ratio is equal ...
... Interpretation of results. Ratio of the fluorescence intensities is proportional to the ratio of 'copy number of DNA sequences' in the test and reference genomes. Altered Cy 3 : Cy 5 ratio indicates a loss or gain of the patient DNA at that specific genomic region If Cy 3 : Cy 5 ratio is equal ...
Week 5: The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, population differences
... wrote that he’d “never done anything ‘useful’” never made a discovery that made “the least difference in the amenity of the world.” He was very wrong on this. ...
... wrote that he’d “never done anything ‘useful’” never made a discovery that made “the least difference in the amenity of the world.” He was very wrong on this. ...
study of mendelian and non mendelian inheritance pattern
... In untreated persons homozygous for one of the PKU alleles (BB), PAH activity is close to zero, [phe] ten to forty times standard, and the individual manifests PKU. In the AB heterozygote, PAH activity is only 30% (not 50%) of standard, blood [phe] is elevated two-fold, and the person does not manif ...
... In untreated persons homozygous for one of the PKU alleles (BB), PAH activity is close to zero, [phe] ten to forty times standard, and the individual manifests PKU. In the AB heterozygote, PAH activity is only 30% (not 50%) of standard, blood [phe] is elevated two-fold, and the person does not manif ...
BLOA #11 Sample Essay
... There may have been a correlation between the IQ of the parents and the children which was unaccounted Often adoption agencies attempt to place children into families that they are similar to This may be the cause of the concordance rate between the adopted children and their adoptive family Lack of ...
... There may have been a correlation between the IQ of the parents and the children which was unaccounted Often adoption agencies attempt to place children into families that they are similar to This may be the cause of the concordance rate between the adopted children and their adoptive family Lack of ...
Natural selection
... Natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow can alter allele frequencies in a population – If the five conditions for the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are not met in a population, the population s gene pool may change – Mutations are rare and random and have little effect on the gene pool – If ...
... Natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow can alter allele frequencies in a population – If the five conditions for the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are not met in a population, the population s gene pool may change – Mutations are rare and random and have little effect on the gene pool – If ...
The Ancestry of a Gene - 2009
... does not become fixed in the population, rather crossing over during the fixation process entails that at every locus the genes have an ancestral pool rather than a common ancestor. If one wants to think of mutations becoming fixed, mutations must be viewed as the base pair which mutates, not the ge ...
... does not become fixed in the population, rather crossing over during the fixation process entails that at every locus the genes have an ancestral pool rather than a common ancestor. If one wants to think of mutations becoming fixed, mutations must be viewed as the base pair which mutates, not the ge ...
A/A : A/S
... If, however, a minority group mates nearly exclusively with other members of the minority group, then the frequency of affected individuals in the minority group would be (q2min) = 0.0025. Because the minority group is one tenth of the entire population, the true frequency of disease in the total ...
... If, however, a minority group mates nearly exclusively with other members of the minority group, then the frequency of affected individuals in the minority group would be (q2min) = 0.0025. Because the minority group is one tenth of the entire population, the true frequency of disease in the total ...
Co dominance - The Grange School Blogs
... COPY LO: To be able to describe and predict outcomes for co-dominance and multiple alleles ...
... COPY LO: To be able to describe and predict outcomes for co-dominance and multiple alleles ...
Developmental Systems Theory: A Search for Human Nature
... different households have become golden children, of sorts, for genetic research, and are often cited when a gene "for" a certain trait is claimed to be discovered. Because these pairs of individuals have identical genomes at birth, the ...
... different households have become golden children, of sorts, for genetic research, and are often cited when a gene "for" a certain trait is claimed to be discovered. Because these pairs of individuals have identical genomes at birth, the ...
AP Biology - LangdonBiology.org
... Your original population of 200 (from question 3 above) was hit by a tidal wave and 100 organisms were wiped out, leaving 36 homozygous recessive out of the 100 survivors. If we assume that all individuals were equally likely to be wiped out, how did the tidal wave affect the predicted frequencies o ...
... Your original population of 200 (from question 3 above) was hit by a tidal wave and 100 organisms were wiped out, leaving 36 homozygous recessive out of the 100 survivors. If we assume that all individuals were equally likely to be wiped out, how did the tidal wave affect the predicted frequencies o ...
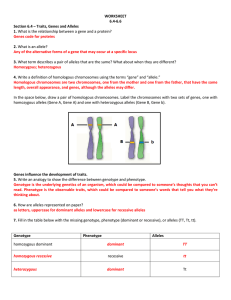
WORKSHEET 6.4-6.6 Section 6.4 – Traits, Genes and Alleles 1
... 7. If genes A and B are located on separate, nonhomologous chromosomes, will they follow Mendel’s law of independent assortment? Explain. Yes. The chromosomes carrying those genes will line up randomly and separate randomly during meiosis. 8. If genes A and B are located at opposite ends on the same ...
... 7. If genes A and B are located on separate, nonhomologous chromosomes, will they follow Mendel’s law of independent assortment? Explain. Yes. The chromosomes carrying those genes will line up randomly and separate randomly during meiosis. 8. If genes A and B are located at opposite ends on the same ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.