Advanced Animal Science Curriculum | Sam Houston State University
... the genotype. Since gametes contain only one copy of each gene, a single bead also represents a gamete. ...
... the genotype. Since gametes contain only one copy of each gene, a single bead also represents a gamete. ...
Mendel and the Gene Idea Patterns of Inheritance
... The law of independent assortment states that each pair of alleles segregates independently of each other pair of alleles during gamete formation This law applies only to genes on different, nonhomologous chromosomes Genes located near each other on the same chromosome tend to be inherited tog ...
... The law of independent assortment states that each pair of alleles segregates independently of each other pair of alleles during gamete formation This law applies only to genes on different, nonhomologous chromosomes Genes located near each other on the same chromosome tend to be inherited tog ...
Peppered Moths
... natural selection happen because of the genes – genotype – of the plant or because of the height – phenotype – of the plant?) ...
... natural selection happen because of the genes – genotype – of the plant or because of the height – phenotype – of the plant?) ...
Policies, Measures and Experiences Regarding Intellectual
... this broad purpose, Australia assesses applications based on GR by applying the same patentability requirements as for all other applications, irrespective of their technological field. Also, Australia’s plant breeder’s rights system provides protection for new plant varieties. Under the standard te ...
... this broad purpose, Australia assesses applications based on GR by applying the same patentability requirements as for all other applications, irrespective of their technological field. Also, Australia’s plant breeder’s rights system provides protection for new plant varieties. Under the standard te ...
General background text Pharmacogenetics
... The process of genotyping is used to determine the genotype. It indicates which alleles of the gene for TPMT are present in the tested individual. Each allele has a name that consists of a star (*) and a number, an example of a possible TPMT genotype is TPMT*1/*3A. Many variations exist for TPMT, mo ...
... The process of genotyping is used to determine the genotype. It indicates which alleles of the gene for TPMT are present in the tested individual. Each allele has a name that consists of a star (*) and a number, an example of a possible TPMT genotype is TPMT*1/*3A. Many variations exist for TPMT, mo ...
Genetics - TeacherWeb
... • Traits are passed on from one generation to the next. • Traits are controlled by genes. • Organisms inherit genes in pairs (2 alleles for every trait – 1 from mom, 1 from dad). • Some genes are dominant, some are recessive. • Dominant genes hide recessive genes when both are inherited by an organi ...
... • Traits are passed on from one generation to the next. • Traits are controlled by genes. • Organisms inherit genes in pairs (2 alleles for every trait – 1 from mom, 1 from dad). • Some genes are dominant, some are recessive. • Dominant genes hide recessive genes when both are inherited by an organi ...
GeneticsProtocol Lab student hand out
... The gene that results in the development of male anatomy is located on the Y chromosome. This gene is called SRY, which stands for sex-determining region of the Y chromosome. If a zygote has a Y chromosome with the SRY gene, the embryo will develop testes and male anatomy. If a zygote does not have ...
... The gene that results in the development of male anatomy is located on the Y chromosome. This gene is called SRY, which stands for sex-determining region of the Y chromosome. If a zygote has a Y chromosome with the SRY gene, the embryo will develop testes and male anatomy. If a zygote does not have ...
Extensions of Mendelian Genetics
... gene products (proteins) are written in plain text. For example, a gene that has been associated with breast cancer in women is BRCA1, and the protein it encodes is BRCA1. ...
... gene products (proteins) are written in plain text. For example, a gene that has been associated with breast cancer in women is BRCA1, and the protein it encodes is BRCA1. ...
AQF 613 - RUFORUM
... Sex-linked genes are known only in ornamental fish, and most information about this type of inheritance comes from the guppy and platyfish. Most qualitative phenotypes that have been deciphered genetically in food fish are controlled by single autosomal genes with two alleles per locus. In general, ...
... Sex-linked genes are known only in ornamental fish, and most information about this type of inheritance comes from the guppy and platyfish. Most qualitative phenotypes that have been deciphered genetically in food fish are controlled by single autosomal genes with two alleles per locus. In general, ...
How to catch epistasis: theory and practice - Montefiore
... ??? Can we use the statistical evidence of epistasis at the population level to infer biological or genetical epistasis in an individual? ??? Does biological evidence of epistasis imply that statistical evidence will be found? ...
... ??? Can we use the statistical evidence of epistasis at the population level to infer biological or genetical epistasis in an individual? ??? Does biological evidence of epistasis imply that statistical evidence will be found? ...
Role of Mendelian genes in "sporadic" Parkinson`s disease
... The pathology and physiopathology of Parkinson’s disease (PD), a motor syndrome due to neurodegeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta, are relatively well understood, but not the underlying cause. PD, thought to be mainly sporadic, caused by environmental factors, is ...
... The pathology and physiopathology of Parkinson’s disease (PD), a motor syndrome due to neurodegeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta, are relatively well understood, but not the underlying cause. PD, thought to be mainly sporadic, caused by environmental factors, is ...
an R interface to SOLAR for variance component analysis
... The bivariate polygenic model partitions phenotypic variance observed in two traits trait1 and trait2 into genetic and environmental components. The model also introduces correlation coefficients per component between traits. mod2 <- solarPolygenic(trait1+trait2~1, dat30, polygenic.options = ’-testr ...
... The bivariate polygenic model partitions phenotypic variance observed in two traits trait1 and trait2 into genetic and environmental components. The model also introduces correlation coefficients per component between traits. mod2 <- solarPolygenic(trait1+trait2~1, dat30, polygenic.options = ’-testr ...
Mendel explained how a dominant allele can mask the
... • An organism with two of the same alleles for a particular trait is homozygous for that trait (YY or yy). • An organism with two different alleles for a particular trait is heterozygous for that trait (Yy). • In heterozygous individuals, the dominant trait will be observed. ...
... • An organism with two of the same alleles for a particular trait is homozygous for that trait (YY or yy). • An organism with two different alleles for a particular trait is heterozygous for that trait (Yy). • In heterozygous individuals, the dominant trait will be observed. ...
Newton E. Morton - The American Society of Human Genetics
... corresponding effect of inbreeding, and A measures the amount of expressed damage when F = 0. An estimate of B/A with an unusually high value would be suspect if the residual variance were significant, but that was not found. Covariance of S with environment cannot be estimated reliably and has not ...
... corresponding effect of inbreeding, and A measures the amount of expressed damage when F = 0. An estimate of B/A with an unusually high value would be suspect if the residual variance were significant, but that was not found. Covariance of S with environment cannot be estimated reliably and has not ...
Heredity
... segregate independently of one another. • Linked genes are genes that reside on the SAME chromosome and thus cannot segregate because they are physically connected. • Genes that are linked are usually inherited together. ...
... segregate independently of one another. • Linked genes are genes that reside on the SAME chromosome and thus cannot segregate because they are physically connected. • Genes that are linked are usually inherited together. ...
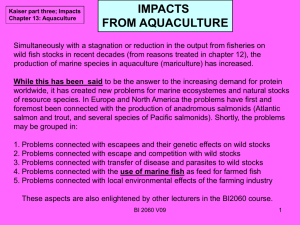
BI 2060 V09 English Chapter 13 Effects from Aquaculture
... Looking once more at the underlying assumptions for the H-W law: 1. Panmixia (random mating) 2. No mutation (can be relaxed in short term) 3. No random genetic drift (i.e. infinitely large population) 4. No gene flow from other populations (with different allele frequencies) 5. No selection (neither ...
... Looking once more at the underlying assumptions for the H-W law: 1. Panmixia (random mating) 2. No mutation (can be relaxed in short term) 3. No random genetic drift (i.e. infinitely large population) 4. No gene flow from other populations (with different allele frequencies) 5. No selection (neither ...
Pierce Genetics: A Conceptual Approach 3e
... backcrossed to the parent with round seeds, what proportion of the progeny will have winkled seeds? ( Use a Punnett ...
... backcrossed to the parent with round seeds, what proportion of the progeny will have winkled seeds? ( Use a Punnett ...
Animal breeders use test crosses to determine whether an individual
... dominant phenotypes this notation would never be encountered ...
... dominant phenotypes this notation would never be encountered ...
An Integrated Genetic Analysis Package Using R
... package can easily be adapted for analysis of large datasets involving either SNPs or multiallelic markers. Some are utility functions, e.g. muvar and whscore, which will be part of the other analysis routines in the future. For users, all functions have unified format. For developers, it is able to ...
... package can easily be adapted for analysis of large datasets involving either SNPs or multiallelic markers. Some are utility functions, e.g. muvar and whscore, which will be part of the other analysis routines in the future. For users, all functions have unified format. For developers, it is able to ...
Against Maladaptationism - Open Research Exeter
... more recent conditions. (And, of course, that there was enough time for our early human ancestors to adapt to the conditions they encountered, whatever those were.) So how much time is enough? How fast is evolution? It is still common, and underlies this part of the Evolutionary Psychologists’ argum ...
... more recent conditions. (And, of course, that there was enough time for our early human ancestors to adapt to the conditions they encountered, whatever those were.) So how much time is enough? How fast is evolution? It is still common, and underlies this part of the Evolutionary Psychologists’ argum ...
Mendelian Inheritance
... coded in the nuclear genome. The third, and most recent, advance is that mutations in the mtDNA lead to a number of genetic disorders. The full range of diseases that have a mitochondrial component is unknown but clearly involve rare disorders, such as Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy, and common ...
... coded in the nuclear genome. The third, and most recent, advance is that mutations in the mtDNA lead to a number of genetic disorders. The full range of diseases that have a mitochondrial component is unknown but clearly involve rare disorders, such as Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy, and common ...
LAB 1: Scientific Method/Tools of Scientific Inquiry
... Gene pools can also change due to the introduction of new genetic alleles to the gene pool. Novel alleles arise when the DNA sequence of an existing allele is changed in any way, even by just one nucleotide. Any change in a DNA sequence is called a mutation, and mutations can occur as a result of se ...
... Gene pools can also change due to the introduction of new genetic alleles to the gene pool. Novel alleles arise when the DNA sequence of an existing allele is changed in any way, even by just one nucleotide. Any change in a DNA sequence is called a mutation, and mutations can occur as a result of se ...
LAB 11 Natural Selection
... This is the Hardy-Weinberg equation in which p represents the frequency of one genetic allele in a population (e.g., the B allele in your predator/prey simulations), and q represents the frequency of the other allele (e.g., the b allele). Under conditions of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, these alleles ...
... This is the Hardy-Weinberg equation in which p represents the frequency of one genetic allele in a population (e.g., the B allele in your predator/prey simulations), and q represents the frequency of the other allele (e.g., the b allele). Under conditions of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, these alleles ...
Naturally occurring genetic variation affects Drosophila
... genetic variation is interesting to study from a number of perspectives. First, it provides the material basis for biological evolution. It is thus important to know the distribution of allelic effects in natural populations: how many genes contribute variation to each particular trait, how large ar ...
... genetic variation is interesting to study from a number of perspectives. First, it provides the material basis for biological evolution. It is thus important to know the distribution of allelic effects in natural populations: how many genes contribute variation to each particular trait, how large ar ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.