pdf
... technique that allows the interactions between ultracold atoms to be controlled, thus making a true fermionic condensate possible. This technique takes advantage of resonant scattering between atoms, and allows the strength of the interactions between the atoms to be tuned with an external magnetic ...
... technique that allows the interactions between ultracold atoms to be controlled, thus making a true fermionic condensate possible. This technique takes advantage of resonant scattering between atoms, and allows the strength of the interactions between the atoms to be tuned with an external magnetic ...
Part II - TTU Physics
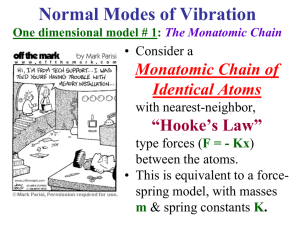
... contain considerable qualitative physics that carries over to the observed vibrational frequencies for many real materials. • So, much of the physics contained in the diatomic chain results can teach us something about the physics contained in the normal modes of many real materials. • In particular ...
... contain considerable qualitative physics that carries over to the observed vibrational frequencies for many real materials. • So, much of the physics contained in the diatomic chain results can teach us something about the physics contained in the normal modes of many real materials. • In particular ...
Beam Dynamics in High Energy Colliders
... without getting dizzy" twist and turn so as to give an intended interpretation, "The President's spokesmen had to spin the story to make it less embarrassing" a distinctive interpretation (especially as used by politicians to sway public opinion), "the campaign put a favorable spin on the story" ...
... without getting dizzy" twist and turn so as to give an intended interpretation, "The President's spokesmen had to spin the story to make it less embarrassing" a distinctive interpretation (especially as used by politicians to sway public opinion), "the campaign put a favorable spin on the story" ...
Quantum Measurements with Dynamically Bistable Systems
... < 1. This means that the intensity of phase fluctuations may be We assume that κ ph ∼ comparable to the intensity of quantum fluctuations associated with damping, which is ∝ λ Γ , see below, but that Γ ph ≪ Γ . Metastable decay was studied earlier for additively and parametrically driven oscillators ...
... < 1. This means that the intensity of phase fluctuations may be We assume that κ ph ∼ comparable to the intensity of quantum fluctuations associated with damping, which is ∝ λ Γ , see below, but that Γ ph ≪ Γ . Metastable decay was studied earlier for additively and parametrically driven oscillators ...
Poster 1
... curve is below the red line Thus we have observed some polarization entanglement 1000s of data per curve, taken while sweeping the cavity ...
... curve is below the red line Thus we have observed some polarization entanglement 1000s of data per curve, taken while sweeping the cavity ...
XIII. GRAVITATION RESEARCH Academic and Research Staff Prof
... The apparatus is shown in Fig. XIII-1. 5145 Alight from a single longitudinal-mode Argon ion laser is passed through a molecular beam of 12 at right angles. The laserinduced resonance fluorescence is detected on a photmuliplier located below the interaction region. Figure XIII-2 shows the resonance ...
... The apparatus is shown in Fig. XIII-1. 5145 Alight from a single longitudinal-mode Argon ion laser is passed through a molecular beam of 12 at right angles. The laserinduced resonance fluorescence is detected on a photmuliplier located below the interaction region. Figure XIII-2 shows the resonance ...
Resonance
In physics, resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when a given system is driven by another vibrating system or external force to oscillate with greater amplitude at a specific preferential frequency.Frequencies at which the response amplitude is a relative maximum are known as the system's resonant frequencies, or resonance frequencies. At resonant frequencies, small periodic driving forces have the ability to produce large amplitude oscillations. This is because the system stores vibrational energy.Resonance occurs when a system is able to store and easily transfer energy between two or more different storage modes (such as kinetic energy and potential energy in the case of a pendulum). However, there are some losses from cycle to cycle, called damping. When damping is small, the resonant frequency is approximately equal to the natural frequency of the system, which is a frequency of unforced vibrations. Some systems have multiple, distinct, resonant frequencies.Resonance phenomena occur with all types of vibrations or waves: there is mechanical resonance, acoustic resonance, electromagnetic resonance, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), electron spin resonance (ESR) and resonance of quantum wave functions. Resonant systems can be used to generate vibrations of a specific frequency (e.g., musical instruments), or pick out specific frequencies from a complex vibration containing many frequencies (e.g., filters).The term Resonance (from Latin resonantia, 'echo', from resonare, 'resound') originates from the field of acoustics, particularly observed in musical instruments, e.g. when strings started to vibrate and to produce sound without direct excitation by the player.