Figure 2 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence
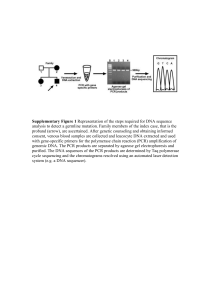
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
Evolution by natural selection - BioGeoWiki-4ESO
... Example of natural selection leading to speciation. Can no longer ...
... Example of natural selection leading to speciation. Can no longer ...
HGT
... Why they are interesting? • Bacteria can steal a beneficial gene that arose in another cell instead of waiting for it to evolve, e.g. o Antibiotic Resistance o Pathogenecity ...
... Why they are interesting? • Bacteria can steal a beneficial gene that arose in another cell instead of waiting for it to evolve, e.g. o Antibiotic Resistance o Pathogenecity ...
What is a Designer Baby?
... resulting offspring will have. Essentially it is a term used by journalists, not scientists. A more realistic term would be “Selected Baby”. It is currently not attainable to insert genes into embryos in hopes of desired characteristic traits or physical features, however advanced technologies can b ...
... resulting offspring will have. Essentially it is a term used by journalists, not scientists. A more realistic term would be “Selected Baby”. It is currently not attainable to insert genes into embryos in hopes of desired characteristic traits or physical features, however advanced technologies can b ...
Apple Molecular Biology: Animation 2
... A plasmid is a small circular strand of chromosome, and is found in bacteria. Generally, they include some region of DNA that confers antibiotic resistance so any organism containing the plasmid can be selected on a growth media containing the appropriate antibiotic. Scientists have learned how to m ...
... A plasmid is a small circular strand of chromosome, and is found in bacteria. Generally, they include some region of DNA that confers antibiotic resistance so any organism containing the plasmid can be selected on a growth media containing the appropriate antibiotic. Scientists have learned how to m ...
Adapted
... Genetic Transformation of Plants: Methods and Approaches to Develop Transgenic plants ...
... Genetic Transformation of Plants: Methods and Approaches to Develop Transgenic plants ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... • Genetic engineering, engineering recombinant DNA technology, genetic modification/manipulation (GM) and gene splicing are terms that are applied to the direct manipulation of an organisms genes. • Recombinant DNA is a form of artificial DNA which is engineered through the combination or insertion ...
... • Genetic engineering, engineering recombinant DNA technology, genetic modification/manipulation (GM) and gene splicing are terms that are applied to the direct manipulation of an organisms genes. • Recombinant DNA is a form of artificial DNA which is engineered through the combination or insertion ...
Examples of Gene flow File
... Gene flow is the exchange of genes between two separate populations. This is most often accomplished when animals or spores from plants migrate to a new area. Any time a gene is introduced into a population where that gene once did not exist, gene flow has occurred. ...
... Gene flow is the exchange of genes between two separate populations. This is most often accomplished when animals or spores from plants migrate to a new area. Any time a gene is introduced into a population where that gene once did not exist, gene flow has occurred. ...
Adaption Variation and Natural Selection
... passed on when BOTH parents have the trait or are carriers for the trait The blood no longer flows easily through the body. Many times the blood starts to clot in the veins and arteries – not allowing regular blood flow to the organs in the body! ...
... passed on when BOTH parents have the trait or are carriers for the trait The blood no longer flows easily through the body. Many times the blood starts to clot in the veins and arteries – not allowing regular blood flow to the organs in the body! ...
DNA And Traits
... On top of that, it is random which egg and sperm come together to form the zygote. When you look at it this way, it’s not at all surprising that some people look different from their family members. This is true for all sexually reproducing forms of life. For example, purebred dogs may look much lik ...
... On top of that, it is random which egg and sperm come together to form the zygote. When you look at it this way, it’s not at all surprising that some people look different from their family members. This is true for all sexually reproducing forms of life. For example, purebred dogs may look much lik ...
File - Mr. Lambdin`s Biology
... organisms inserted into their DNA • Bacteria = human insulin producers • Animals = lab rats with human immune systems, bovine growth hormone • Plants = plants that have genes that make them resistant to insects, herbicides, and drought ...
... organisms inserted into their DNA • Bacteria = human insulin producers • Animals = lab rats with human immune systems, bovine growth hormone • Plants = plants that have genes that make them resistant to insects, herbicides, and drought ...
Lecture 3: More Transmission Genetics
... both about equally affected (indicates autosomal inheritance) ...
... both about equally affected (indicates autosomal inheritance) ...
The Transfer of Genetic Characteristics
... The genes that control a trait have two forms called alleles. Each trait in a human such as the type of hair, is controlled by two alleles, the dominant allele and the recessive allele. ...
... The genes that control a trait have two forms called alleles. Each trait in a human such as the type of hair, is controlled by two alleles, the dominant allele and the recessive allele. ...
Heredity and Behavior
... Dominant Gene expressed when paired genes are different Recessive Gene one that is masked when paired genes are different Detached earlobe (D) Attached (R) ...
... Dominant Gene expressed when paired genes are different Recessive Gene one that is masked when paired genes are different Detached earlobe (D) Attached (R) ...
GENETIC MODIFICATION and pGLO
... spiders with goats to produce large quantities of spider-silk in lactating females. ...
... spiders with goats to produce large quantities of spider-silk in lactating females. ...
Common Misconceptions in Genetics
... In fact, Gregor Mendel, the father of genetics, first discovered how genes function during his study on pea plants! Genetically modified food crops differ from regular food crops because they have genes from other organisms introduced into their genome. Specifically, the most common modifications ar ...
... In fact, Gregor Mendel, the father of genetics, first discovered how genes function during his study on pea plants! Genetically modified food crops differ from regular food crops because they have genes from other organisms introduced into their genome. Specifically, the most common modifications ar ...
Genetics Vocabulary Answers The offspring of organisms often grow
... The offspring of organisms often grow up to look like one or both of their parents. This is because offspring inherit information from their parents that directs their development. ...
... The offspring of organisms often grow up to look like one or both of their parents. This is because offspring inherit information from their parents that directs their development. ...
Why Should Our Community Care?
... “bio-economy” owned by, and for the benefit of, the Global North Patents are being sought on: ...
... “bio-economy” owned by, and for the benefit of, the Global North Patents are being sought on: ...
Tuesday5/10
... reduces the error rate to 1/1 billion base pairs. Cells can repair many errors; Humans have 130 known DNA repair enzymes! ...
... reduces the error rate to 1/1 billion base pairs. Cells can repair many errors; Humans have 130 known DNA repair enzymes! ...
Module_2_Key_Facts
... Variation in a species provides a significant survival advantage. When environmental conditions change, it is more likely that there will be some individuals that are adapted to the changed conditions, and so the species will not be wiped out. Some species include both asexual and sexual reproductio ...
... Variation in a species provides a significant survival advantage. When environmental conditions change, it is more likely that there will be some individuals that are adapted to the changed conditions, and so the species will not be wiped out. Some species include both asexual and sexual reproductio ...
Genetic diversity for yield and its component traits in green gram
... S. S. GADAKH, A.M. DETHE, M.N. KATHALE AND N.S. KAHATE Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding College of Agriculture, Latur M.A.U., Parbhani, Maharashtra Received: 27-2-2013, Revised: 25-4-2013, Accepted: 15-5-2013 ABSTRACT Genetic diversity analysis is a powerful tool in quantifying the degree o ...
... S. S. GADAKH, A.M. DETHE, M.N. KATHALE AND N.S. KAHATE Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding College of Agriculture, Latur M.A.U., Parbhani, Maharashtra Received: 27-2-2013, Revised: 25-4-2013, Accepted: 15-5-2013 ABSTRACT Genetic diversity analysis is a powerful tool in quantifying the degree o ...
The Human Genome
... Pedigree Chart—shows relationships within a family; can be used to determine how a trait is passed from one generation to the next ...
... Pedigree Chart—shows relationships within a family; can be used to determine how a trait is passed from one generation to the next ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.























