Heritability - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
... Since only P can be observed or measured directly, heritability must be estimated from the similarities observed in subjects varying in their level of genetic or environmental similarity. The statistical analyses required to estimate the genetic and environmental components of variance depend on the ...
... Since only P can be observed or measured directly, heritability must be estimated from the similarities observed in subjects varying in their level of genetic or environmental similarity. The statistical analyses required to estimate the genetic and environmental components of variance depend on the ...
From out of old fields comes all this new corn
... large amounts of dominance variance, but once the populations were random mated for several generations the ratio of s2D / s2A was became <1, this was likely due to recombination among repulsion phase loci A b a ...
... large amounts of dominance variance, but once the populations were random mated for several generations the ratio of s2D / s2A was became <1, this was likely due to recombination among repulsion phase loci A b a ...
Genetic Diseases - Noadswood Science
... In groups of 4 then split into two pairs Each pair need to create an information leaflet (1 A4 side only) cystic fibrosis and polydactyly. You will also need to create a 5 question quiz. In the leaflet include: - How it is inherited, a genetic diagram e.g. punnet square would be good (include allel ...
... In groups of 4 then split into two pairs Each pair need to create an information leaflet (1 A4 side only) cystic fibrosis and polydactyly. You will also need to create a 5 question quiz. In the leaflet include: - How it is inherited, a genetic diagram e.g. punnet square would be good (include allel ...
Natural Selection
... 3. In the clean environment (which caused the trees to be covered in white lichen) which moth survived better? 4. In the clean environment, which color moth will increase in frequency in the next generation due to natural selection? 5. Color in peppered moths is similar to eye color in humans. In hu ...
... 3. In the clean environment (which caused the trees to be covered in white lichen) which moth survived better? 4. In the clean environment, which color moth will increase in frequency in the next generation due to natural selection? 5. Color in peppered moths is similar to eye color in humans. In hu ...
What is individual quality? An evolutionary
... quality’ remains a somewhat elusive concept within ecology [5,6]. At the heart of the problem is that researchers in different fields often invest the term with subtle, but potentially important differences in meaning. Consequently, if not carefully defined ‘individual quality’ is a rather ambiguous ...
... quality’ remains a somewhat elusive concept within ecology [5,6]. At the heart of the problem is that researchers in different fields often invest the term with subtle, but potentially important differences in meaning. Consequently, if not carefully defined ‘individual quality’ is a rather ambiguous ...
Sewall Wright, shifting balance theory, and the
... counterintuitive, for Wright always maintained that subdivision of a population into small, partially isolated demes provides the balance between random genetic drift and natural selection that is most favorable for rapid adaptive evolution. On this view, drift and selection act together in adaptive ...
... counterintuitive, for Wright always maintained that subdivision of a population into small, partially isolated demes provides the balance between random genetic drift and natural selection that is most favorable for rapid adaptive evolution. On this view, drift and selection act together in adaptive ...
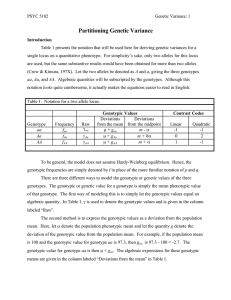
Partitioning Genetic Variance
... many further equations may be derived.2 Additive genetic variance For a single locus, the total genetic variance is partitioned into two types of variance, the additive genetic variance and dominance variance. Here we give the derivation for additive genetic variance. We begin by noting the orthogon ...
... many further equations may be derived.2 Additive genetic variance For a single locus, the total genetic variance is partitioned into two types of variance, the additive genetic variance and dominance variance. Here we give the derivation for additive genetic variance. We begin by noting the orthogon ...
Natural Selection Student Handout
... moth survived better in your simulation? 2. Why do you think that color of moth survived better? 3. In the clean environment (which caused the trees to be covered in white lichen) which moth survived better? 4. In the clean environment, which color moth will increase in frequency in the next generat ...
... moth survived better in your simulation? 2. Why do you think that color of moth survived better? 3. In the clean environment (which caused the trees to be covered in white lichen) which moth survived better? 4. In the clean environment, which color moth will increase in frequency in the next generat ...
Linkage and Segregation Analysis of Black and Brindle Coat Color
... known as the Extension locus (because different alleles could extend the amount of yellow vs. black pigment), and loss-of-function Mc1r mutations were known as recessive yellow (e). Most dogs with a uniform black appearance, e.g., the Newfoundland, the flat-coated retriever, black Labrador retriever ...
... known as the Extension locus (because different alleles could extend the amount of yellow vs. black pigment), and loss-of-function Mc1r mutations were known as recessive yellow (e). Most dogs with a uniform black appearance, e.g., the Newfoundland, the flat-coated retriever, black Labrador retriever ...
Genetic epidemiology of personality disorders
... within cluster B indicated that borderline PD and antisocial PD appeared to share genetic risk factors above and beyond those shared in common with the other cluster B disorders,43 and a twin study of cluster C PDs suggested that genetic factors influencing obsessive-compulsive PD appeared to be rel ...
... within cluster B indicated that borderline PD and antisocial PD appeared to share genetic risk factors above and beyond those shared in common with the other cluster B disorders,43 and a twin study of cluster C PDs suggested that genetic factors influencing obsessive-compulsive PD appeared to be rel ...
On the explanatory roles of natural selection
... constant (Sober 1984: 149, 155). On this strategy we can explain population level changes by the differential reproductive success of static variants. Based on this view, Elliott Sober makes the argument that selection can explain facts about populations but cannot explain facts about the individual ...
... constant (Sober 1984: 149, 155). On this strategy we can explain population level changes by the differential reproductive success of static variants. Based on this view, Elliott Sober makes the argument that selection can explain facts about populations but cannot explain facts about the individual ...
Full Version - TS
... portray CNV calls using SNP chip genotype data from an initial sample of 210 TS cases and 285 controls ascertained in two Latin American populations (genetically closely related and expected to show an enrichment for shared predisposing factors for complex genetic conditions, such as TS). For this s ...
... portray CNV calls using SNP chip genotype data from an initial sample of 210 TS cases and 285 controls ascertained in two Latin American populations (genetically closely related and expected to show an enrichment for shared predisposing factors for complex genetic conditions, such as TS). For this s ...
12.04.518 Preconception Testing for Carrier Status of Genetic
... genetic disorder but may be at risk for passing it on to their children. A carrier of a genetic disorder has one abnormal allele for a disorder. Carriers of an autosomal recessive mutation are typically unaffected. Offspring who inherit the mutation from both parents usually manifest the disorder. W ...
... genetic disorder but may be at risk for passing it on to their children. A carrier of a genetic disorder has one abnormal allele for a disorder. Carriers of an autosomal recessive mutation are typically unaffected. Offspring who inherit the mutation from both parents usually manifest the disorder. W ...
Basic Plant and Animal Breeding
... Later cells descending from this parent cell in which the new mutation occurred could show the new mutation, providing it were dominant and could have effects different than observed in other cells in the surrounding tissues. An example is the appearance of brown spot within the otherwise blue eye i ...
... Later cells descending from this parent cell in which the new mutation occurred could show the new mutation, providing it were dominant and could have effects different than observed in other cells in the surrounding tissues. An example is the appearance of brown spot within the otherwise blue eye i ...
Nature Genetics: doi:10.1038/ng.3791
... 2. Ohler, U., Liao, G.-c. C., Niemann, H. & Rubin, G. M. Computational analysis of core promoters in the Drosophila genome. Genome biology 3, Research0087 (2002). ...
... 2. Ohler, U., Liao, G.-c. C., Niemann, H. & Rubin, G. M. Computational analysis of core promoters in the Drosophila genome. Genome biology 3, Research0087 (2002). ...
Estimated numbers and prevalence of PI*S -antitrypsin deficiency in Asia
... frequencies, cohorts from countries with excessively high PI*S frequencies will give a deceptively higher PFS than others with much lower PI*S frequencies, but similar or higher PI*Z frequencies. Therefore, PFS should be adapted to different regions and countries, by adjusting the PFS rise by PI*S f ...
... frequencies, cohorts from countries with excessively high PI*S frequencies will give a deceptively higher PFS than others with much lower PI*S frequencies, but similar or higher PI*Z frequencies. Therefore, PFS should be adapted to different regions and countries, by adjusting the PFS rise by PI*S f ...
Gene Genealogy and Properties of Test Statistics of
... of the most important issues of this development is to relate the genetic diversity with the population genetic processes. For this purpose, some test statistics of neutrality that detect deviations of DNA polymorphisms from neutral expectations have been developed under the assumptions of constant ...
... of the most important issues of this development is to relate the genetic diversity with the population genetic processes. For this purpose, some test statistics of neutrality that detect deviations of DNA polymorphisms from neutral expectations have been developed under the assumptions of constant ...
Appendix 5 Laboratory Projects List
... meeting (see Chapter 3). Prefixes like “*NIH*” identify funded projects and the project’s source of support. Initials in parentheses indicate who in the lab was working on the project. Many other abbreviations are present (e.g., MSH1, ps); these would be familiar within the laboratory, such as for c ...
... meeting (see Chapter 3). Prefixes like “*NIH*” identify funded projects and the project’s source of support. Initials in parentheses indicate who in the lab was working on the project. Many other abbreviations are present (e.g., MSH1, ps); these would be familiar within the laboratory, such as for c ...
Multifactorial Traits
... Mendel’s laws, or linked on the same chromosome. Many single-gene disorders are very rare, each affecting one in hundreds or even thousands of individuals. Using Mendel’s laws, geneticists can predict the probability that certain family members will inherit single-gene conditions. Most more common t ...
... Mendel’s laws, or linked on the same chromosome. Many single-gene disorders are very rare, each affecting one in hundreds or even thousands of individuals. Using Mendel’s laws, geneticists can predict the probability that certain family members will inherit single-gene conditions. Most more common t ...
Introduction to Genetics
... Because there are only 20 amino acids that need to be coded (using A, C, U or G), the genetic code can be said to be degenerate, with the third position ...
... Because there are only 20 amino acids that need to be coded (using A, C, U or G), the genetic code can be said to be degenerate, with the third position ...
An extreme cytoplasmic bottleneck in the modern European
... Burbank, possessed cpSSR haplotype A and comparisons with previous cpRFLP studies which included this cultivar (Hosaka & Hanneman 1988b; Waugh et al. 1990; Powell et al. 1993) con¢rm that the predominant A haplotype corresponds to the T-type cytoplasm. Between four and nine alleles were detected at ...
... Burbank, possessed cpSSR haplotype A and comparisons with previous cpRFLP studies which included this cultivar (Hosaka & Hanneman 1988b; Waugh et al. 1990; Powell et al. 1993) con¢rm that the predominant A haplotype corresponds to the T-type cytoplasm. Between four and nine alleles were detected at ...
Genetics: Mendel and Beyond
... factors controlling a given characteristic; these could be identical (as in true-breeding plants) or different (as in hybrid plant) and in this case one dominates the other; these factors separate and go to different gametes when a parent reproduces These “factors” are now called genes. The differen ...
... factors controlling a given characteristic; these could be identical (as in true-breeding plants) or different (as in hybrid plant) and in this case one dominates the other; these factors separate and go to different gametes when a parent reproduces These “factors” are now called genes. The differen ...
Notes on Population Genetics
... We can define an inbred individual as an individual whose parents are more closely related to each other than two random individuals drawn from some reference population. When two related individuals produce an offspring, that individual can receive two alleles that are identical by descent, i.e. th ...
... We can define an inbred individual as an individual whose parents are more closely related to each other than two random individuals drawn from some reference population. When two related individuals produce an offspring, that individual can receive two alleles that are identical by descent, i.e. th ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.