Lecture ? Einstein-Debye theory
... There is a close analogy between photons and phonons: both are “unconserved” bosons. Distinctions: (a) the speed of propagation of phonons (~ the speed of sound waves) is by a factor of 105 less than that for light, (b) sound waves can be longitudinal as well as transversal, thus 3 polarizations (2 ...
... There is a close analogy between photons and phonons: both are “unconserved” bosons. Distinctions: (a) the speed of propagation of phonons (~ the speed of sound waves) is by a factor of 105 less than that for light, (b) sound waves can be longitudinal as well as transversal, thus 3 polarizations (2 ...
HOW DOES THE SUN GENERATE ENERGY? - IDC
... Matter is still in the form of plasma (the vast majority of hydrogen ions), but begins to have a behavior similar to an ocean. Convection processes occur where spin columns will generate large amounts of heat that carry hot materials to the photosphere of the Sun and other ionized atoms returning le ...
... Matter is still in the form of plasma (the vast majority of hydrogen ions), but begins to have a behavior similar to an ocean. Convection processes occur where spin columns will generate large amounts of heat that carry hot materials to the photosphere of the Sun and other ionized atoms returning le ...
Traditional versus PIN Diode Geiger Counter
... Everybody who attended school should know the photoelectric effect. Radiation from visible or invisible sources is able to break out electrons from specific materials that can be detected as a current. The resulting electrical energy of the emitted electrons is equivalent to the energy of the radiat ...
... Everybody who attended school should know the photoelectric effect. Radiation from visible or invisible sources is able to break out electrons from specific materials that can be detected as a current. The resulting electrical energy of the emitted electrons is equivalent to the energy of the radiat ...
Kinetic Molecular Theory KMT
... developed for subsonic commercial aviation. This advanced wing enhances the airplane's ability to climb quickly and cruise at higher altitudes than competing airplanes while achieving higher cruise speeds. It also allows the airplane to carry full passenger payloads out of many high-elevation, ...
... developed for subsonic commercial aviation. This advanced wing enhances the airplane's ability to climb quickly and cruise at higher altitudes than competing airplanes while achieving higher cruise speeds. It also allows the airplane to carry full passenger payloads out of many high-elevation, ...
Week 13 - Electromagnetic Waves
... a) By measuring the electric and magnetic fields at a point in space where there is an electromagnetic wave, can you determine the direction from which the wave came? Explain. Solution: Yes you can. Assuming you measured both the direction of the electric and the mangnetic field you can find the pro ...
... a) By measuring the electric and magnetic fields at a point in space where there is an electromagnetic wave, can you determine the direction from which the wave came? Explain. Solution: Yes you can. Assuming you measured both the direction of the electric and the mangnetic field you can find the pro ...
Stellar Atmospheres
... spectrum of the light generated here is dominated by Hwavelength. Temperature of Chromosphere is up to 20,000K. Transition Region: In the Sun, a region between the Chromosphere and Corona. Corona: In the Sun, a type of plasma atmosphere that extends millions of kilometers into space. High temperat ...
... spectrum of the light generated here is dominated by Hwavelength. Temperature of Chromosphere is up to 20,000K. Transition Region: In the Sun, a region between the Chromosphere and Corona. Corona: In the Sun, a type of plasma atmosphere that extends millions of kilometers into space. High temperat ...
Ch. 11: Gases
... In this chapter we will focus on a study of gases. Using prior knowledge, draw a molecular view of a solid, a liquid, and a gas. Explain the amount of movement of the molecules at each state of matter on the lines below the boxes. ...
... In this chapter we will focus on a study of gases. Using prior knowledge, draw a molecular view of a solid, a liquid, and a gas. Explain the amount of movement of the molecules at each state of matter on the lines below the boxes. ...
Inverse Square Law, Blackbody Radiation y
... The Inverse Square Law for Radiation The amount of energy emitted in one second by a source of light is called its luminosity and is measured in watts. A source of light with a luminosity of 1 watt emits one joule of energy per second. The luminosity of the Sun is 3.86×1026 watts. As light travels a ...
... The Inverse Square Law for Radiation The amount of energy emitted in one second by a source of light is called its luminosity and is measured in watts. A source of light with a luminosity of 1 watt emits one joule of energy per second. The luminosity of the Sun is 3.86×1026 watts. As light travels a ...
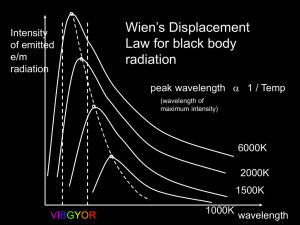
Blackbody Radiation, Stellar temperature and types
... Spectral types are OBAFGMK with a digit 0 to 9 in order from hottest (O1) to coolest (K9). A Roman numeral is added to the classification to indicate size: I = giant to V = dwarf. ...
... Spectral types are OBAFGMK with a digit 0 to 9 in order from hottest (O1) to coolest (K9). A Roman numeral is added to the classification to indicate size: I = giant to V = dwarf. ...
Document
... For a perfectly reflecting surface, p = 2 U / c and P = 2 S / c For a surface with a reflectivity somewhere between a perfect reflector and a perfect absorber, the momentum delivered to the surface will be somewhere in between U/c and 2U/c For direct sunlight, the radiation pressure is ...
... For a perfectly reflecting surface, p = 2 U / c and P = 2 S / c For a surface with a reflectivity somewhere between a perfect reflector and a perfect absorber, the momentum delivered to the surface will be somewhere in between U/c and 2U/c For direct sunlight, the radiation pressure is ...
The Dynamics of Small Bodies Dissipative and Radiation Forces
... the gegenshein. It is concentrated in the central Solar system, within Mars’s orbit. ❑ This dust should be removed by radiation effects in a time much smaller than the age of the Solar system. That it is still there, is an indication that it gets replenished frequently. ❑ Comet tails and asteroid co ...
... the gegenshein. It is concentrated in the central Solar system, within Mars’s orbit. ❑ This dust should be removed by radiation effects in a time much smaller than the age of the Solar system. That it is still there, is an indication that it gets replenished frequently. ❑ Comet tails and asteroid co ...
Dipole radiation during collisions
... scatter from a scattering center? For unit current density (1 particle per unit time across unit area of beam cross section) ...
... scatter from a scattering center? For unit current density (1 particle per unit time across unit area of beam cross section) ...
Radiation pressure

Radiation pressure is the pressure exerted upon any surface exposed to electromagnetic radiation. Radiation pressure implies an interaction between electromagnetic radiation and bodies of various types, including clouds of particles or gases. The interactions can be absorption, reflection, or some of both (the common case). Bodies also emit radiation and thereby experience a resulting pressure.The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too small to be detected under everyday circumstances; however, they do play a crucial role in some settings, such as astronomy and astrodynamics. For example, had the effects of the sun's radiation pressure on the spacecraft of the Viking program been ignored, the spacecraft would have missed Mars orbit by about 15,000 kilometers.This article addresses the macroscopic aspects of radiation pressure. Detailed quantum mechanical aspects of interactions are addressed in specialized articles on the subject. The details of how photons of various wavelengths interact with atoms can be explored through links in the See also section.