Chapter 20
... progeny than others, and the rate at which they do so is affected by phenotype and behavior – Artificial selection (human influenced) – Natural selection ...
... progeny than others, and the rate at which they do so is affected by phenotype and behavior – Artificial selection (human influenced) – Natural selection ...
Map Quest: New Techniques Reveal How the
... Even as they dig deeper into the mechanisms at play in Burkitt lymphoma, Dr. Basu and his collaborators continue to refine their understanding of the various mechanisms by which lymphocytes operate within the immune system to monitor progression of cancer and onset of many other diseases. In Novembe ...
... Even as they dig deeper into the mechanisms at play in Burkitt lymphoma, Dr. Basu and his collaborators continue to refine their understanding of the various mechanisms by which lymphocytes operate within the immune system to monitor progression of cancer and onset of many other diseases. In Novembe ...
Ecophysiology of Thioploca ingrica as revealed by the
... employed whole-genome multiple displacement amplification to obtain sufficient amounts of DNA for sequencing from single bacterial filaments that are expected to consist of clonal cells. The singlefilament approach may be effective for coping with genetic diversities among the morphologically indist ...
... employed whole-genome multiple displacement amplification to obtain sufficient amounts of DNA for sequencing from single bacterial filaments that are expected to consist of clonal cells. The singlefilament approach may be effective for coping with genetic diversities among the morphologically indist ...
A Genetic Link Between an mRNA-Specific Translational
... Isolation and manipulation of P E T 1 2 3 The PET123 gene was cloned from a yeast genomic bank in the vector YCp50 (ROSEet al. 1987), selecting for complementation of the Pet"' allele pet123-1. T w o independent clones were obtained, oneof which was within the other.A 1.9-kb XhoIBamHI fragment (this ...
... Isolation and manipulation of P E T 1 2 3 The PET123 gene was cloned from a yeast genomic bank in the vector YCp50 (ROSEet al. 1987), selecting for complementation of the Pet"' allele pet123-1. T w o independent clones were obtained, oneof which was within the other.A 1.9-kb XhoIBamHI fragment (this ...
as a PDF
... Following this breakage, it is assumed that dissociation of the chains would occur over the length of the gene. A cycle of 6 steps is then postulated for the matching of each slave in turn against the master, namely: (1) breakage of the complementary chain of the slave at the terminus (non-operator) ...
... Following this breakage, it is assumed that dissociation of the chains would occur over the length of the gene. A cycle of 6 steps is then postulated for the matching of each slave in turn against the master, namely: (1) breakage of the complementary chain of the slave at the terminus (non-operator) ...
Numbering the hairs on our heads: The shared
... (GWA) studies. GWA studies (e.g., ref. 12) are powerful when a causal allele is common enough to be present in multiple individuals in a sample and penetrance is as low as 10%, enabling alleles with small ORs of 1.1 or so to be detected, if sample size is very large. Common alleles, however, almost ...
... (GWA) studies. GWA studies (e.g., ref. 12) are powerful when a causal allele is common enough to be present in multiple individuals in a sample and penetrance is as low as 10%, enabling alleles with small ORs of 1.1 or so to be detected, if sample size is very large. Common alleles, however, almost ...
Familial Colorectal Cancers: Hereditary Non-Polyposis
... this test is positive (usually done on the affected family member's tumor) for a genetic abnormality, other family members at risk can then be tested for the same abnormality. If no abnormality is detected in the family member's tumor, then testing other family members would not be informative. Howe ...
... this test is positive (usually done on the affected family member's tumor) for a genetic abnormality, other family members at risk can then be tested for the same abnormality. If no abnormality is detected in the family member's tumor, then testing other family members would not be informative. Howe ...
Evolution 3
... In Mendelian Inheritance alleles are shuffled each generation into new bodies in a way similar to which cards are shuffled into hands in different rounds of a card game. The process of Mendelian Inheritance preserves genetic diversity from one generation to the next. A recessive allele may not be vi ...
... In Mendelian Inheritance alleles are shuffled each generation into new bodies in a way similar to which cards are shuffled into hands in different rounds of a card game. The process of Mendelian Inheritance preserves genetic diversity from one generation to the next. A recessive allele may not be vi ...
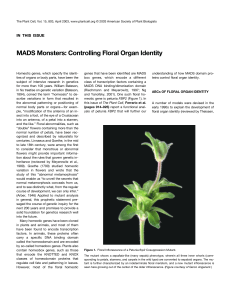
MADS Monsters: Controlling Floral Organ Identity
... 1894), coined the term “homeosis” to describe variations in form that resulted in the abnormal patterning or positioning of normal body parts or organs—for example, “modification of the antenna of an insect into a foot, of the eye of a Crustacean into an antenna, of a petal into a stamen, and the li ...
... 1894), coined the term “homeosis” to describe variations in form that resulted in the abnormal patterning or positioning of normal body parts or organs—for example, “modification of the antenna of an insect into a foot, of the eye of a Crustacean into an antenna, of a petal into a stamen, and the li ...
Programming and Problem Solving with Java: Chapter 14
... 3. Determine the fitness of each chromosome. 4. Apply crossover and mutation to selected chromosomes from the current generation to generate a new population of chromosomes (the next generation). 5. Return to step 2. ...
... 3. Determine the fitness of each chromosome. 4. Apply crossover and mutation to selected chromosomes from the current generation to generate a new population of chromosomes (the next generation). 5. Return to step 2. ...
Transposons ※ Transposons are DNA elements that can hop, or
... 2. Transposase bound at one end cuts the DNA at the other end and vice versa to leave 3’ OH ends at each end of transposon. 3. These activated 3’ OH ends attack the phosphodiester bond on the other strand, forming 3’-5’ phosphodiester hairpins. This cuts the transposon out of the donor DNA. 4. When ...
... 2. Transposase bound at one end cuts the DNA at the other end and vice versa to leave 3’ OH ends at each end of transposon. 3. These activated 3’ OH ends attack the phosphodiester bond on the other strand, forming 3’-5’ phosphodiester hairpins. This cuts the transposon out of the donor DNA. 4. When ...
CHEM642-14 Powerpoint
... serve as a probe that can be readily detected. The base on the nucleoside triphosphate shown is an analog of thymine in which the methyl group on T has been replaced by a spacer arm linked to the plant steroid digoxigenin. To visualize the probe, the digoxigenin is detected by a specific antibody co ...
... serve as a probe that can be readily detected. The base on the nucleoside triphosphate shown is an analog of thymine in which the methyl group on T has been replaced by a spacer arm linked to the plant steroid digoxigenin. To visualize the probe, the digoxigenin is detected by a specific antibody co ...
Evolution of genetic code through isologous diversification of
... metabolic reaction dynamics). Through interaction between organisms, the difference in phenotypic dynamics are amplified and the phenotype states tend to be grouped into two (or more) types. The dynamical systems mechanism for such differentiation was first discussed as clustering [13], and then ext ...
... metabolic reaction dynamics). Through interaction between organisms, the difference in phenotypic dynamics are amplified and the phenotype states tend to be grouped into two (or more) types. The dynamical systems mechanism for such differentiation was first discussed as clustering [13], and then ext ...
Genes - Dallas ISD
... Alleles for different traits are sorted independently of each other. All combinations of alleles are distributed to gametes with equal ...
... Alleles for different traits are sorted independently of each other. All combinations of alleles are distributed to gametes with equal ...
Possibilities and Limitations of Genetic Engineering
... such as tolerance to abiotic and biotic stresses, forage quality, and herbicide resistance. Alfalfa is also being engineered to produce novel compounds for industrial and diagnostic purposes. This research will likely lead to the production of improved cultivars, as well as new uses for alfalfa. INT ...
... such as tolerance to abiotic and biotic stresses, forage quality, and herbicide resistance. Alfalfa is also being engineered to produce novel compounds for industrial and diagnostic purposes. This research will likely lead to the production of improved cultivars, as well as new uses for alfalfa. INT ...
Mutations in human pathology - diss.fu
... exon1390. When a mutation affects the splice donor site, this results in skipping of the upstream exon1393. Some nonsense mutations have also been reported to induce exon skipping1388. Sometimes, mutations can cause abnormal RNA splicing by activation of cryptic splice sites: a sequence which normal ...
... exon1390. When a mutation affects the splice donor site, this results in skipping of the upstream exon1393. Some nonsense mutations have also been reported to induce exon skipping1388. Sometimes, mutations can cause abnormal RNA splicing by activation of cryptic splice sites: a sequence which normal ...
Appendix_1_SimpleNomenclature(plain)
... region of prokaryotes. They are transcribed into an RNA message by RNA polymerase then interpreted by ribosomes that assemble particular amino acids into a polypeptide strand (also known as a protein) based on the sequence of nucleotides. In a cell, proteins can act as enzymes, structural features, ...
... region of prokaryotes. They are transcribed into an RNA message by RNA polymerase then interpreted by ribosomes that assemble particular amino acids into a polypeptide strand (also known as a protein) based on the sequence of nucleotides. In a cell, proteins can act as enzymes, structural features, ...
Chapter 4 The role of mutation in evolution
... At one level it would appear that mutations are mistakes. The elaborate machinery that cells use to copy their DNA, to proofread and correct replication errors, and to assure that the chromosomes divide properly into daughter cells suggests that cells are doing everything in their power to prevent m ...
... At one level it would appear that mutations are mistakes. The elaborate machinery that cells use to copy their DNA, to proofread and correct replication errors, and to assure that the chromosomes divide properly into daughter cells suggests that cells are doing everything in their power to prevent m ...
TEL1, a Gene Involved in Controlling Telomere Length in S
... cycle in response to DNA damage or incompletely replicated DNA (AI-Khodairy and Carr, 1992; Jimenez et al., 1992; Kato and Ogawa, 1994; Weinert et al., 1994). In addition, a yeast chromosome that loses a telomere causes a temporary R A D 9 - d e p e n d e n t cell cycle arrest (Sandell ...
... cycle in response to DNA damage or incompletely replicated DNA (AI-Khodairy and Carr, 1992; Jimenez et al., 1992; Kato and Ogawa, 1994; Weinert et al., 1994). In addition, a yeast chromosome that loses a telomere causes a temporary R A D 9 - d e p e n d e n t cell cycle arrest (Sandell ...
Introduction to Genetic Algorithms
... through the juxtaposition of short, low-order, highperformance schemata, called the building blocks ...
... through the juxtaposition of short, low-order, highperformance schemata, called the building blocks ...
Body Axis Determination in Birds and Mammals
... Segment identity controlled by segment identity (aka homeotic, aka selector) genes. Discovered through homeotic mutations. This is a mutation that causes the transformation of one structure to another homologous structure. (Homologs have evolutionarily related ancestry—both derived from a common anc ...
... Segment identity controlled by segment identity (aka homeotic, aka selector) genes. Discovered through homeotic mutations. This is a mutation that causes the transformation of one structure to another homologous structure. (Homologs have evolutionarily related ancestry—both derived from a common anc ...
Lecture#18 - Chromosome Rearrangements
... They involve breaks in the DNA duplex -- both strands -- followed by the rejoining of the broken ends. ...
... They involve breaks in the DNA duplex -- both strands -- followed by the rejoining of the broken ends. ...
Lecture
... them, as do most other retroviruses, and helper T cells are vitally important in defending us against infection. Second, the provirus tends to persist in a latent state in the chromosomes of an infected cell without producing virus until it is activated by an unknown rare event; this ability to hide ...
... them, as do most other retroviruses, and helper T cells are vitally important in defending us against infection. Second, the provirus tends to persist in a latent state in the chromosomes of an infected cell without producing virus until it is activated by an unknown rare event; this ability to hide ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.