Beanbag Population Genetics
... a) Using the tweezers, and without looking at the beans, one student draws 5 beans from the 50R/50W container, where the gene frequency of the red beans is 0.5. The 5 beans are placed in the student=s empty container. Count the number of red beans in the container, thereby determining the gene frequ ...
... a) Using the tweezers, and without looking at the beans, one student draws 5 beans from the 50R/50W container, where the gene frequency of the red beans is 0.5. The 5 beans are placed in the student=s empty container. Count the number of red beans in the container, thereby determining the gene frequ ...
Plant Hormones
... the tip is separated from the shoot by a piece of impermeable material (such as a block of mica), then phototropism did not occur. 7. What is the major difference in the agar material versus the mica material? ...
... the tip is separated from the shoot by a piece of impermeable material (such as a block of mica), then phototropism did not occur. 7. What is the major difference in the agar material versus the mica material? ...
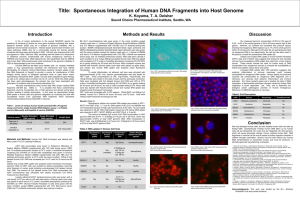
Title: Spontaneous Integration of Human DNA Fragments into Host
... A trio of recent publications in the journal NEURON reports the presence of hundreds of diverse de novo gene mutations indicating that autism spectrum disorder (ASD) may be a disease of genomic instability, with a significant environmental component. Altered double strand break formation and repair ...
... A trio of recent publications in the journal NEURON reports the presence of hundreds of diverse de novo gene mutations indicating that autism spectrum disorder (ASD) may be a disease of genomic instability, with a significant environmental component. Altered double strand break formation and repair ...
Genetic Testing of Inherited Cardiac Disorders
... Interpretation of genetic test results There are several possible outcomes of the initial genetic testing performed in the affected member of a family. Firstly, a potential disease-causing mutation may be identified. With recent technological advances that enable high-throughput sequencing of multip ...
... Interpretation of genetic test results There are several possible outcomes of the initial genetic testing performed in the affected member of a family. Firstly, a potential disease-causing mutation may be identified. With recent technological advances that enable high-throughput sequencing of multip ...
Law of Ind. Assortment
... 1. Traits are controlled by factors: Alternate forms of genes called alleles. 2. Some factors are dominant and some recessive: G or g 3. Law of Dominance Dominant vs Rec In humans ...
... 1. Traits are controlled by factors: Alternate forms of genes called alleles. 2. Some factors are dominant and some recessive: G or g 3. Law of Dominance Dominant vs Rec In humans ...
Genetics PowerPoint
... Pea plants are normally self-pollinated, but can be easily cross-pollinated by the plant breeder. Therefore, the breeder can control which traits are crossed. ...
... Pea plants are normally self-pollinated, but can be easily cross-pollinated by the plant breeder. Therefore, the breeder can control which traits are crossed. ...
No Slide Title
... • Try homologous candidates from other species • Examine all Open Reading Frames (ORFs) within a QTL confidence interval – Expression array analysis of these ORFs – Lack of tissue-specific expression does not exclude a gene ...
... • Try homologous candidates from other species • Examine all Open Reading Frames (ORFs) within a QTL confidence interval – Expression array analysis of these ORFs – Lack of tissue-specific expression does not exclude a gene ...
Question How does DNA control a cell?By controlling Protein
... Adds nucleotides to 3` end of growing RNA strand Enzyme moves 5` 3` (of RNA strand) Rate is about 60 nucleotides per second ...
... Adds nucleotides to 3` end of growing RNA strand Enzyme moves 5` 3` (of RNA strand) Rate is about 60 nucleotides per second ...
Document
... The globin gene family = two clusters of loci coding for component subunits of hemoglobin: α-like cluster on chromosome 16 includes 3 functional loci β-like cluster on chromosome 11 includes 5 functional loci • Each locus codes for a polypeptide (protein subunit) of hemoglobin. • Two of the protein ...
... The globin gene family = two clusters of loci coding for component subunits of hemoglobin: α-like cluster on chromosome 16 includes 3 functional loci β-like cluster on chromosome 11 includes 5 functional loci • Each locus codes for a polypeptide (protein subunit) of hemoglobin. • Two of the protein ...
Study Guides
... Main Idea: Gene flow is the movement of alleles between populations. Fill in the word or phrase that best completes each statement. ...
... Main Idea: Gene flow is the movement of alleles between populations. Fill in the word or phrase that best completes each statement. ...
Bioreactors and transgenic animals
... The new life form will depend for its ability to replicate itself and metabolize on the molecular machinery of the cell into which it has been injected, and in that sense it will not be a wholly synthetic life form. Pat Mooney, director of a Canadian bioethics organization, ETC Group: "Governments, ...
... The new life form will depend for its ability to replicate itself and metabolize on the molecular machinery of the cell into which it has been injected, and in that sense it will not be a wholly synthetic life form. Pat Mooney, director of a Canadian bioethics organization, ETC Group: "Governments, ...
Chromosomal rearrangements in Salmonella spp. s2-2
... of replication). Additive genetic changes (due to lateral transfer resulting in insertion of non-homologous DNA) have resulted h " pathogenicity islands" containing blocks of DNA which provide new genes to specific strains, thus driving rapid evolution of new traits. ...
... of replication). Additive genetic changes (due to lateral transfer resulting in insertion of non-homologous DNA) have resulted h " pathogenicity islands" containing blocks of DNA which provide new genes to specific strains, thus driving rapid evolution of new traits. ...
FEMS ML 00 CODH cooF
... cally related to the CooS of Methanococcus and Archaeoglobus. cooS genes from other methanogenic archaea, such as M. thermoautotrophicum and M. soehngenii, cluster together and are distinct from the cooS genes from anaerobic bacteria and Methanococcus/Archaeoglobus. A functionally essential cysteine ...
... cally related to the CooS of Methanococcus and Archaeoglobus. cooS genes from other methanogenic archaea, such as M. thermoautotrophicum and M. soehngenii, cluster together and are distinct from the cooS genes from anaerobic bacteria and Methanococcus/Archaeoglobus. A functionally essential cysteine ...
Recombinant "Paper" Plasmid Background:
... bacterium, a process called transformation. Plasmids can also incorporate into their DNA sequence pieces of DNA from different organisms. Plasmids that incorporate new DNA are called recombinant plasmida Recombinant plasmids are used In biotechnology to carry DNA that codes for substances, such as h ...
... bacterium, a process called transformation. Plasmids can also incorporate into their DNA sequence pieces of DNA from different organisms. Plasmids that incorporate new DNA are called recombinant plasmida Recombinant plasmids are used In biotechnology to carry DNA that codes for substances, such as h ...
The Evolutionary Role of Wildfire in the Northern Rockies and
... hundreds of miles from its tree of origin (Erdtman, 1954) in its migration. Seed, too, can be an effective vehicle for carrying genes far from their source (further discussed later). However, distance between populations is usually an effective barrier to migration. Wright (1962, p. 26) concludes th ...
... hundreds of miles from its tree of origin (Erdtman, 1954) in its migration. Seed, too, can be an effective vehicle for carrying genes far from their source (further discussed later). However, distance between populations is usually an effective barrier to migration. Wright (1962, p. 26) concludes th ...
Biological Ontologies in Rice Databases. An Introduction to the
... the users to ask the following questions: find all mutant phenotypes evaluated for a trait ‘plant height’, and show which ones have a sequenced gene associated with it. If there is a sequenced gene, what is its (known/putative) molecular function and what biological process does it work in. In addit ...
... the users to ask the following questions: find all mutant phenotypes evaluated for a trait ‘plant height’, and show which ones have a sequenced gene associated with it. If there is a sequenced gene, what is its (known/putative) molecular function and what biological process does it work in. In addit ...
Document
... that is 4,700 bp in length. In an actual experiment, a more thorough lod analysis would be conducted to determine if linkage is considered likely. If so, the 4,700 bp RFLP may either contain the gene that confers herbicide resistance or, as is more likely, the two may be linked. If the 4,700 bp RFLP ...
... that is 4,700 bp in length. In an actual experiment, a more thorough lod analysis would be conducted to determine if linkage is considered likely. If so, the 4,700 bp RFLP may either contain the gene that confers herbicide resistance or, as is more likely, the two may be linked. If the 4,700 bp RFLP ...
S1.An RFLP marker is located 1 million bp away from a gene of
... that is 4,700 bp in length. In an actual experiment, a more thorough lod analysis would be conducted to determine if linkage is considered likely. If so, the 4,700 bp RFLP may either contain the gene that confers herbicide resistance or, as is more likely, the two may be linked. If the 4,700 bp RFLP ...
... that is 4,700 bp in length. In an actual experiment, a more thorough lod analysis would be conducted to determine if linkage is considered likely. If so, the 4,700 bp RFLP may either contain the gene that confers herbicide resistance or, as is more likely, the two may be linked. If the 4,700 bp RFLP ...
Genetics Review PowerPoint
... genetic disorders, which of the following would be a concern? A. different chromosomes of different lengths B. two X chromosomes C. twenty-three pairs of chromosomes D. three chromosomes in any one set ...
... genetic disorders, which of the following would be a concern? A. different chromosomes of different lengths B. two X chromosomes C. twenty-three pairs of chromosomes D. three chromosomes in any one set ...
3.2 Probability Student pages
... 1. A gene is a section of DNA, with many bases that code for a protein. This results in a trait. 2. Traits are controlled by genes. Genes are found on chromosomes and have a genetic code for a protein. The position of the gene on the chromosome is called the locus. 3. Different versions of a gene fo ...
... 1. A gene is a section of DNA, with many bases that code for a protein. This results in a trait. 2. Traits are controlled by genes. Genes are found on chromosomes and have a genetic code for a protein. The position of the gene on the chromosome is called the locus. 3. Different versions of a gene fo ...
Junk DNA - repetitive sequences
... From the immediate point of view, transposons have no necessary function in the cell - called, junk DNA"; or "selfish DNA", as transposons propagate on behalf of the cellular resources. On a wider scale, the motility of the retrotransposable elements can be important for genome plasticity. Occasiona ...
... From the immediate point of view, transposons have no necessary function in the cell - called, junk DNA"; or "selfish DNA", as transposons propagate on behalf of the cellular resources. On a wider scale, the motility of the retrotransposable elements can be important for genome plasticity. Occasiona ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.