non-disclosure testing - Reproductive Genetic Innovations
... wish to learn their own genetic status but would like to ensure that their children do not inherit this disease. RGI offers two different methods by which non-disclosure testing can occur. Indirect Non-Disclosure Testing Indirect non-disclosure testing utilizes a process called linkage analysis. Thi ...
... wish to learn their own genetic status but would like to ensure that their children do not inherit this disease. RGI offers two different methods by which non-disclosure testing can occur. Indirect Non-Disclosure Testing Indirect non-disclosure testing utilizes a process called linkage analysis. Thi ...
Strand 3 - Biological Sciences
... C. more molecules move across than with diffusion D. water molecules stream across a membrane 6. Homeostasis can best be describe as the: A. period of an organism’s life when no growth is occurring B. maintaining a relatively stable internal environment C. maintaining a constant body temperature for ...
... C. more molecules move across than with diffusion D. water molecules stream across a membrane 6. Homeostasis can best be describe as the: A. period of an organism’s life when no growth is occurring B. maintaining a relatively stable internal environment C. maintaining a constant body temperature for ...
Classify the following genetic disorders as being caused by addition
... 9. A four nucleotide insertion in the gene that codes for the protein fibrillin results in TaySachs disease, which is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder. In its most common variant, known as infantile Tay–Sachs disease, it causes a relentless deterioration of mental and physical abilities that ...
... 9. A four nucleotide insertion in the gene that codes for the protein fibrillin results in TaySachs disease, which is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder. In its most common variant, known as infantile Tay–Sachs disease, it causes a relentless deterioration of mental and physical abilities that ...
Human Biology Unit III: INHERITANCE AND HUMAN GENETIC
... Introduction: Humans begin life as just one cell and in adult form contain over 100 trillion cells. Cell Division allows this metamorphosis, and in the process of cell division chromosomes and DNA can be altered. These alterations cause variation, mutations, and genetic disease. Genetics, DNA, and g ...
... Introduction: Humans begin life as just one cell and in adult form contain over 100 trillion cells. Cell Division allows this metamorphosis, and in the process of cell division chromosomes and DNA can be altered. These alterations cause variation, mutations, and genetic disease. Genetics, DNA, and g ...
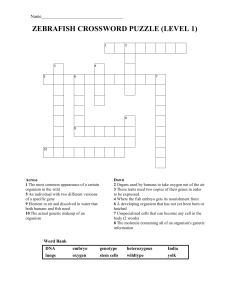
Zebrafish Crossword Puzzles
... Across 1 Tool used to pull small things out of water 4 Surrounds and protects the fish embryo 7 An individual with two identical copies of the same gene 12 How we test our ideas in science 14 Pumps blood through the body 15 The study of biological inheritance of traits 16 The most common appearance ...
... Across 1 Tool used to pull small things out of water 4 Surrounds and protects the fish embryo 7 An individual with two identical copies of the same gene 12 How we test our ideas in science 14 Pumps blood through the body 15 The study of biological inheritance of traits 16 The most common appearance ...
Basic Genetics
... 2. What sex chromosomes do females have? 3. What sex chromosomes do males have? 4. What sex chromosomes do birds and reptiles have? 5. What chromosomes do birds and reptile males have? 6. What chromosomes do birds and reptile females have? 7. What determines the sex of alligators, crocodiles and mos ...
... 2. What sex chromosomes do females have? 3. What sex chromosomes do males have? 4. What sex chromosomes do birds and reptiles have? 5. What chromosomes do birds and reptile males have? 6. What chromosomes do birds and reptile females have? 7. What determines the sex of alligators, crocodiles and mos ...
AND DNA Genes are located on chromosomes in the nucleus of
... Long strings of amino acids make proteins which send messages determining our traits. Adenine binds to thymine, while guanine and cytosine bind. Mutations, caused by mutagens like radiation, occur when the order of bases in DNA changes. With genetic engineering they use mutations in a beneficial way ...
... Long strings of amino acids make proteins which send messages determining our traits. Adenine binds to thymine, while guanine and cytosine bind. Mutations, caused by mutagens like radiation, occur when the order of bases in DNA changes. With genetic engineering they use mutations in a beneficial way ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... Trisomy 21, or Down syndrome, occurs when there is a normal diploid chromosomal complement of 46 chromosomes plus one (extra) chromosome #21. Such individuals therefore have 47 chromosomes. While there is impaired fertility of both sexes, females are more likely to be fertile than males. Assume that ...
... Trisomy 21, or Down syndrome, occurs when there is a normal diploid chromosomal complement of 46 chromosomes plus one (extra) chromosome #21. Such individuals therefore have 47 chromosomes. While there is impaired fertility of both sexes, females are more likely to be fertile than males. Assume that ...
Nature, Nurture and Human Disease, A
... www.-ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/, which provides a catalogue of human genes and genetic disorders). Is it then too extrapolative to suggest that all diseases and traits, each of which has some familial and imputed inherited component, will be caused by a corrupted piece of double helix? Is Watson’s genet ...
... www.-ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/, which provides a catalogue of human genes and genetic disorders). Is it then too extrapolative to suggest that all diseases and traits, each of which has some familial and imputed inherited component, will be caused by a corrupted piece of double helix? Is Watson’s genet ...
Document
... Cloning produces individuals that are genetically identical (including sex). A cloned population is less likely to survive on environmental change, especially the introduction of a new pathogen. Any species brought back to life may not walk the Earth again for any length of time – there could be a s ...
... Cloning produces individuals that are genetically identical (including sex). A cloned population is less likely to survive on environmental change, especially the introduction of a new pathogen. Any species brought back to life may not walk the Earth again for any length of time – there could be a s ...
Genetic disorders - narragansett.k12.ri.us
... the disease strikes people between the ages of 40 and 70, and as many as 30,000 Americans have the disease at any given time This monogenic mutation is believed to make a defective protein that is toxic to motor nerve cells. A common first symptom is a painless weakness in a hand, foot, arm or l ...
... the disease strikes people between the ages of 40 and 70, and as many as 30,000 Americans have the disease at any given time This monogenic mutation is believed to make a defective protein that is toxic to motor nerve cells. A common first symptom is a painless weakness in a hand, foot, arm or l ...
DrMoran
... Long stretches of DNA make up genes. Genes make different things for our body. They are packaged up into chromosomes Chromosomes are like a big recipe box for our bodies and DNA is the recipe! ...
... Long stretches of DNA make up genes. Genes make different things for our body. They are packaged up into chromosomes Chromosomes are like a big recipe box for our bodies and DNA is the recipe! ...
Genetics Unit Overview
... Overview: Genetics is the oldest, yet fastest growing science today. For thousands of years, even before written word, man has been selectively breeding crops and animals for desired traits. This involved countless days, nights, months, and years of careful observation, study and hands on experiment ...
... Overview: Genetics is the oldest, yet fastest growing science today. For thousands of years, even before written word, man has been selectively breeding crops and animals for desired traits. This involved countless days, nights, months, and years of careful observation, study and hands on experiment ...
Practice Questions 1: Genetics
... 4. Base your answer to the question on the passage below and on your knowledge of biology. Better Rice The production of new types of food crops will help raise the quantity of food grown by farmers. Research papers released by the National Academy of Sciences announced the development of two new s ...
... 4. Base your answer to the question on the passage below and on your knowledge of biology. Better Rice The production of new types of food crops will help raise the quantity of food grown by farmers. Research papers released by the National Academy of Sciences announced the development of two new s ...
GENETICS EXAM 3 FALL 2004 Student Name
... b) Of those that were able to ligate to the vector, which, if any, would you definitely be able to separate away from the vector by cutting with SfoI? ...
... b) Of those that were able to ligate to the vector, which, if any, would you definitely be able to separate away from the vector by cutting with SfoI? ...
The Stages of Meiosis
... identical because they are the result of mitosis. They are all descended from a single cell – a zygote. A zygote is formed when two haploid gametes fuse. These gametes are genetically unique because, unlike somatic cells, they were formed by a special form of cell division called meiosis. ...
... identical because they are the result of mitosis. They are all descended from a single cell – a zygote. A zygote is formed when two haploid gametes fuse. These gametes are genetically unique because, unlike somatic cells, they were formed by a special form of cell division called meiosis. ...
Genetic mechanisms
... Genetic structure/function – of DNA, chromosomes, genes and genomes; also including size and arrangement both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Mechanisms of replication, transcription and translation including enzymes for proks., euks. and viruses. ...
... Genetic structure/function – of DNA, chromosomes, genes and genomes; also including size and arrangement both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Mechanisms of replication, transcription and translation including enzymes for proks., euks. and viruses. ...
Heredity Influences on Development Chapter 3
... Alleles: human characteristics that are influenced by one pair of genes (one from the mother, one from the father). 1) Dominant-recessive: a pattern of inheritance in which one allele dominates another so that its phenotype is only expressed 2) Dominant: a powerful gene expressed phenotypically mask ...
... Alleles: human characteristics that are influenced by one pair of genes (one from the mother, one from the father). 1) Dominant-recessive: a pattern of inheritance in which one allele dominates another so that its phenotype is only expressed 2) Dominant: a powerful gene expressed phenotypically mask ...
Chapter 3 Section 1
... Involved in what type of reproduction Type of cells which undergo the process Reason for this process to occur Stages involves (list all of the stages) Number of cells produced Number of chromosomes in the resulting cells How does resulting cell compare to the parent cell genetically? ...
... Involved in what type of reproduction Type of cells which undergo the process Reason for this process to occur Stages involves (list all of the stages) Number of cells produced Number of chromosomes in the resulting cells How does resulting cell compare to the parent cell genetically? ...
Word file
... Montreal, Canada, 1958, the map was sparse, but rich in visual impact. This remarkable exhibit showed the linkage groups of the mouse genome as they were known at the time, with each locus on the exhibit represented by live mutant mice (in their cages) and corresponding to the known genetic markers ...
... Montreal, Canada, 1958, the map was sparse, but rich in visual impact. This remarkable exhibit showed the linkage groups of the mouse genome as they were known at the time, with each locus on the exhibit represented by live mutant mice (in their cages) and corresponding to the known genetic markers ...
Biotechnology
... Classical Biotech Follows ancient Makes wide spread use of methods from ancient, especially fermentation Methods adapted to industrial productionFollows ancient Makes wide spread use of methods from ancient, especially fermentation Methods adapted to industrial production ...
... Classical Biotech Follows ancient Makes wide spread use of methods from ancient, especially fermentation Methods adapted to industrial productionFollows ancient Makes wide spread use of methods from ancient, especially fermentation Methods adapted to industrial production ...
Genetics
... • Medical or Criminal Forensicsbecause every organism has its own unique DNA… • DNA fingerprinting or profiling is done where the test sample is matched with actual DNA of humans and other organisms • This has been used as evidence in many criminal cases. ...
... • Medical or Criminal Forensicsbecause every organism has its own unique DNA… • DNA fingerprinting or profiling is done where the test sample is matched with actual DNA of humans and other organisms • This has been used as evidence in many criminal cases. ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.