EnsEmbl – Genome Browser
... Sequence repositories - GenBank et al. GenBank / EMBL / DDBJ • Highly redundant (many versions of same gene) • Cross-updated daily • Version history is recorded • Previous sequence records can be retrieved ...
... Sequence repositories - GenBank et al. GenBank / EMBL / DDBJ • Highly redundant (many versions of same gene) • Cross-updated daily • Version history is recorded • Previous sequence records can be retrieved ...
population
... What happens to the frequencies of two alleles at a single gene when the four evolutionary forces (Natural selection, mutation, migration, genetic drift) are not acting on a population, and where mating is random? If allele frequencies are the same between a parental and offspring generation → no ev ...
... What happens to the frequencies of two alleles at a single gene when the four evolutionary forces (Natural selection, mutation, migration, genetic drift) are not acting on a population, and where mating is random? If allele frequencies are the same between a parental and offspring generation → no ev ...
here
... The first row contains the names of strains. The first column includes a variant index. The second column includes a variant name. The third column includes a variant chromosome. The fourth column includes a variant genomic position. o The names of each strain and each variant should be unique. o ...
... The first row contains the names of strains. The first column includes a variant index. The second column includes a variant name. The third column includes a variant chromosome. The fourth column includes a variant genomic position. o The names of each strain and each variant should be unique. o ...
Avian genetic diversity - UC Genetic Resources Conservation Program
... been purged from the inbred strain, it can theofollowed by selective breeding of the higherretically be bred to essentially complete homozyranked individuals and families to produce the gosity while maintaining reasonable reproductive next generation. Many factors can affect the rate performance tra ...
... been purged from the inbred strain, it can theofollowed by selective breeding of the higherretically be bred to essentially complete homozyranked individuals and families to produce the gosity while maintaining reasonable reproductive next generation. Many factors can affect the rate performance tra ...
You Light Up My Life
... Thus, each new organism has a probability of three chances in four of having at least one dominant allele in the above example. ...
... Thus, each new organism has a probability of three chances in four of having at least one dominant allele in the above example. ...
Unit A: Nervous and Endocrine Systems Key terms: neuron nerve
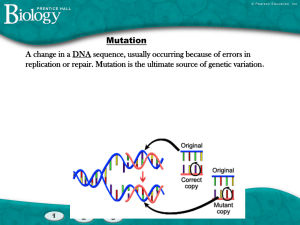
... 3.4 Explain, in general, how restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules into smaller fragments and how ligases reassemble them. 3.5 Explain, in general, how cells may be transformed by inserting new DNA sequences into their genomes. 3.6 Explain how a random change (mutation) in the sequence of bases resu ...
... 3.4 Explain, in general, how restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules into smaller fragments and how ligases reassemble them. 3.5 Explain, in general, how cells may be transformed by inserting new DNA sequences into their genomes. 3.6 Explain how a random change (mutation) in the sequence of bases resu ...
CRS 7210 QUANTITATIVE GENETIC THEORY
... Students with will be equipped with techniques to plan and design breeding experiments by providing a solid background in quantitative genetics and relevant statistical methodologies. The key topics to be covered include: An introduction to statistical tools; Causes of genetic variation at single an ...
... Students with will be equipped with techniques to plan and design breeding experiments by providing a solid background in quantitative genetics and relevant statistical methodologies. The key topics to be covered include: An introduction to statistical tools; Causes of genetic variation at single an ...
Ch. 10 Mendel`s Genetics
... 3. Some alleles are dominant; some recessive. 4. Principle of SEGREGATION: Alleles for each trait segregate (separate) during gamete formation (Anaphase I of meiosis) ...
... 3. Some alleles are dominant; some recessive. 4. Principle of SEGREGATION: Alleles for each trait segregate (separate) during gamete formation (Anaphase I of meiosis) ...
Indigenous Peoples - Council for Responsible Genetics
... research aside in order to insure that indigenous peoples human rights and interests would be protected in the face of the new biotechnologies. Dr. Dukepoo was a founding member of the board of directors of the IPCB, and a treasured mentor and friend. He was the co-author of the original version of ...
... research aside in order to insure that indigenous peoples human rights and interests would be protected in the face of the new biotechnologies. Dr. Dukepoo was a founding member of the board of directors of the IPCB, and a treasured mentor and friend. He was the co-author of the original version of ...
Inheritance The passing of traits from parents to offspring Genetics
... ½ of sons -Affected father has no affected children, but passes the trait on to all daughters who will be carriers for the trait Comment -Watch how questions with sex linkage are phrased: Chance of children? All Possibilities Chance of males? Male Possibilities ...
... ½ of sons -Affected father has no affected children, but passes the trait on to all daughters who will be carriers for the trait Comment -Watch how questions with sex linkage are phrased: Chance of children? All Possibilities Chance of males? Male Possibilities ...
History of Biotechnology
... • 1972: The DNA composition of humans is shown to be 99% similar to that of chimps and gorillas • 1977: Genetically-engineered bacteria are used to make human growth protein • 1978: North Carolina scientists, Hutchinson and Edgell, prove it is possible to introduce specific mutations at specific sit ...
... • 1972: The DNA composition of humans is shown to be 99% similar to that of chimps and gorillas • 1977: Genetically-engineered bacteria are used to make human growth protein • 1978: North Carolina scientists, Hutchinson and Edgell, prove it is possible to introduce specific mutations at specific sit ...
Evolution Acts on the Phenotype
... The gene pool is the complete set of genes and alleles within a population. For example, Tay-Sachs disease is a recessive human genetic disorder. That means only individuals with the homozygous recessive genotype, rr will be affected. Affected individuals usually die from complications of the diseas ...
... The gene pool is the complete set of genes and alleles within a population. For example, Tay-Sachs disease is a recessive human genetic disorder. That means only individuals with the homozygous recessive genotype, rr will be affected. Affected individuals usually die from complications of the diseas ...
A Novel Genetic Programming Based Approach for
... proposed method works according to the evolutionary computation paradigm. The set of prototypes describing all the classes make up an individual of the evolving population. Given an individual and a sample, classification consists in attributing the sample to one of the classes (i.e. in associating ...
... proposed method works according to the evolutionary computation paradigm. The set of prototypes describing all the classes make up an individual of the evolving population. Given an individual and a sample, classification consists in attributing the sample to one of the classes (i.e. in associating ...
The Law of the Jungle: Moral Alternatives and
... Clearly if there were an inherited tendency for each bird to take the ticks out of any other bird's head, this would help the survival of any group in which that tendency happened to arise-for the ticks are dangerous: they can cause death. Someone who believed in group selection would, therefore, ex ...
... Clearly if there were an inherited tendency for each bird to take the ticks out of any other bird's head, this would help the survival of any group in which that tendency happened to arise-for the ticks are dangerous: they can cause death. Someone who believed in group selection would, therefore, ex ...
VII. Natural Selection - Effingham County Schools
... The chance of an individual migrating to another population and sharing it’s genes there. ...
... The chance of an individual migrating to another population and sharing it’s genes there. ...
Chapter Outline - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... master blueprint for all cellular structures and activities for the life span of the organism. The Human Genome Project which began in the 1970s is mapping out the human genome. The Collaborative Gene It was recently discovered that humans have only about 30,000 to 35,000 genes instead of the 5 ...
... master blueprint for all cellular structures and activities for the life span of the organism. The Human Genome Project which began in the 1970s is mapping out the human genome. The Collaborative Gene It was recently discovered that humans have only about 30,000 to 35,000 genes instead of the 5 ...
ANTH 161 - University of South Carolina
... 1) The science of anthropology and the models and mechanisms of human evolution; 2) Modern human variation and adaptation, and our relationships to non-human primates; and 3) The origin, development, and dispersal of humans using evidence from the fossil record (paleoanthropology) and archaeological ...
... 1) The science of anthropology and the models and mechanisms of human evolution; 2) Modern human variation and adaptation, and our relationships to non-human primates; and 3) The origin, development, and dispersal of humans using evidence from the fossil record (paleoanthropology) and archaeological ...
The Law of the Jungle: Moral Alternatives and
... Clearly if there were an inherited tendency for each bird to take the ticks out of any other bird's head, this would help the survival of any group in which that tendency happened to arise-for the ticks are dangerous: they can cause death. Someone who believed in group selection would, therefore, ex ...
... Clearly if there were an inherited tendency for each bird to take the ticks out of any other bird's head, this would help the survival of any group in which that tendency happened to arise-for the ticks are dangerous: they can cause death. Someone who believed in group selection would, therefore, ex ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... 1. Interpret Tables- Genotypes are listed in the (left/right) column of the table, while phenotypes are on the (left/right). 2. Infer- Why are there more genotypes than phenotypes for blood types? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________ ...
... 1. Interpret Tables- Genotypes are listed in the (left/right) column of the table, while phenotypes are on the (left/right). 2. Infer- Why are there more genotypes than phenotypes for blood types? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________ ...
How Populations Evolve - Scranton Prep Biology
... A. Genetic drift is a changein a genepool of a small populationdue to chance.The effect of a loss of individuals from a populationis much gleater when there are fewer individuals. The bottleneck effect is geneticdrift resultingfrom a disasterthat reduces populationsize (suchas the exampleof the elep ...
... A. Genetic drift is a changein a genepool of a small populationdue to chance.The effect of a loss of individuals from a populationis much gleater when there are fewer individuals. The bottleneck effect is geneticdrift resultingfrom a disasterthat reduces populationsize (suchas the exampleof the elep ...
Analytical challenges in the genetic diagnosis of Lynch
... and specific surveillance programs for high-risk individuals who carry a pathogenic mutation. The prediction and prevention schemes reduce the impact of cancer in high-risk families in a cost-effective manner. Genetic tests for LS are well standardized and broadly used, although there remain some sp ...
... and specific surveillance programs for high-risk individuals who carry a pathogenic mutation. The prediction and prevention schemes reduce the impact of cancer in high-risk families in a cost-effective manner. Genetic tests for LS are well standardized and broadly used, although there remain some sp ...
Slide 1
... • Population is homogeneous but each individual’s genome is a mosaic of segments from different populations • May be used to map disease loci – multiple sclerosis susceptibility – Reich et al 2005, Nature Genetics ...
... • Population is homogeneous but each individual’s genome is a mosaic of segments from different populations • May be used to map disease loci – multiple sclerosis susceptibility – Reich et al 2005, Nature Genetics ...
Population structure
... • Theoretical issues – Very difficult for a population that has crossed a valley to spread throughout rest of population – The interaction between epistatic selection and genetic drift may be important in reproductive isolation • e.g. recessive epistatic interactions important in Haldane’s rule of u ...
... • Theoretical issues – Very difficult for a population that has crossed a valley to spread throughout rest of population – The interaction between epistatic selection and genetic drift may be important in reproductive isolation • e.g. recessive epistatic interactions important in Haldane’s rule of u ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.