Temperature Considerations for DC Relays
... appropriate relay data. It must be stressed that the values obtained here apply to DC relays operated continuously at these values. Intermittent duty (with short, i.e. less than 1 minute, “on” times and longer “off” times) may result in substantially lower temperatures. Therefore if a specific known ...
... appropriate relay data. It must be stressed that the values obtained here apply to DC relays operated continuously at these values. Intermittent duty (with short, i.e. less than 1 minute, “on” times and longer “off” times) may result in substantially lower temperatures. Therefore if a specific known ...
Document
... Lightning is spectacular example pf electric current in a natural phenomenon. There is much variability to lightning bolts, but a typical event can transfer 109 J of energy across a potential difference of perhaps 5x107 V during a time interval of about 0.2 s. Use this information to estimate (a) th ...
... Lightning is spectacular example pf electric current in a natural phenomenon. There is much variability to lightning bolts, but a typical event can transfer 109 J of energy across a potential difference of perhaps 5x107 V during a time interval of about 0.2 s. Use this information to estimate (a) th ...
Slide 1
... special semiconductor materials, which are optimized for the Seebeck effect. The simplest thermoelectric power generator consists of a thermocouple, comprising a p-type and n-type material connected electrically in series and thermally in parallel. Heat is applied into one side of the couple and rej ...
... special semiconductor materials, which are optimized for the Seebeck effect. The simplest thermoelectric power generator consists of a thermocouple, comprising a p-type and n-type material connected electrically in series and thermally in parallel. Heat is applied into one side of the couple and rej ...
EUP7982 300mA Low-Noise Ultra Low-Dropout CMOS Regulator with Fault Indicator
... ground significantly reduces noise on the regulator output. This cap is connected directly to a high impedance node in the bandgap reference circuit. Any significant loading on this node will cause a change on the regulated output voltage. For this reason, DC leakage current through this pin must be ...
... ground significantly reduces noise on the regulator output. This cap is connected directly to a high impedance node in the bandgap reference circuit. Any significant loading on this node will cause a change on the regulated output voltage. For this reason, DC leakage current through this pin must be ...
lines of 150 kV XLPE power cables at 2.5 m depth
... (OHL) conductor. Cables can be installed using duct, tunnel or pipes, we called closed type, and by direct buried method we called open type. In several big cities of developed countries, high-voltage cable transmission lines have been used through the tunnel. The tunnel is in addition to the power ...
... (OHL) conductor. Cables can be installed using duct, tunnel or pipes, we called closed type, and by direct buried method we called open type. In several big cities of developed countries, high-voltage cable transmission lines have been used through the tunnel. The tunnel is in addition to the power ...
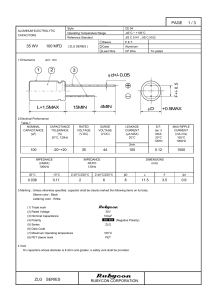
φd+/-0.05
... trouble that high leakage current possibly causes, voltage treatment is recommended for the capacitors that have been stored for a long time.
*Aluminum electrolytic capacitors should not be stored in high temperatures or where there is a high level of humidity. The suitable
stora ...
... trouble that high leakage current possibly causes, voltage treatment is recommended for the capacitors that have been stored for a long time.
FMB3906 MMPQ3906 FFB3906 PNP Multi-Chip General Purpose Amplifier
... PNP Multi-Chip General Purpose Amplifier This device is designed for general purpose amplifier and switching applications at collector currents of 10 µA to 100 mA. Sourced from Process 66. ...
... PNP Multi-Chip General Purpose Amplifier This device is designed for general purpose amplifier and switching applications at collector currents of 10 µA to 100 mA. Sourced from Process 66. ...
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
... The resistance of some semiconducting materials actually decreases with increasing temperature These materials are often found in high-resolution detection devices for optical measurements or particle detectors ...
... The resistance of some semiconducting materials actually decreases with increasing temperature These materials are often found in high-resolution detection devices for optical measurements or particle detectors ...
Course Lectures of Basics of Electrical Engineering Electrical
... (iii) to decrease the resistance of insulators (such as paper, rubber, glass, mica etc.) and partial conductors such as carbon. the temperature-coefficient of a material (α) may be defined as : A constant which represents the increase in resistance per ohm original resistance (per °C) rise in temper ...
... (iii) to decrease the resistance of insulators (such as paper, rubber, glass, mica etc.) and partial conductors such as carbon. the temperature-coefficient of a material (α) may be defined as : A constant which represents the increase in resistance per ohm original resistance (per °C) rise in temper ...
Electric Current (KW)
... The DIFFERENCE in POTENTIAL (energy) per unit ………………. of the current flowing between two points in the circuit. Measured by a ………………... ...
... The DIFFERENCE in POTENTIAL (energy) per unit ………………. of the current flowing between two points in the circuit. Measured by a ………………... ...
BUL129D
... UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED ...
... UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED ...
Thermal runaway

Thermal runaway refers to a situation where an increase in temperature changes the conditions in a way that causes a further increase in temperature, often leading to a destructive result. It is a kind of uncontrolled positive feedback.In other words, ""thermal runaway"" describes a process which is accelerated by increased temperature, in turn releasing energy that further increases temperature. In chemistry (and chemical engineering), this risk is associated with strongly exothermic reactions that are accelerated by temperature rise. In electrical engineering, thermal runaway is typically associated with increased current flow and power dissipation, although exothermic chemical reactions can be of concern here too. Thermal runaway can occur in civil engineering, notably when the heat released by large amounts of curing concrete is not controlled. In astrophysics, runaway nuclear fusion reactions in stars can lead to nova and several types of supernova explosions, and also occur as a less dramatic event in the normal evolution of solar mass stars, the ""helium flash"".There are also concerns regarding global warming that a global average increase of 3-4 degrees Celsius above the preindustrial baseline could lead to a further unchecked increase in surface temperatures. For example, releases of methane, a greenhouse gas more potent than CO2, from wetlands, melting permafrost and continental margin seabed clathrate deposits could be subject to positive feedback.