Ohms Law Ohmic Resistors versus Lightbulbs
... collide with the atoms in their paths. This opposition is called the resistance of the wire. The total resistance of a circuit can be related to the ratio of the potential difference applied to the ends of the wire to the current flowing through it, or R = r L / A = V/I ...
... collide with the atoms in their paths. This opposition is called the resistance of the wire. The total resistance of a circuit can be related to the ratio of the potential difference applied to the ends of the wire to the current flowing through it, or R = r L / A = V/I ...
Basic Principles of Electricity
... • Measured as pulses per second (PPS) Individual pulse = rise and fall in amplitude As frequency ___________, amplitude ...
... • Measured as pulses per second (PPS) Individual pulse = rise and fall in amplitude As frequency ___________, amplitude ...
High Power RF Lightning Protection
... connector. Standard protectors on the market have reduced geometry internals, providing power capability more similar to N connectors. The center conductor will predominate in heat generation since it has a much smaller circumference than the inner surface of the outer conductor. Dielectric dissipat ...
... connector. Standard protectors on the market have reduced geometry internals, providing power capability more similar to N connectors. The center conductor will predominate in heat generation since it has a much smaller circumference than the inner surface of the outer conductor. Dielectric dissipat ...
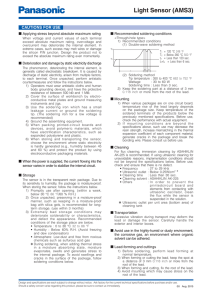
RF3376 - Qorvo
... Care should also be taken in the resistor selection to ensure that the current into the part never exceeds 40mA over the planned operating temperature. This means that a resistor between the supply and this pin is always required, even if a supply near 3.4V is available, to provide DC feedback to pr ...
... Care should also be taken in the resistor selection to ensure that the current into the part never exceeds 40mA over the planned operating temperature. This means that a resistor between the supply and this pin is always required, even if a supply near 3.4V is available, to provide DC feedback to pr ...
Chapter 25 – Current, Resistance and Electromotive Force
... a circuit, the potential rise ε as it passes through the ideal source is equal to the potential drop Vab as it passes through reminder of circuit. -The current is same at every point of a circuit, even if wire thickness different at different points of circuit. Charge is conserved and cannot be accu ...
... a circuit, the potential rise ε as it passes through the ideal source is equal to the potential drop Vab as it passes through reminder of circuit. -The current is same at every point of a circuit, even if wire thickness different at different points of circuit. Charge is conserved and cannot be accu ...
Section 16.3 - CPO Science
... The current in a circuit depends on voltage and resistance. Ohm’s law relates current, voltage, and resistance with one formula. If you know two of the three quantities, you can use Ohm’s law to find the third. ...
... The current in a circuit depends on voltage and resistance. Ohm’s law relates current, voltage, and resistance with one formula. If you know two of the three quantities, you can use Ohm’s law to find the third. ...
Potential difference - School
... Metal atoms (ions) in a wire have delocalised electrons which are free to move and carry the electric current around the circuit. The electrons moving around the circuit collide with the ions. This is called resistance. Components with high resistance (e.g. filament bulbs) often get hot. This is bec ...
... Metal atoms (ions) in a wire have delocalised electrons which are free to move and carry the electric current around the circuit. The electrons moving around the circuit collide with the ions. This is called resistance. Components with high resistance (e.g. filament bulbs) often get hot. This is bec ...
Unit 51: Electrical Technology
... mobile, as in a solid salt then electrolysis cannot occur. – A direct current (DC) supply : provides the energy necessary to create or discharge the ions in the electrolyte. Electric current is carried by electrons in the external circuit. – Two electrodes : an electrical conductor which provides th ...
... mobile, as in a solid salt then electrolysis cannot occur. – A direct current (DC) supply : provides the energy necessary to create or discharge the ions in the electrolyte. Electric current is carried by electrons in the external circuit. – Two electrodes : an electrical conductor which provides th ...
TEemperature Sensor
... parasitic thermocouple junctions formed where the thermocouple wire is connected to the measuring instrument. To accurately measure temperature at the junction of interest, you must compensate for the effects of these parasitic cold junctions. • The classical solution is to make an additional refere ...
... parasitic thermocouple junctions formed where the thermocouple wire is connected to the measuring instrument. To accurately measure temperature at the junction of interest, you must compensate for the effects of these parasitic cold junctions. • The classical solution is to make an additional refere ...
TEemperature Sensor - Gadjah Mada University
... parasitic thermocouple junctions formed where the thermocouple wire is connected to the measuring instrument. To accurately measure temperature at the junction of interest, you must compensate for the effects of these parasitic cold junctions. • The classical solution is to make an additional refere ...
... parasitic thermocouple junctions formed where the thermocouple wire is connected to the measuring instrument. To accurately measure temperature at the junction of interest, you must compensate for the effects of these parasitic cold junctions. • The classical solution is to make an additional refere ...
Thermal runaway

Thermal runaway refers to a situation where an increase in temperature changes the conditions in a way that causes a further increase in temperature, often leading to a destructive result. It is a kind of uncontrolled positive feedback.In other words, ""thermal runaway"" describes a process which is accelerated by increased temperature, in turn releasing energy that further increases temperature. In chemistry (and chemical engineering), this risk is associated with strongly exothermic reactions that are accelerated by temperature rise. In electrical engineering, thermal runaway is typically associated with increased current flow and power dissipation, although exothermic chemical reactions can be of concern here too. Thermal runaway can occur in civil engineering, notably when the heat released by large amounts of curing concrete is not controlled. In astrophysics, runaway nuclear fusion reactions in stars can lead to nova and several types of supernova explosions, and also occur as a less dramatic event in the normal evolution of solar mass stars, the ""helium flash"".There are also concerns regarding global warming that a global average increase of 3-4 degrees Celsius above the preindustrial baseline could lead to a further unchecked increase in surface temperatures. For example, releases of methane, a greenhouse gas more potent than CO2, from wetlands, melting permafrost and continental margin seabed clathrate deposits could be subject to positive feedback.