Introduction - Wave Structure of Matter (WSM)
... of the space-resonance is transformed into an outward spherical wave when it arrives at the wave-center. The only way that Nature allows this to happen in the geometry of 3D space is by a spherical rotation, or phase shift of the spherical in-wave, using the SU(2) group math above. The amount of pha ...
... of the space-resonance is transformed into an outward spherical wave when it arrives at the wave-center. The only way that Nature allows this to happen in the geometry of 3D space is by a spherical rotation, or phase shift of the spherical in-wave, using the SU(2) group math above. The amount of pha ...
Physics of Polarized Protons/Electrons in Accelerators
... For an ideal machine, i.e. the closed orbit is zero, the stable spin direction is along the direction of the guiding field The stable spin direction n̂0 for a particle on the closed orbit is the eigenvector of its one turn spin transfer matrix ...
... For an ideal machine, i.e. the closed orbit is zero, the stable spin direction is along the direction of the guiding field The stable spin direction n̂0 for a particle on the closed orbit is the eigenvector of its one turn spin transfer matrix ...
Rotational Spectroscopy of Diatomic Molecules - Assets
... Molecular spectroscopy involves the study of the absorption or emission of electromagnetic radiation by matter; the radiation may be detected directly, or indirectly through its effects on other molecular properties. The primary purpose of spectroscopic studies is to understand the nature of the nuc ...
... Molecular spectroscopy involves the study of the absorption or emission of electromagnetic radiation by matter; the radiation may be detected directly, or indirectly through its effects on other molecular properties. The primary purpose of spectroscopic studies is to understand the nature of the nuc ...
Negative photoconductivity due to coherent trapping of electrons in
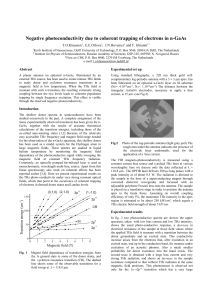
... intensity: saturation of the 2p+1 and the CR transition. The influence of the bias current at constant maximum THz intensity is presented in fig. 5. With increasing bias current the sample resistance in the absence of THz radiation decreases strongly. (the increase with increasing B-field is due to ...
... intensity: saturation of the 2p+1 and the CR transition. The influence of the bias current at constant maximum THz intensity is presented in fig. 5. With increasing bias current the sample resistance in the absence of THz radiation decreases strongly. (the increase with increasing B-field is due to ...
ece477_4_0
... c) Variations in the refractive index; the lower refractive index of the material in regions 1 and 5 creates an optical barrier around the waveguide because of the higher band-gap energy of this material. ...
... c) Variations in the refractive index; the lower refractive index of the material in regions 1 and 5 creates an optical barrier around the waveguide because of the higher band-gap energy of this material. ...
Absence of spin liquid in non-frustrated correlated systems
... over wavevectors. We compute N (ω + iη) at ω = 0 for a few values of the Lorenzian broadening η and extrapolate η → 0 using a polynomial fit. The result of this extrapolation should vanish in the insulating solution, but not in the metallic solution. This extrapolated density of states is shown (das ...
... over wavevectors. We compute N (ω + iη) at ω = 0 for a few values of the Lorenzian broadening η and extrapolate η → 0 using a polynomial fit. The result of this extrapolation should vanish in the insulating solution, but not in the metallic solution. This extrapolated density of states is shown (das ...
1 Introduction - Wiley-VCH
... noninteracting model, which was sufficient for the simple Ni2+ system described above, was not working in many cases. Real life required to go beyond paramagnetism, to explore the interacting systems in which the magnetic properties require the presence of unpaired electrons that must weakly interact ...
... noninteracting model, which was sufficient for the simple Ni2+ system described above, was not working in many cases. Real life required to go beyond paramagnetism, to explore the interacting systems in which the magnetic properties require the presence of unpaired electrons that must weakly interact ...
Mathematical structure of magnons in quantum
... representation of the low-temperature elementary excitations of a spin system. The basic steps in the understanding of this phenomenon were made by Bloch [1], Holstein–Primakoff [2], van Kramendonk–van Vleck [3] and, in the more technical work, by Dyson [4, 5]. From the point of view of mathematical ...
... representation of the low-temperature elementary excitations of a spin system. The basic steps in the understanding of this phenomenon were made by Bloch [1], Holstein–Primakoff [2], van Kramendonk–van Vleck [3] and, in the more technical work, by Dyson [4, 5]. From the point of view of mathematical ...
Nitrogen-vacancy center

The nitrogen-vacancy center (N-V center) is one of numerous point defects in diamond. Its most explored and useful property is photoluminescence, which can be easily detected from an individual N-V center, especially those in the negative charge state (N-V−). Electron spins at N-V centers, localized at atomic scales, can be manipulated at room temperature by applying a magnetic field, electric field, microwave radiation or light, or a combination, resulting in sharp resonances in the intensity and wavelength of the photoluminescence. These resonances can be explained in terms of electron spin related phenomena such as quantum entanglement, spin-orbit interaction and Rabi oscillations, and analysed using advanced quantum optics theory. An individual N-V center can be viewed as a basic unit of a quantum computer, and it has potential applications in novel, more efficient fields of electronics and computational science including quantum cryptography and spintronics.