Crazy Traits - CPO Science
... of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction, (3) competition for limited resources, and (4) the proliferation of those organisms that are better able to survive and reproduce in the environment. ...
... of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction, (3) competition for limited resources, and (4) the proliferation of those organisms that are better able to survive and reproduce in the environment. ...
Week 2 - University of Texas Health Science Center at San
... Trait: A distinguishing feature, a genetically determined characteristic or condition. Allele: Versions of a gene Genotype: Genetic makeup, distinguished from the physical appearance. (G for genetic and genotype) Phenotype: The observable physical or biochemical characteristics as determined by both ...
... Trait: A distinguishing feature, a genetically determined characteristic or condition. Allele: Versions of a gene Genotype: Genetic makeup, distinguished from the physical appearance. (G for genetic and genotype) Phenotype: The observable physical or biochemical characteristics as determined by both ...
Mendel`s crosses - Uniwersytet otwarty UG
... characters are controlled by unit factors that exist in pairs in individual organisms; when two unlike factors responsible for a single character are present in a single individual, one unit factor is dominant to the other, which is said to be recessive; during the formation of gametes, the paired u ...
... characters are controlled by unit factors that exist in pairs in individual organisms; when two unlike factors responsible for a single character are present in a single individual, one unit factor is dominant to the other, which is said to be recessive; during the formation of gametes, the paired u ...
Single-Gene Inheritance (Learning Objectives) • Review the
... phenotype, allele, autosomal dominant and recessive traits, and a monohybrid cross. Explain Mendel’s law of allele segregation. Learn what is meant by a test cross and when it is used. Explain Mendel’s law of independent assortment for the simultaneous inheritance or two characters. Understand and u ...
... phenotype, allele, autosomal dominant and recessive traits, and a monohybrid cross. Explain Mendel’s law of allele segregation. Learn what is meant by a test cross and when it is used. Explain Mendel’s law of independent assortment for the simultaneous inheritance or two characters. Understand and u ...
FOSS notes Heredity - Southington Public Schools
... Chromosomes come in almost identical pairs Chromosomes have specific active locations called alleles. The two alleles in identical locations on paired chromosomes make up a gene. ...
... Chromosomes come in almost identical pairs Chromosomes have specific active locations called alleles. The two alleles in identical locations on paired chromosomes make up a gene. ...
349 POLYMORPHISM OF THE Β
... the Merino population. (Corral et al, 2010) The number of animals with genotype GG was probably too low to reveal significant associations, in 403 milk samples of East Friesian Dairy and Lacaune sheep (Giambra et al, 2014) In two Czech national sheep populations (Sumava and Valachian), molecular ana ...
... the Merino population. (Corral et al, 2010) The number of animals with genotype GG was probably too low to reveal significant associations, in 403 milk samples of East Friesian Dairy and Lacaune sheep (Giambra et al, 2014) In two Czech national sheep populations (Sumava and Valachian), molecular ana ...
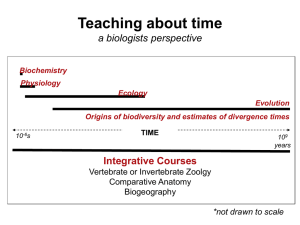
Teaching deep time through macroevolution and
... 3. Students align sequences, calculate the number of differences among taxa and use a computer program to generate a phylogenetic tree [more complex iteration of initial exercise; introduces bioinformatics] 4. Students download cytb sequence and generate another tree for the same taxa [repeat tree m ...
... 3. Students align sequences, calculate the number of differences among taxa and use a computer program to generate a phylogenetic tree [more complex iteration of initial exercise; introduces bioinformatics] 4. Students download cytb sequence and generate another tree for the same taxa [repeat tree m ...
Steve Downes
... units high, an organism with AA is 2.0 units high but an organism with Aa is also only 2.0 units high. Variance in phenotype can result from gene interaction effects, or epistactic variance, VI: alleles at one locus have an effect on the phenotype that is dependent upon alleles at one or more other ...
... units high, an organism with AA is 2.0 units high but an organism with Aa is also only 2.0 units high. Variance in phenotype can result from gene interaction effects, or epistactic variance, VI: alleles at one locus have an effect on the phenotype that is dependent upon alleles at one or more other ...
Inherited Representations are Read in
... different genotypes are found over evolutionary time (Condition (a)). Where a genotype G gives rise to a heritable phenotypic difference P, it may be selected. A phenotype P will be selected because of the way it interacts with some feature E of the environment (including existing features of conspe ...
... different genotypes are found over evolutionary time (Condition (a)). Where a genotype G gives rise to a heritable phenotypic difference P, it may be selected. A phenotype P will be selected because of the way it interacts with some feature E of the environment (including existing features of conspe ...
(Microsoft PowerPoint - Mendel`s genetic laws [jen pro \350ten\355
... organism, or an individual PHENOTYPE - organism's observable characteristics or traits ALLELE - One member of a pair of genes occupying a specific spot on a chromosome that controls the same trait. ...
... organism, or an individual PHENOTYPE - organism's observable characteristics or traits ALLELE - One member of a pair of genes occupying a specific spot on a chromosome that controls the same trait. ...
Exploring Evolutionary Constraints Is a Task for an Integrative
... change in different directions within trait space for patterns or modules made up of serial repeats of the same basic element (Brakefield 2003). The evolution of mammalian dentition and of the subsets of teeth with divergent morphologies provide further examples of this type of modular pattern for w ...
... change in different directions within trait space for patterns or modules made up of serial repeats of the same basic element (Brakefield 2003). The evolution of mammalian dentition and of the subsets of teeth with divergent morphologies provide further examples of this type of modular pattern for w ...
Traversing the biological complexity in the hierarchy
... of common multifactorial diseases, such as CAD, cancer, diabetes and the psychiatric disorders (Sing et al. 1992, Sing & Moll 1990, Sing & Reilly 1993, Weiss 1993). In every case, a particular manifestation of disease may aggregate in families but only in rare instances does it segregate according t ...
... of common multifactorial diseases, such as CAD, cancer, diabetes and the psychiatric disorders (Sing et al. 1992, Sing & Moll 1990, Sing & Reilly 1993, Weiss 1993). In every case, a particular manifestation of disease may aggregate in families but only in rare instances does it segregate according t ...
The quest for the entrepreneurial gene
... strong their association is. For example, we know that approximately 70 percent of all genes are expressed in the brain and that brain function influences behavior. Thus, it is very possible to derive a seemingly plausible hypothesis for practically every gene (and therefore every SNP), and each of ...
... strong their association is. For example, we know that approximately 70 percent of all genes are expressed in the brain and that brain function influences behavior. Thus, it is very possible to derive a seemingly plausible hypothesis for practically every gene (and therefore every SNP), and each of ...
Genetic markers in beef and sheep breeding
... to an animal’s performance, its appearance, or its susceptibility to disease. The ability to test the DNA of an animal and identify those animals that carry either specific alleles or the characteristic markers associated with those alleles means that we can now identify animals with the ‘best’ gene ...
... to an animal’s performance, its appearance, or its susceptibility to disease. The ability to test the DNA of an animal and identify those animals that carry either specific alleles or the characteristic markers associated with those alleles means that we can now identify animals with the ‘best’ gene ...
Parallel Machine Scheduling with Sequence
... Genetic algorithms are motivated by an analogy to “real” genetics A chromosome is composed of genes, generally randomly selected initially ...
... Genetic algorithms are motivated by an analogy to “real” genetics A chromosome is composed of genes, generally randomly selected initially ...
osb week06 geneticsproblems
... What are the potential types and proportions of offspring from this cross? What is the outcome if two plants from the F1 generation are crossed? 12) How would you determine the genotype of a tall, red-fruited tomato plant? What would be the results of the test-cross if the tall, red-fruited plant wa ...
... What are the potential types and proportions of offspring from this cross? What is the outcome if two plants from the F1 generation are crossed? 12) How would you determine the genotype of a tall, red-fruited tomato plant? What would be the results of the test-cross if the tall, red-fruited plant wa ...
Unit 10 Powerpoint
... also occurs in such cases, YY gametes are formed, leading to XYY males these males are fertile and may be ...
... also occurs in such cases, YY gametes are formed, leading to XYY males these males are fertile and may be ...
Linkage disequilibrium mapping in trisomic populations: analytical approaches and an application to congenital heart defects in Down syndrome.
... suggests that factors other than general overexpression of genes on chromosome 21 may be involved in the susceptibility of these traits. Three factors have been proposed to explain this variation: (1) stochastic factors, (2) extrinsic factors, and (3) genetics differences [Epstein, 2001]. Most likel ...
... suggests that factors other than general overexpression of genes on chromosome 21 may be involved in the susceptibility of these traits. Three factors have been proposed to explain this variation: (1) stochastic factors, (2) extrinsic factors, and (3) genetics differences [Epstein, 2001]. Most likel ...
chapter 15 - Scranton Prep Biology
... Genetic recombination : The production of offspring with new combinations of events the from results different from those combinatibns found in the parents; meiosis and random fertilization. 1. The recombination of unlinked genes: independent assortment of chromosomes Mendel discoveredthat some offs ...
... Genetic recombination : The production of offspring with new combinations of events the from results different from those combinatibns found in the parents; meiosis and random fertilization. 1. The recombination of unlinked genes: independent assortment of chromosomes Mendel discoveredthat some offs ...
16-4 PowerPoint
... Not all homologous structures have important functions. Vestigial structures are inherited from ancestors, but have lost much or all of their original function due to different selection pressures acting on the descendant. The hipbones of bottlenose dolphins are vestigial structures. In their ancest ...
... Not all homologous structures have important functions. Vestigial structures are inherited from ancestors, but have lost much or all of their original function due to different selection pressures acting on the descendant. The hipbones of bottlenose dolphins are vestigial structures. In their ancest ...
The Combination of Genetic Programming and Genetic Algorithm for
... important factor that effect on fitness value when N increase fitness value is decrease and verse versa . P : penalty number , this value is terming throw experiments , we find the small value (0.0001) is better from large value 0.1 because the large value enable to create small size networks with h ...
... important factor that effect on fitness value when N increase fitness value is decrease and verse versa . P : penalty number , this value is terming throw experiments , we find the small value (0.0001) is better from large value 0.1 because the large value enable to create small size networks with h ...
studies handedness, sexual selection and niche
... exploring gene–culture interactions through the use of gene–culture coevolutionary models. These studies explore (i) the evolution of handedness, (ii) sexual selection with a culturally transmitted mating preference, and (iii) cultural niche construction and human evolution. In §3 I attempt to synth ...
... exploring gene–culture interactions through the use of gene–culture coevolutionary models. These studies explore (i) the evolution of handedness, (ii) sexual selection with a culturally transmitted mating preference, and (iii) cultural niche construction and human evolution. In §3 I attempt to synth ...
1 Agro/ANSC/Biol/Gene/Hort 305 Fall, 2016 MENDELIAN
... was dominant over the other (recessive) trait. b. The dominant trait was always displayed in the F1 generation. In the F2 generation the dominant trait was present in the majority (75%) of the plants, while the recessive trait was present in the minority (25%) of the plants. c. The genetic informati ...
... was dominant over the other (recessive) trait. b. The dominant trait was always displayed in the F1 generation. In the F2 generation the dominant trait was present in the majority (75%) of the plants, while the recessive trait was present in the minority (25%) of the plants. c. The genetic informati ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.