COMPLEXITY - Carlos Eduardo Maldonado
... A problem is tractable (or easy) if there exists a Ptime algorithm to solve it A problem is intractable (or difficult) if no P-time algorithm exists to solve the problem C/A complexity theory of problems deals with decision problems. A decision problem always has a yes or no answer ...
... A problem is tractable (or easy) if there exists a Ptime algorithm to solve it A problem is intractable (or difficult) if no P-time algorithm exists to solve the problem C/A complexity theory of problems deals with decision problems. A decision problem always has a yes or no answer ...
CAP6938 Neuroevolution and Artificial Embryogeny Evolutionary
... • New genes appeared over biological evolution as well • Nature has a solution to still know which is which – Process of aligning and matching genes is called synapsis – Uses homology to align genes: “. . .Crossing over thus generates homologous recombination; that is, it occurs between 2 regions of ...
... • New genes appeared over biological evolution as well • Nature has a solution to still know which is which – Process of aligning and matching genes is called synapsis – Uses homology to align genes: “. . .Crossing over thus generates homologous recombination; that is, it occurs between 2 regions of ...
STAT 361: Computational Statistics
... Resampling. Data partitioning. Cross-validation. Bootstraping. Jackknifing. ...
... Resampling. Data partitioning. Cross-validation. Bootstraping. Jackknifing. ...
Bayesian Network and Influence Diagram
... Expert System if the system’s problem solving ability is restricted to particular area • The techniques that enable us to construct devices and services that are able to – Perform reasoning and decision making under uncertainty – Acquire knowledge from data/experience – Solve problems efficiently an ...
... Expert System if the system’s problem solving ability is restricted to particular area • The techniques that enable us to construct devices and services that are able to – Perform reasoning and decision making under uncertainty – Acquire knowledge from data/experience – Solve problems efficiently an ...
Lecture 1
... that could perform basic mathematical functions such as, addition, subtraction, division and multiplication. ...
... that could perform basic mathematical functions such as, addition, subtraction, division and multiplication. ...
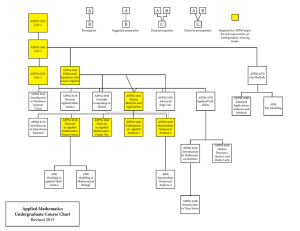
Chart of Course Options
... Required for APPM major. For full requirements see Undergraduate Advising Guide. ...
... Required for APPM major. For full requirements see Undergraduate Advising Guide. ...
Herbert A. Simon - History Committee archive
... computational theory of human intelligence. The two chess programs Simon has constructed with colleagues (the NSS program with Newell and Shaw [1958], and the MATER program with George W. Baylor) contrast with more powerful programs like DeepThought and HighTech, the former modeling highly selective ...
... computational theory of human intelligence. The two chess programs Simon has constructed with colleagues (the NSS program with Newell and Shaw [1958], and the MATER program with George W. Baylor) contrast with more powerful programs like DeepThought and HighTech, the former modeling highly selective ...
Metody Inteligencji Obliczeniowej
... • no need for vector spaces (structured objects), • more general than fuzzy approach (F-rules are reduced to P-rules), • includes kNN, MLPs, RBFs, separable function networks, SVMs, kernel methods and many others! Components => Models; systematic search selects optimal combination of parameters and ...
... • no need for vector spaces (structured objects), • more general than fuzzy approach (F-rules are reduced to P-rules), • includes kNN, MLPs, RBFs, separable function networks, SVMs, kernel methods and many others! Components => Models; systematic search selects optimal combination of parameters and ...
Lesson Plan: Quantum Mechanics
... a discussion of the role of predictability in science, the nature of causality and the relationship between physics and metaphysics. Slides 4 and 5 from PowerPoint Resource 2: ‘What is Quantum Theory?’ stress the difference between quantum theory and Newtonian mechanics especially in regard to what ...
... a discussion of the role of predictability in science, the nature of causality and the relationship between physics and metaphysics. Slides 4 and 5 from PowerPoint Resource 2: ‘What is Quantum Theory?’ stress the difference between quantum theory and Newtonian mechanics especially in regard to what ...
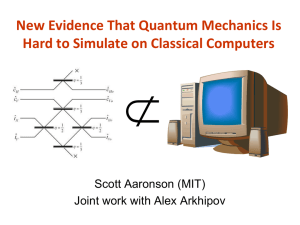
Another version - Scott Aaronson
... Shepherd, Bremner 2009: “Instantaneous quantum computing” can solve sampling problems that might be hard classically Bremner, Jozsa, Shepherd 2010: Efficient simulation of instantaneous quantum computing would collapse PH ...
... Shepherd, Bremner 2009: “Instantaneous quantum computing” can solve sampling problems that might be hard classically Bremner, Jozsa, Shepherd 2010: Efficient simulation of instantaneous quantum computing would collapse PH ...
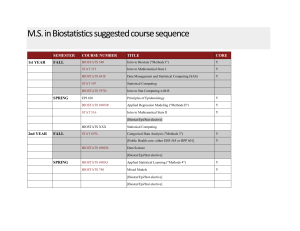
M.S. in Biostatistics suggested course sequence
... M.S. in Biostatistics suggested course sequence 1st YEAR ...
... M.S. in Biostatistics suggested course sequence 1st YEAR ...
Embedded Algorithm in Hardware: A Scalable Compact Genetic
... obtain solutions starting from a set of candidate solutions, using improving operators to “evolve” solutions. Improving operators are inspired by natural evolution. ...
... obtain solutions starting from a set of candidate solutions, using improving operators to “evolve” solutions. Improving operators are inspired by natural evolution. ...
Extremely Large-Ratio Quantum Down Conversion
... Department of Physics, Harvard University, 2Department of Physics, Stanford University, 3Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, ...
... Department of Physics, Harvard University, 2Department of Physics, Stanford University, 3Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, ...
Genetic Algorithms
... the first part of the second (genomes are divided in random position) 1. Select pairs of genomes and flipping a coin to determine whether they split and swap. 2. If they do crossover, then a random position is chosen and the children of the original genomes replace them in the next generation 3. Rep ...
... the first part of the second (genomes are divided in random position) 1. Select pairs of genomes and flipping a coin to determine whether they split and swap. 2. If they do crossover, then a random position is chosen and the children of the original genomes replace them in the next generation 3. Rep ...
lecture #6
... cognitive psychology and computer science to develop artificial systems that display some aspects of humanlike intelligence ...
... cognitive psychology and computer science to develop artificial systems that display some aspects of humanlike intelligence ...
Collaborative Filtering
... • Tree Augmented naïve Bayes and naïve Bayes optimized by Extended Logic Regression (ELR) – Require extended training periods to produce results beyond simple Bayesian and Pearson correlation ...
... • Tree Augmented naïve Bayes and naïve Bayes optimized by Extended Logic Regression (ELR) – Require extended training periods to produce results beyond simple Bayesian and Pearson correlation ...
1. Layered Architecture of Communication Networks
... Why do we need Communication Networks? Need to communicate and share information among different devices Direct connectivity between each and every device is not feasible Direct connectivity between each and every device is not actually necessary ...
... Why do we need Communication Networks? Need to communicate and share information among different devices Direct connectivity between each and every device is not feasible Direct connectivity between each and every device is not actually necessary ...
Abstract - 1000kv technologies
... software and libraries transparently. The emerging technologies such as Web services [12] are expected to play a leading role in defining application services. They build on computational and data services provided by the Grid. An example system that can be used to develop such services is NetSolve ...
... software and libraries transparently. The emerging technologies such as Web services [12] are expected to play a leading role in defining application services. They build on computational and data services provided by the Grid. An example system that can be used to develop such services is NetSolve ...
Introduction to knowledge-based systems
... - Neural Networks can be : - Biological models - Artificial models ...
... - Neural Networks can be : - Biological models - Artificial models ...
Test Bank #1
... C- games may generate extremely large and complex search spaces. D- such games have well-defined set of rules making state space generation easier. 22- Heuristics in A.I. refers to A- playing board games that may generate extremely large & complex search space. B- techniques for determining what alt ...
... C- games may generate extremely large and complex search spaces. D- such games have well-defined set of rules making state space generation easier. 22- Heuristics in A.I. refers to A- playing board games that may generate extremely large & complex search space. B- techniques for determining what alt ...
EX3504-03
... b. Gaussian software package is a most popular quantum chemistry software in the field of computational chemistry. Please write down an input file of a Hartree-Fock calculation for the ground state of a CO2 molecule. ...
... b. Gaussian software package is a most popular quantum chemistry software in the field of computational chemistry. Please write down an input file of a Hartree-Fock calculation for the ground state of a CO2 molecule. ...