Lecture 8a - Magnetism
... Velocity selector, or filter: crossed E and B fields. Some electronic devices and experiments need a beam of charged particles all moving at nearly the same velocity. This can be achieved using both a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field, arranged so they are at right angles to each o ...
... Velocity selector, or filter: crossed E and B fields. Some electronic devices and experiments need a beam of charged particles all moving at nearly the same velocity. This can be achieved using both a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field, arranged so they are at right angles to each o ...
Synthesis of Macrocyclic Complexes of Nickel(II)
... Determination of Magnetic Susceptibility The magnetic susceptibility of a substance has traditionally been determined by measuring the change in the behavior of a sample when placed in a magnetic field. There are a number of ways of detecting this change. The classical (Gouy) method involves the det ...
... Determination of Magnetic Susceptibility The magnetic susceptibility of a substance has traditionally been determined by measuring the change in the behavior of a sample when placed in a magnetic field. There are a number of ways of detecting this change. The classical (Gouy) method involves the det ...
PowerPoint
... cannot change a charged particle’s potential energy or electric potential. But electric fields can do work. This equation shows that a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field, which can change a charged particle’s potential energy. This induced electric field is responsible for induced emf. ...
... cannot change a charged particle’s potential energy or electric potential. But electric fields can do work. This equation shows that a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field, which can change a charged particle’s potential energy. This induced electric field is responsible for induced emf. ...
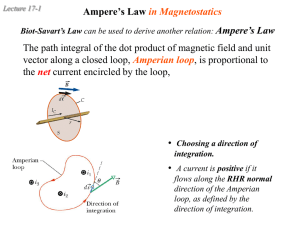
Magnetism
... pushes them to the right (labeled "R") side of the strip. This accumulates negative charge on the R-sid e and leaves the left side (labeled "L") of the strip positively charged. As a result of the accumulated charge, an electric field E is generated as shown in the figure so that the electric force ...
... pushes them to the right (labeled "R") side of the strip. This accumulates negative charge on the R-sid e and leaves the left side (labeled "L") of the strip positively charged. As a result of the accumulated charge, an electric field E is generated as shown in the figure so that the electric force ...
ppt document - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
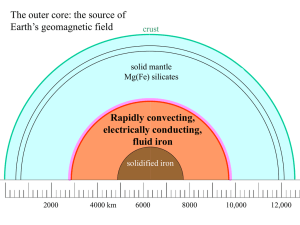
... unlike poles attract, just as electric charges do. However, unlike charges, we always have two poles! If we break a magnet (which has two poles) in half, we have not separated the two poles, rather we have two (smaller) magnets that both have two poles! ...
... unlike poles attract, just as electric charges do. However, unlike charges, we always have two poles! If we break a magnet (which has two poles) in half, we have not separated the two poles, rather we have two (smaller) magnets that both have two poles! ...