Population Genetics - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... 1) Large population 2) No mutation 3) No gene flow (no immigration or emigration) 4) Random mating (no mating preference for particular phenotype) 5) No natural selection (all genotypes have an = chance of surviving & reproducing) ...
... 1) Large population 2) No mutation 3) No gene flow (no immigration or emigration) 4) Random mating (no mating preference for particular phenotype) 5) No natural selection (all genotypes have an = chance of surviving & reproducing) ...
Population Genetics - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... **So why study population genetics? Why use the H-W Theorem? 1) shows how genetics is related to evolution; 2) provides a benchmark genetic equilibrium against which change can be noted; 3) permits an estimation of gene frequencies; especially useful in estimating the number of carriers of lethal ...
... **So why study population genetics? Why use the H-W Theorem? 1) shows how genetics is related to evolution; 2) provides a benchmark genetic equilibrium against which change can be noted; 3) permits an estimation of gene frequencies; especially useful in estimating the number of carriers of lethal ...
AP Biology Ch 21 Notes
... - change in allele frequencies due to chance events - can occur in small populations - the smaller a sample, the greater the chance of deviations from the expected results - the disproportion of results is called sampling error - example: flip a coin 10 times 7 heads & 3 tails is within reason fli ...
... - change in allele frequencies due to chance events - can occur in small populations - the smaller a sample, the greater the chance of deviations from the expected results - the disproportion of results is called sampling error - example: flip a coin 10 times 7 heads & 3 tails is within reason fli ...
Evolution - MarsicanoBiology
... • A change over time • A process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms • Theory- a broad, well tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations ...
... • A change over time • A process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms • Theory- a broad, well tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations ...
1. Explain what is meant by the “modern synthesis”.
... in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium If the gene pool was originally in disequilibrium, only one generation would be necessary for equilibrium to be established (as long as random mating is occurring in the population) ...
... in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium If the gene pool was originally in disequilibrium, only one generation would be necessary for equilibrium to be established (as long as random mating is occurring in the population) ...
The genetics and bioinformatics of haploid selection We are looking
... resulted in haploid selection having been largely discarded. However, there is growing evidence that genetic and epigenetic effects transferred through gametes may affect the fitness of offspring, as exemplified by very recent results produced in our lab which show provide striking evidence for an e ...
... resulted in haploid selection having been largely discarded. However, there is growing evidence that genetic and epigenetic effects transferred through gametes may affect the fitness of offspring, as exemplified by very recent results produced in our lab which show provide striking evidence for an e ...
Evolution Unit 1 Free Response Practice
... for the occurrence of evolution in a population. If only Mendelian segregation and recombination of alleles at fertilization are involved, then the gene pool of a population will remain constant from one generation to the next, as described by the Hardy-Weinberg principle. In a sentence or two, list ...
... for the occurrence of evolution in a population. If only Mendelian segregation and recombination of alleles at fertilization are involved, then the gene pool of a population will remain constant from one generation to the next, as described by the Hardy-Weinberg principle. In a sentence or two, list ...
05 ICA 5 Microevolution Rubric
... squirrels. Prior to climate change, genotypic and phenotypic variation existed in the population of squirrels, so the frequency of alleles was different. Some squirrels have genotypes that results in a phenotype of early breeding. These squirrels have a preadaptation that will allow them flourish wi ...
... squirrels. Prior to climate change, genotypic and phenotypic variation existed in the population of squirrels, so the frequency of alleles was different. Some squirrels have genotypes that results in a phenotype of early breeding. These squirrels have a preadaptation that will allow them flourish wi ...
Causes of microevolution
... that the frequencies of alleles and genotypes in a population’s gene pool remain constant over the generations unless acted upon by agents other than sexual recombination. So sexual shuffling of alleles due to meiosis and random fertilization have no effect on the overall genetic structure of a popu ...
... that the frequencies of alleles and genotypes in a population’s gene pool remain constant over the generations unless acted upon by agents other than sexual recombination. So sexual shuffling of alleles due to meiosis and random fertilization have no effect on the overall genetic structure of a popu ...
Ch 23 – Evolution of Populations
... – Occurs when individuals of one sex (usually females) are choosy in selecting their mates from individuals of the other sex – May depend on the showiness of the male’s ...
... – Occurs when individuals of one sex (usually females) are choosy in selecting their mates from individuals of the other sex – May depend on the showiness of the male’s ...
Population Genetics: Genetic Drift, Natural Selection, and Mutation.
... “live” to reproduce. If the dice lands on 1, then the marble will not be added to the F1 progeny. However, if the dice lands on 2, 3, or 4, then the marble will survive to reproduce. In this example, the blue marble has a 75% chance of survival. Again, the students will be asked to compare these fin ...
... “live” to reproduce. If the dice lands on 1, then the marble will not be added to the F1 progeny. However, if the dice lands on 2, 3, or 4, then the marble will survive to reproduce. In this example, the blue marble has a 75% chance of survival. Again, the students will be asked to compare these fin ...
Biology memory tricks
... Cloners – twinning! Dolly – egg injection and treatment Clones are not diverse……… Unit 4 Evolution Terms evolution – change over time – simple to complex , adaptation – a trick to survive, variation is diversity in a population Peppered moth story - population evolution and adaptation. Natural selec ...
... Cloners – twinning! Dolly – egg injection and treatment Clones are not diverse……… Unit 4 Evolution Terms evolution – change over time – simple to complex , adaptation – a trick to survive, variation is diversity in a population Peppered moth story - population evolution and adaptation. Natural selec ...
Presentation
... 1. Involves selecting qualities within individuals of a breed that are desired so that these qualities may be passed on to the next ...
... 1. Involves selecting qualities within individuals of a breed that are desired so that these qualities may be passed on to the next ...
Evolution Reading Guide 1. Explain what Darwin meant when he
... 1. What are five conditions that must be met for evolution NOT to occur based on the Hardy-Weinberg assumptions.(Refer to Section 13.3) 2. Explain the five evolutionary forces that have the potential to significantly alter allele frequencies in populations. Be detailed in your response. 13.5 Forms o ...
... 1. What are five conditions that must be met for evolution NOT to occur based on the Hardy-Weinberg assumptions.(Refer to Section 13.3) 2. Explain the five evolutionary forces that have the potential to significantly alter allele frequencies in populations. Be detailed in your response. 13.5 Forms o ...
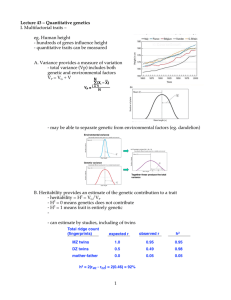
1 Lecture 43 â Quantitative genetics I. Multifactorial traits â eg
... - weight F2 fruit and genotype across genome “p/l” vs “l/l” - does weight differ? - For most genotypes, the answer is no but for a few it is yes (these are loci that contribute to the trait, in this case fruit size) - identified 28 loci responsible for fruit size B. How can we study QTLs in humans? ...
... - weight F2 fruit and genotype across genome “p/l” vs “l/l” - does weight differ? - For most genotypes, the answer is no but for a few it is yes (these are loci that contribute to the trait, in this case fruit size) - identified 28 loci responsible for fruit size B. How can we study QTLs in humans? ...
Speciation - Mr. Croft
... • In addition, mutations can change the frequency of the alleles already present in the gene pool. • The occurrence of mutation in most alleles is too low to cause major changes in the allele frequencies of an entire population. ...
... • In addition, mutations can change the frequency of the alleles already present in the gene pool. • The occurrence of mutation in most alleles is too low to cause major changes in the allele frequencies of an entire population. ...
Evolution Definitions
... Analogous Structures – Body parts that do not have a common evolutionary origin but are similar in function e.g. bird and insect wings Vestigial Structures – A body structure in a present day organism that no longer serves its original purpose e.g. Human appendix Gene Pool – All the alleles of a po ...
... Analogous Structures – Body parts that do not have a common evolutionary origin but are similar in function e.g. bird and insect wings Vestigial Structures – A body structure in a present day organism that no longer serves its original purpose e.g. Human appendix Gene Pool – All the alleles of a po ...
Population Genetics: Evolution at the Gene Level
... How does natural Selection affect allele frequency? Mutations provide the raw material on which ________________________________ can act. Evolution depends on _____________ because this is the only way that _____________ among organisms are created Evolution acts on populations not ___________ ...
... How does natural Selection affect allele frequency? Mutations provide the raw material on which ________________________________ can act. Evolution depends on _____________ because this is the only way that _____________ among organisms are created Evolution acts on populations not ___________ ...
Introduction to some evolutionary terms and concepts Variation and
... Evolution is defined in many ways. Descent with modification (Darwin's expression) or change in the allele frequency of a population from one generation to the next are popular definitions. Allelic evolution occurs within a local population of interbreeding individuals, and it is usually inferred fr ...
... Evolution is defined in many ways. Descent with modification (Darwin's expression) or change in the allele frequency of a population from one generation to the next are popular definitions. Allelic evolution occurs within a local population of interbreeding individuals, and it is usually inferred fr ...
Biological Evolution
... different conditions on the island. This causes a shift in allele frequency in the island population because of selection pressures. ...
... different conditions on the island. This causes a shift in allele frequency in the island population because of selection pressures. ...
Allele Frequency, Gene Pools, and Species Variation
... Population X consists of a group of hares (rabbits) that are genetically similar. Population Y consists of a group of hares (rabbits) that are genetically varied. If they both live in the same habitat and something changes in their habitat, which population is more likely to survive? Explain. ...
... Population X consists of a group of hares (rabbits) that are genetically similar. Population Y consists of a group of hares (rabbits) that are genetically varied. If they both live in the same habitat and something changes in their habitat, which population is more likely to survive? Explain. ...
Selection, Drift, Mutation, and Gene Flow Use the Allele A1 software
... To see what effect drift can have (even when mutations have a selective advantage!) repeat the above experiment, but this time set population size = 10. Now what is the likely fate of the mutant allele under Cases 1 and 2 (same parameters as above, except for population size)? 1. Repeat this simulat ...
... To see what effect drift can have (even when mutations have a selective advantage!) repeat the above experiment, but this time set population size = 10. Now what is the likely fate of the mutant allele under Cases 1 and 2 (same parameters as above, except for population size)? 1. Repeat this simulat ...
practice questions
... 6. Lamarck’s theory of evolution includes the concept that new organs in a species appear as a result of a. continual increases in population size. b. the actions of organisms as they use or fail to use body structures. c. an unchanging local environment. d. the natural variations already present wi ...
... 6. Lamarck’s theory of evolution includes the concept that new organs in a species appear as a result of a. continual increases in population size. b. the actions of organisms as they use or fail to use body structures. c. an unchanging local environment. d. the natural variations already present wi ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.







![122 [Study Guide] 23-1 Genetic Basis for Evolution](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003184976_1-2e5629bb9721bbd54c7bd35f91ff5978-300x300.png)