A Simply Regularized Derivation of the Casimir Force
... Therefore, the Hamiltonian operator for the EM fields is equivalent to the Hamiltonian operator for a system of infinite number of independent oscillators. The lowest energy, the zero-point energy (quantum field theoretically: the vacuum energy), for one mode is 12 ~ω = 21 ~ck; thus, since there are ...
... Therefore, the Hamiltonian operator for the EM fields is equivalent to the Hamiltonian operator for a system of infinite number of independent oscillators. The lowest energy, the zero-point energy (quantum field theoretically: the vacuum energy), for one mode is 12 ~ω = 21 ~ck; thus, since there are ...
Bound States in the Compactified Gravity
... levels. A black hole creation in LHC (Krasnikov & Matveev, 2004) could be the first expected example. Explanation of how multidimensionality influences the gravitation does not need necessarily a framework of the string theory, Kaluza-Klein theory or even general relativity. In the present paper, th ...
... levels. A black hole creation in LHC (Krasnikov & Matveev, 2004) could be the first expected example. Explanation of how multidimensionality influences the gravitation does not need necessarily a framework of the string theory, Kaluza-Klein theory or even general relativity. In the present paper, th ...
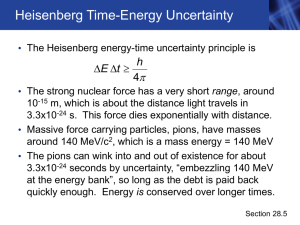
Chapter 28 - Purdue Physics
... The STM can form images of individual atoms even though the tip is larger than the atoms Section 28.6 ...
... The STM can form images of individual atoms even though the tip is larger than the atoms Section 28.6 ...
Objective of the course Aim of the course is to introduce the basic
... Objective of the course Aim of the course is to introduce the basic notions of non-relativistic quantum mechanics and its interpretation. At the end of the course the students should: 1) have understood the definition of physical state and the superposition principle in quantum mechanics, the defini ...
... Objective of the course Aim of the course is to introduce the basic notions of non-relativistic quantum mechanics and its interpretation. At the end of the course the students should: 1) have understood the definition of physical state and the superposition principle in quantum mechanics, the defini ...
x 100 QUANTUM NUMBERS AND SYMBOLS
... 5. What type of orbital in an atom is designated by quantum numbers n=4, l =3, and ml =0? 6. A subshell in an atom has the values, n = 3, l =2. How many orbitals are there in this ...
... 5. What type of orbital in an atom is designated by quantum numbers n=4, l =3, and ml =0? 6. A subshell in an atom has the values, n = 3, l =2. How many orbitals are there in this ...
Exercise 1, from the final exam in AST4220, 2005 Exercise 2
... are not understood in detail and lack a solid empirical foundation. However, that doesn’t stop theorists from speculating about what a quantum version ...
... are not understood in detail and lack a solid empirical foundation. However, that doesn’t stop theorists from speculating about what a quantum version ...
Particle Notes
... This motivates us to think of (t, ~x ) as a four-vector that transforms according to the Lorentz transformations, in a “spacetime vector space,” and there should be some kind of “inner product,” or contraction, of these vectors that leaves ∆τ a scalar. This can be done by defining the Minkowski metr ...
... This motivates us to think of (t, ~x ) as a four-vector that transforms according to the Lorentz transformations, in a “spacetime vector space,” and there should be some kind of “inner product,” or contraction, of these vectors that leaves ∆τ a scalar. This can be done by defining the Minkowski metr ...
Microsoft PowerPoint
... – Davison and Germer’s electron-Nickel crystal scattering experiment supported Bohr-de-Broglie’s theorem (1927), so electrons are wave like, or matters (with nonzero static mass) can be wave like ...
... – Davison and Germer’s electron-Nickel crystal scattering experiment supported Bohr-de-Broglie’s theorem (1927), so electrons are wave like, or matters (with nonzero static mass) can be wave like ...
Quantum Communication: A real Enigma
... * Cover & Thomas, Elements of information theory. * Nielsen & Chuang, Quantum computation and quantum information. (and references therein) Part II: Papers available at arxiv.org: * Devetak, The private classical capacity and quantum capacity of a quantum channel, quant-ph/0304127 * Devetak, Harrow ...
... * Cover & Thomas, Elements of information theory. * Nielsen & Chuang, Quantum computation and quantum information. (and references therein) Part II: Papers available at arxiv.org: * Devetak, The private classical capacity and quantum capacity of a quantum channel, quant-ph/0304127 * Devetak, Harrow ...
Consider two point particles of mass m1 and m2 with position
... relative momentum is defined to be p~ = µ (~v1 − ~v2 ) . The expression for the kinetic energy in terms of the momenta is ...
... relative momentum is defined to be p~ = µ (~v1 − ~v2 ) . The expression for the kinetic energy in terms of the momenta is ...
Physics 880.06: Problem Set 5
... Physics 880.06: Problem Set 5 Due Tuesday, May 17 by 11:59 P. M. 1. Consider the Ginzburg-Landau differential equation for ψ as applied to an order parameter ψ which varies in only one spatial direction, say z. If there is no vector potential, this differential equation can be written h̄2 ′′ ψ (z) = ...
... Physics 880.06: Problem Set 5 Due Tuesday, May 17 by 11:59 P. M. 1. Consider the Ginzburg-Landau differential equation for ψ as applied to an order parameter ψ which varies in only one spatial direction, say z. If there is no vector potential, this differential equation can be written h̄2 ′′ ψ (z) = ...