Hereditary diseases of a man
... Nullisomy: nullisomics are those individuals, which lack a single pair of homologous chromosomes, so that the chromosome formula would be 2n-2, and not 2n-1-1, which would mean a double monosomic. E.R.Sears had isolated all the 21 nullisomics in wheat. Trisomy: trisomics are those organisms, which h ...
... Nullisomy: nullisomics are those individuals, which lack a single pair of homologous chromosomes, so that the chromosome formula would be 2n-2, and not 2n-1-1, which would mean a double monosomic. E.R.Sears had isolated all the 21 nullisomics in wheat. Trisomy: trisomics are those organisms, which h ...
Document
... 9. Why does each parent organism in the F1 generation have four alleles listed in Figure 5.5? _______________________________________________________________ 10. Suppose an organism had the genotype AABb. What two types of gametes could result from this allele combination? __________________________ ...
... 9. Why does each parent organism in the F1 generation have four alleles listed in Figure 5.5? _______________________________________________________________ 10. Suppose an organism had the genotype AABb. What two types of gametes could result from this allele combination? __________________________ ...
2015 JUNIOR GENETICS EASY 4455 (easy) HIH1040-1/ES94
... A: An abnormal condition that an animal possesses at birth ...
... A: An abnormal condition that an animal possesses at birth ...
Lesson Plan - Dominant Recessive Sampling Basic Model
... This is a simple system model that demonstrates passing on a recessive allele to one’s offspring. Genotypes from parents are calculated via random numbers, which consequently determine the expression (or lack thereof) of the recessive allele in their kid. If, by random chance, both parents pass on t ...
... This is a simple system model that demonstrates passing on a recessive allele to one’s offspring. Genotypes from parents are calculated via random numbers, which consequently determine the expression (or lack thereof) of the recessive allele in their kid. If, by random chance, both parents pass on t ...
PDF Links - Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences
... polymorphism in the Italian Jersey breed and to verify its effect on milk production traits. ...
... polymorphism in the Italian Jersey breed and to verify its effect on milk production traits. ...
Jeopardy - Mahtomedi Middle School
... Perry the Platypus met Pinky the Platypus at the park. Perry is homozygous for his teal-green color. Pinky is heterozygous for her pink color. What are the genotypes of the parents? ...
... Perry the Platypus met Pinky the Platypus at the park. Perry is homozygous for his teal-green color. Pinky is heterozygous for her pink color. What are the genotypes of the parents? ...
MCB317 Topic 10, part 4, A Story of Txn Sp14
... Which, if any encode txn factors? Secondary screen to identify possible txn factors ...
... Which, if any encode txn factors? Secondary screen to identify possible txn factors ...
Text S4.
... Next, if parameter a 0, then following YRI mixture, there are a generations of random mixture between the admixed individuals only. This can roughly be thought of as simulating genetic drift, since admixture. This procedure is repeated to create the genomes of 20 admixed individuals and pairs of h ...
... Next, if parameter a 0, then following YRI mixture, there are a generations of random mixture between the admixed individuals only. This can roughly be thought of as simulating genetic drift, since admixture. This procedure is repeated to create the genomes of 20 admixed individuals and pairs of h ...
Information entropy as an anthropomorphic concept
... Let b and c be two distinct populations of not homogeneous members. The members of both populations are of the same kind; their characteristics can be described by a vector V of v variables that are valid for all members. It is clear that if the diversity of b with respect to V is higher than the di ...
... Let b and c be two distinct populations of not homogeneous members. The members of both populations are of the same kind; their characteristics can be described by a vector V of v variables that are valid for all members. It is clear that if the diversity of b with respect to V is higher than the di ...
Research Project Final Report
... the second parent. These lines have been used to make a genetic map that will inform future studies of quantitative variation in seed bleaching under field conditions. Besides this ‘open’ approach to gene identification, we have studied variation in two candidate genes, either or both of which may i ...
... the second parent. These lines have been used to make a genetic map that will inform future studies of quantitative variation in seed bleaching under field conditions. Besides this ‘open’ approach to gene identification, we have studied variation in two candidate genes, either or both of which may i ...
Jeopardy - Mahtomedi Middle School
... Perry the Platypus met Pinky the Platypus at the park. Perry is homozygous for his teal-green color. Pinky is heterozygous for her pink color. What are the genotypes of the parents? ...
... Perry the Platypus met Pinky the Platypus at the park. Perry is homozygous for his teal-green color. Pinky is heterozygous for her pink color. What are the genotypes of the parents? ...
Conspecific versus heterospecific gene exchange between
... gene exchange between populations of Darwin’s finches Peter R. Grant* and B. Rosemary Grant Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544, USA This study addresses the extent and consequences of gene exchange between populations of Darwin’s finches. Four s ...
... gene exchange between populations of Darwin’s finches Peter R. Grant* and B. Rosemary Grant Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544, USA This study addresses the extent and consequences of gene exchange between populations of Darwin’s finches. Four s ...
Supernumerary teeth (hyperdontia)
... The size of both the teeth and the jaws is influenced by genetic and environmental factors and considerable variation occurs. Studies of twins have shown that for the teeth, at least, genetic factors account for a large part of this variation. The terms 'macrodontia' and 'microdontia' are used to de ...
... The size of both the teeth and the jaws is influenced by genetic and environmental factors and considerable variation occurs. Studies of twins have shown that for the teeth, at least, genetic factors account for a large part of this variation. The terms 'macrodontia' and 'microdontia' are used to de ...
CHAPTER 3 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... populations dies out Eliminates gene flow between the remaining distant populations The other populations can become reproductively isolated. ...
... populations dies out Eliminates gene flow between the remaining distant populations The other populations can become reproductively isolated. ...
Complex Inheritance - Incomplete Dominance and Codominance
... 1. Many genetic traits have a stronger dominant allele and a weaker recessive allele. This is known as complete dominance. What is a trait, however, is NOT completely dominant and/or recessive. Summarize the difference between incomplete dominance and codominance. Incomplete dominance – Neither trai ...
... 1. Many genetic traits have a stronger dominant allele and a weaker recessive allele. This is known as complete dominance. What is a trait, however, is NOT completely dominant and/or recessive. Summarize the difference between incomplete dominance and codominance. Incomplete dominance – Neither trai ...
A molecular marker map for roses - Wageningen UR E
... from both parents, 321 could be placed on seven linkage groups (data not shown). The female parent 93/1-117 contributed 129, the male parent 93/1-119 contributed 155 markers to the data set (Table 1). A relatively large number of 81 markers (22%) segregate from both parents (Table 1). This is most p ...
... from both parents, 321 could be placed on seven linkage groups (data not shown). The female parent 93/1-117 contributed 129, the male parent 93/1-119 contributed 155 markers to the data set (Table 1). A relatively large number of 81 markers (22%) segregate from both parents (Table 1). This is most p ...
- Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute
... (e.g., Vacquier and Payne 1973; Glabe and Vacquier 1977; Vacquier and Moy 1977; Brandriff et al. 1978; Vacquier 1978). With the advent of techniques to amplify and sequence nucleic acids, the identification of fertilization proteins was only one step away from permitting studies of genetic control o ...
... (e.g., Vacquier and Payne 1973; Glabe and Vacquier 1977; Vacquier and Moy 1977; Brandriff et al. 1978; Vacquier 1978). With the advent of techniques to amplify and sequence nucleic acids, the identification of fertilization proteins was only one step away from permitting studies of genetic control o ...
Basic Genetics - The Institute of Canine Biology
... possibility, and in fact as DNA analysis advances, it may become rare. Even without such analysis, however, there are many loci where three phenotypes (appearances) come from two alleles. An example is merle in the dog. This is often treated as a dominant, but in fact it is a type of inheritance in ...
... possibility, and in fact as DNA analysis advances, it may become rare. Even without such analysis, however, there are many loci where three phenotypes (appearances) come from two alleles. An example is merle in the dog. This is often treated as a dominant, but in fact it is a type of inheritance in ...
Interval mapping of QTLs controlling yield
... The garden pea (Pisum sativum L.) is one of the most important legume crops in Europe. The majority of agriculturally significant traits in pea, as in other plant species, are inherited quantitatively. The complexity of these phenotypic traits exhibiting continuous variation arises from the segregat ...
... The garden pea (Pisum sativum L.) is one of the most important legume crops in Europe. The majority of agriculturally significant traits in pea, as in other plant species, are inherited quantitatively. The complexity of these phenotypic traits exhibiting continuous variation arises from the segregat ...
hereditary diseases of a man - Ставропольская Государственная
... Nullisomy: nullisomics are those individuals, which lack a single pair of homologous chromosomes, so that the chromosome formula would be 2n-2, and not 2n-1-1, which would mean a double monosomic. E.R.Sears had isolated all the 21 nullisomics in wheat. Trisomy: trisomics are those organisms, which h ...
... Nullisomy: nullisomics are those individuals, which lack a single pair of homologous chromosomes, so that the chromosome formula would be 2n-2, and not 2n-1-1, which would mean a double monosomic. E.R.Sears had isolated all the 21 nullisomics in wheat. Trisomy: trisomics are those organisms, which h ...
Presentation #2 - UCLA Human Genetics
... e = unobserved random variable, which adds noise to the observed y (contributes to variation in y). Sometimes referred to as “error”, although it is not necessarily error ...
... e = unobserved random variable, which adds noise to the observed y (contributes to variation in y). Sometimes referred to as “error”, although it is not necessarily error ...
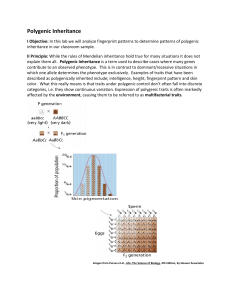
Polygenic Inheritance
... II Principle: While the rules of Mendelian inheritance hold true for many situations it does not explain them all. Polygenic Inheritance is a term used to describe cases where many genes contribute ...
... II Principle: While the rules of Mendelian inheritance hold true for many situations it does not explain them all. Polygenic Inheritance is a term used to describe cases where many genes contribute ...
Section 3 Studying Heredity
... Mendel’s Theory of Heredity Hypotheses 4. When gametes are formed, the alleles for each gene is an individual separate independently of one another. Thus, gametes carry only one allele for each inherited trait. When gametes unite during fertilization, each gamete contributes one allele. Example: Eac ...
... Mendel’s Theory of Heredity Hypotheses 4. When gametes are formed, the alleles for each gene is an individual separate independently of one another. Thus, gametes carry only one allele for each inherited trait. When gametes unite during fertilization, each gamete contributes one allele. Example: Eac ...
mutations
... The effects of mutations on genes vary widely. Some have little or no effect; and some produce beneficial variations. Some negatively disrupt gene function. Whether a mutation is negative or beneficial depends on how its DNA changes relative to the organism’s situation. Mutations are often thought o ...
... The effects of mutations on genes vary widely. Some have little or no effect; and some produce beneficial variations. Some negatively disrupt gene function. Whether a mutation is negative or beneficial depends on how its DNA changes relative to the organism’s situation. Mutations are often thought o ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.