Unicellular Organisms what are they? write down some key
... millions. They are on your skin, in the soil and even in water. Some are harmful and cause diseases yet others are beneficial to us. For example, dairy products such as buttermilk, cottage cheese and yogurt are produced by the action of microorganisms. ...
... millions. They are on your skin, in the soil and even in water. Some are harmful and cause diseases yet others are beneficial to us. For example, dairy products such as buttermilk, cottage cheese and yogurt are produced by the action of microorganisms. ...
Teacher`s Guide for “Heredity” CT State Standards National Science
... 1. Heredity is the passing of traits from parents to offspring. All genes are inherited in pairs. It is these genes that control the expression of traits in offspring. The song uses examples such as eye color, freckles, and tongue folding. 2. The song mentions “map it on your pedigree.” Pedig ...
... 1. Heredity is the passing of traits from parents to offspring. All genes are inherited in pairs. It is these genes that control the expression of traits in offspring. The song uses examples such as eye color, freckles, and tongue folding. 2. The song mentions “map it on your pedigree.” Pedig ...
slides
... • Recombinant DNA is injected into a fertilized embryo in a culture dish, before it starts dividing • As a result, all of the cells of the organism will have the genetic alteration present (whether it’s a plant or an animal). A bacterium, since it is a single cell, obviously just contains the alte ...
... • Recombinant DNA is injected into a fertilized embryo in a culture dish, before it starts dividing • As a result, all of the cells of the organism will have the genetic alteration present (whether it’s a plant or an animal). A bacterium, since it is a single cell, obviously just contains the alte ...
Final Jeopardy - Lindbergh School District
... The process of selecting a few organisms with desired traits to serve as parents of the next generation is called _____________________. ...
... The process of selecting a few organisms with desired traits to serve as parents of the next generation is called _____________________. ...
Modern Genetics Jeopardy
... The process of selecting a few organisms with desired traits to serve as parents of the next generation is called _____________________. ...
... The process of selecting a few organisms with desired traits to serve as parents of the next generation is called _____________________. ...
Mitosis
... Griffith - Used mice to see how a bacteria caused disease (transformation of harmless bacteria into disease causing ones) Avery - Destroyed all cell products but DNA to find what genes are made of Hershey and Chase - Radioactive viruses used to show DNA is molecule of heredity Chargraff - % of “A” = ...
... Griffith - Used mice to see how a bacteria caused disease (transformation of harmless bacteria into disease causing ones) Avery - Destroyed all cell products but DNA to find what genes are made of Hershey and Chase - Radioactive viruses used to show DNA is molecule of heredity Chargraff - % of “A” = ...
Population Genetics I.
... What if a few individuals- or even a single seed- founds a new population far outside the original range, or survives a catastrophe where all other populations of the species are lost? The new population will have greatly reduced genetic diversity compared to the larger ...
... What if a few individuals- or even a single seed- founds a new population far outside the original range, or survives a catastrophe where all other populations of the species are lost? The new population will have greatly reduced genetic diversity compared to the larger ...
Conservation and extinction
... Genetics. Cambridge Univ. Press • Conservation genetics is the application of genetics to preserve species as dynamic entities capable of coping with environmental change – Genetic management of small populations – Resolution of taxonomic uncertainties – Identifying and defining units of conservatio ...
... Genetics. Cambridge Univ. Press • Conservation genetics is the application of genetics to preserve species as dynamic entities capable of coping with environmental change – Genetic management of small populations – Resolution of taxonomic uncertainties – Identifying and defining units of conservatio ...
Conserved genetic modules in male gametes Patrícia Alexandra
... transfer ultimately to the zygote their unique totipotent potential, capable of giving rise to an entirely new organism. Despite the variety of mechanisms distinguishing germ cell differentiation and fertilization strategies in plants and animals, we expect that a defined conserved core set of genet ...
... transfer ultimately to the zygote their unique totipotent potential, capable of giving rise to an entirely new organism. Despite the variety of mechanisms distinguishing germ cell differentiation and fertilization strategies in plants and animals, we expect that a defined conserved core set of genet ...
Unit 4 Evolution Study Guide There are five driving forces of
... Genetic drift: change in allele frequencies because of chance events in small populations Gene flow: change in allele frequencies as genes move from one population to another Mutation: change in allele frequencies due to a random genetic change in an allele Natural Selection: process by which charac ...
... Genetic drift: change in allele frequencies because of chance events in small populations Gene flow: change in allele frequencies as genes move from one population to another Mutation: change in allele frequencies due to a random genetic change in an allele Natural Selection: process by which charac ...
host cell - Ken Cluck Music
... that relax the muscles to DNA and proteins. Nitrogen is not readily available in forms the body can use in the air like oxygen is. Animals get the nitrogen that they need when bacteria fix the nitrogen so plants can absorb it and animals eat the plants. ...
... that relax the muscles to DNA and proteins. Nitrogen is not readily available in forms the body can use in the air like oxygen is. Animals get the nitrogen that they need when bacteria fix the nitrogen so plants can absorb it and animals eat the plants. ...
Human Gene Editing
... In the study, Junjiu Huang, a genetics researcher at Sun Yat-sen University, injected the CRISPR/Cas9 complex into human embryos in order to repair a gene for Beta thalassaemia, a potentially fatal blood disorder that reduces the production of hemoglobin. The embryos, which were obtained from local ...
... In the study, Junjiu Huang, a genetics researcher at Sun Yat-sen University, injected the CRISPR/Cas9 complex into human embryos in order to repair a gene for Beta thalassaemia, a potentially fatal blood disorder that reduces the production of hemoglobin. The embryos, which were obtained from local ...
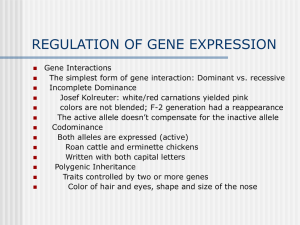
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION
... RNA polymerase binds to promotor, moves across to the genes, & produces mRNA. When cell runs out of the inducer, repressor binds to operator, and the operator is turned off. ...
... RNA polymerase binds to promotor, moves across to the genes, & produces mRNA. When cell runs out of the inducer, repressor binds to operator, and the operator is turned off. ...
What determines who we are?
... and one pair of sex chromosomes • Sex chromosomes control gender • Females have 2 X chromosomes and males have an X and a Y chromosome • Autosomes determine other traits ...
... and one pair of sex chromosomes • Sex chromosomes control gender • Females have 2 X chromosomes and males have an X and a Y chromosome • Autosomes determine other traits ...
Editor(s): Laura Hoopes | http://www.nature.com/scitable/topic/gene
... Next, we turn to the regulation of genes. Genes can't control an organism on their own; rather, they must interact with and respond to the organism's environment. Some genes are constitutive, or always "on," regardless of environmental conditions. Such genes are among the most important elements of ...
... Next, we turn to the regulation of genes. Genes can't control an organism on their own; rather, they must interact with and respond to the organism's environment. Some genes are constitutive, or always "on," regardless of environmental conditions. Such genes are among the most important elements of ...
CHS H Bio Final Exam Review Sheet
... 3. What are the 7 Linnaean taxonomic categories (in order) from the most inclusive (broadest) to the most exclusive (specific)? 4. What are the 3 domains used to classify all living organisms? 5. Molecular evidence has recently shown that which 2 domains are more closely related? 6. Why did prokaryo ...
... 3. What are the 7 Linnaean taxonomic categories (in order) from the most inclusive (broadest) to the most exclusive (specific)? 4. What are the 3 domains used to classify all living organisms? 5. Molecular evidence has recently shown that which 2 domains are more closely related? 6. Why did prokaryo ...
EOC Review Unit 7_Genetics
... What you should know: Genetic Engineering Genetic engineering is the process of replacing genes from one organism into another to make sure the organism expresses a trait. cloning, a copy of a gene or organism is produced. Gene therapy – insert a gene to help an organism produce new proteins S ...
... What you should know: Genetic Engineering Genetic engineering is the process of replacing genes from one organism into another to make sure the organism expresses a trait. cloning, a copy of a gene or organism is produced. Gene therapy – insert a gene to help an organism produce new proteins S ...
Pathogen induced genome instability
... •Specific host genes and most phage genes are packed into the same virion •Transduced bacterial genes are restricted to specific genes adjacent to the prophage insertion site. •In general transduction, host genes are randomly selected and almost any host gene can be transferred. ...
... •Specific host genes and most phage genes are packed into the same virion •Transduced bacterial genes are restricted to specific genes adjacent to the prophage insertion site. •In general transduction, host genes are randomly selected and almost any host gene can be transferred. ...
A1993KF42600001
... genetics unraveled abundant genetic polymorphisms in natural populations of micro-organisms, plants, animals, and humans. Ironically, however, this extensive genetic variation proved theoretically intractable. How much of it is adaptive and contributes to the fitness or organisms? Already during the ...
... genetics unraveled abundant genetic polymorphisms in natural populations of micro-organisms, plants, animals, and humans. Ironically, however, this extensive genetic variation proved theoretically intractable. How much of it is adaptive and contributes to the fitness or organisms? Already during the ...
Microbiology Exam II - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... d. Plasmids e. Sex pili 8. What was one of the first and most useful microscopic tests for classifying bacteria that is still important today? a. Gram stain b. Flagella stains c. Simple stains d. Negative stain for capsule e. Metachromatic granule stain 9. Which is NOT true of virus capsids? a. They ...
... d. Plasmids e. Sex pili 8. What was one of the first and most useful microscopic tests for classifying bacteria that is still important today? a. Gram stain b. Flagella stains c. Simple stains d. Negative stain for capsule e. Metachromatic granule stain 9. Which is NOT true of virus capsids? a. They ...
Question: How can viruses mutate if they`re not considered alive? Is
... of bacteria (i.e., competitive exclusion), but can they kill each other? Yes, bacteria do not play nice. They can excrete wastes that are harmful to other bacteria strains as well as release restriction enzymes that can cut up the DNA of its competitors. Source: Bacteria Fights to the Death Questio ...
... of bacteria (i.e., competitive exclusion), but can they kill each other? Yes, bacteria do not play nice. They can excrete wastes that are harmful to other bacteria strains as well as release restriction enzymes that can cut up the DNA of its competitors. Source: Bacteria Fights to the Death Questio ...
Using restriction enzymes, foreign genes can be added to an
... Restriction Enzymes: How is DNA Manipulated? Using restriction enzymes, foreign genes can be added to an existing organism (or an embryo). This organism has been genetically modified. Adding new genes can create plants that are more resistant to pests or be more tolerant to weather patterns, such as ...
... Restriction Enzymes: How is DNA Manipulated? Using restriction enzymes, foreign genes can be added to an existing organism (or an embryo). This organism has been genetically modified. Adding new genes can create plants that are more resistant to pests or be more tolerant to weather patterns, such as ...
Small Populations
... Chromosome – thread-like, gene carrying bodies in the cell nucleus. Chromosomes are composed primarily of DNA and proteins. DNA – (deoxyribonucleic acid) a large organic molecule that stores the genetic code. DNA is composed of sugars, phosphates and bases arranged in a double helix shaped structure ...
... Chromosome – thread-like, gene carrying bodies in the cell nucleus. Chromosomes are composed primarily of DNA and proteins. DNA – (deoxyribonucleic acid) a large organic molecule that stores the genetic code. DNA is composed of sugars, phosphates and bases arranged in a double helix shaped structure ...
geneflow - International Food Safety Consultancy
... > Wisconsin-Madison and the University of Minnesota-St. Paul, show that genes > from crops rapidly can take over those in related wild plants. The end > result, say the researchers, could be major changes in the genetic make-up > of wild plants, decreases in their population size and the permanent l ...
... > Wisconsin-Madison and the University of Minnesota-St. Paul, show that genes > from crops rapidly can take over those in related wild plants. The end > result, say the researchers, could be major changes in the genetic make-up > of wild plants, decreases in their population size and the permanent l ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.