Lab_Thermometric properties
... multimeter is used to measure the voltage as shown, then you have the makings for a digital thermometer. As with all thermometer scales, you will need to calibrate this thermometer by using a standard thermometer and creating some type of reference chart. This type of temperature probe is extremely ...
... multimeter is used to measure the voltage as shown, then you have the makings for a digital thermometer. As with all thermometer scales, you will need to calibrate this thermometer by using a standard thermometer and creating some type of reference chart. This type of temperature probe is extremely ...
P2.3 Current Electricity
... – You can state Ohm’s law. – Some will be able to rearrange the resistance equation. ...
... – You can state Ohm’s law. – Some will be able to rearrange the resistance equation. ...
DTDG14GP
... The products listed in this document are designed to be used with ordinary electronic equipment or devices (such as audio visual equipment, office-automation equipment, communications devices, electrical appliances and electronic toys). Should you intend to use these products with equipment or devic ...
... The products listed in this document are designed to be used with ordinary electronic equipment or devices (such as audio visual equipment, office-automation equipment, communications devices, electrical appliances and electronic toys). Should you intend to use these products with equipment or devic ...
Dual Low-Voltage H-Bridge IC, DRV8835
... RMS output current being applied to each winding. IOUT(RMS) is equal to the approximately 0.7x the full-scale output current setting. The factor of 2 comes from the fact that there are two H-bridges. The maximum amount of power that can be dissipated in the device is dependent on ambient temperature ...
... RMS output current being applied to each winding. IOUT(RMS) is equal to the approximately 0.7x the full-scale output current setting. The factor of 2 comes from the fact that there are two H-bridges. The maximum amount of power that can be dissipated in the device is dependent on ambient temperature ...
Unit 3(Current Electricity)
... (a) The errors of measurement of the two students are the same. (b) Errors of measurement do depend on the accuracy with which R2 and R1 can be measured. (c) If the student uses large values of R2 and R1, the currents through the arms will be feeble. This will make determination of null point accura ...
... (a) The errors of measurement of the two students are the same. (b) Errors of measurement do depend on the accuracy with which R2 and R1 can be measured. (c) If the student uses large values of R2 and R1, the currents through the arms will be feeble. This will make determination of null point accura ...
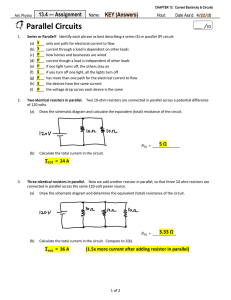
Parallel Circuits - Mr. Britton / FHS Physics
... Series or Parallel? Identify each phrase as best describing a series (S) or parallel (P) circuit: (a) ...
... Series or Parallel? Identify each phrase as best describing a series (S) or parallel (P) circuit: (a) ...
Presentation_12
... If an electric field is set up in a conductor, charge will move (making a current in direction of E) ...
... If an electric field is set up in a conductor, charge will move (making a current in direction of E) ...
NTC Inrush Current Limiter
... balance in the differential equation already given reduces to the following heat balance formula: Power = I2R = δ(T – TA) As more current flows through the device, its steady-state operating temperature will increase and its resistance will decrease. The maximum current rating correlates to a maximu ...
... balance in the differential equation already given reduces to the following heat balance formula: Power = I2R = δ(T – TA) As more current flows through the device, its steady-state operating temperature will increase and its resistance will decrease. The maximum current rating correlates to a maximu ...
stripfet iii and optimal choice of mosfets in high current vrms
... and conduction losses due to the step-down conversion are both critical even if the weights are different for the upper and lower devices. In typical conditions the resulting duty factor is lower than 15% meaning the low-side FET is conducting the other 85% of the time. Moreover I2R conduction losse ...
... and conduction losses due to the step-down conversion are both critical even if the weights are different for the upper and lower devices. In typical conditions the resulting duty factor is lower than 15% meaning the low-side FET is conducting the other 85% of the time. Moreover I2R conduction losse ...
Voltage-Dependent Capacitors in Power Electronic Multi
... A typical example for a multi-domain simulation is the transient calculation of the junction temperature of a power switch during converter operation. The losses of the switch are temperature dependent which has an impact on the converter efficiency and its electrical behaviour, and the electrical b ...
... A typical example for a multi-domain simulation is the transient calculation of the junction temperature of a power switch during converter operation. The losses of the switch are temperature dependent which has an impact on the converter efficiency and its electrical behaviour, and the electrical b ...
Thermal runaway

Thermal runaway refers to a situation where an increase in temperature changes the conditions in a way that causes a further increase in temperature, often leading to a destructive result. It is a kind of uncontrolled positive feedback.In other words, ""thermal runaway"" describes a process which is accelerated by increased temperature, in turn releasing energy that further increases temperature. In chemistry (and chemical engineering), this risk is associated with strongly exothermic reactions that are accelerated by temperature rise. In electrical engineering, thermal runaway is typically associated with increased current flow and power dissipation, although exothermic chemical reactions can be of concern here too. Thermal runaway can occur in civil engineering, notably when the heat released by large amounts of curing concrete is not controlled. In astrophysics, runaway nuclear fusion reactions in stars can lead to nova and several types of supernova explosions, and also occur as a less dramatic event in the normal evolution of solar mass stars, the ""helium flash"".There are also concerns regarding global warming that a global average increase of 3-4 degrees Celsius above the preindustrial baseline could lead to a further unchecked increase in surface temperatures. For example, releases of methane, a greenhouse gas more potent than CO2, from wetlands, melting permafrost and continental margin seabed clathrate deposits could be subject to positive feedback.