Summary Magnetic materials 2015. The magnetic susceptibility, i.e.
... 1. Diamagnetic materials: Magnetic moment is anti-parallel to the applied magnetic field. For small fields, M is linear with H (m is constant and negative of the order of -10-6 to -10-7). This type of effect was discussed in the beginning of chapter 5. An external magnetic field will speed up the s ...
... 1. Diamagnetic materials: Magnetic moment is anti-parallel to the applied magnetic field. For small fields, M is linear with H (m is constant and negative of the order of -10-6 to -10-7). This type of effect was discussed in the beginning of chapter 5. An external magnetic field will speed up the s ...
Electromagnetic Rules
... The maximum EMF (and current) will occur when the direction of the velocity of the wire is perpendicular to the direction of the field. No EMF (or current) will be produced if the velocity and the direction of the field are parallel to each other. When the velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic f ...
... The maximum EMF (and current) will occur when the direction of the velocity of the wire is perpendicular to the direction of the field. No EMF (or current) will be produced if the velocity and the direction of the field are parallel to each other. When the velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic f ...
PHY 410 Final Examination, Spring 2008 April 30, 2008 (5:45-7:45 p.m.)
... 4. Consider an atom with spin S=1 in a crystalline solid at temperature T. The three microstates of the atom are given by m = 1,0,−1 . In the presence of both crystalline field and an external magnetic field B, the energy levels are given by E ( m) = ∆ m 2 − µmB , where ∆ is a constant energy depen ...
... 4. Consider an atom with spin S=1 in a crystalline solid at temperature T. The three microstates of the atom are given by m = 1,0,−1 . In the presence of both crystalline field and an external magnetic field B, the energy levels are given by E ( m) = ∆ m 2 − µmB , where ∆ is a constant energy depen ...
Research: I. Molecular magnetism and single
... I. Molecular magnetism and single-molecule magnets The research in the area of molecular magnetism is focused on molecular assemblies containing a finite number of exchange coupled magnetic ions (metal clusters). These kind of molecular nanomagnets, so-called single molecule magnets (SMMs) can be pl ...
... I. Molecular magnetism and single-molecule magnets The research in the area of molecular magnetism is focused on molecular assemblies containing a finite number of exchange coupled magnetic ions (metal clusters). These kind of molecular nanomagnets, so-called single molecule magnets (SMMs) can be pl ...
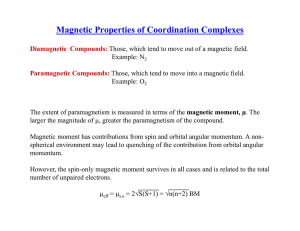
Magnetic Properties of Coordination Complexes √ √ μ
... Total unpaired electrons = 1, S = 1/2 Oxygenated form is low-spin The magnetic moment of Fe3+ and the superoxide radical involves in antiferromagnetic coupling and the oxygenated complex is not paramagnetic ...
... Total unpaired electrons = 1, S = 1/2 Oxygenated form is low-spin The magnetic moment of Fe3+ and the superoxide radical involves in antiferromagnetic coupling and the oxygenated complex is not paramagnetic ...
Band theory
... whereas there is only one 4s level with a capacity of 2 electrons. Filled energy levels can’t contribute a magnetic moment, because the two electrons in each level have opposite spin and thus cancel each other out. ...
... whereas there is only one 4s level with a capacity of 2 electrons. Filled energy levels can’t contribute a magnetic moment, because the two electrons in each level have opposite spin and thus cancel each other out. ...
Class Notes - Ms. Shevlin`s Website
... To carry out an experiment to show the magnetic field around a bar magnet using iron filings and plotting compasses To discuss places where magnets are used in everyday life ...
... To carry out an experiment to show the magnetic field around a bar magnet using iron filings and plotting compasses To discuss places where magnets are used in everyday life ...
Magnetic Forces Practice
... to the plane formed by the field and the moving charge, and is greatest when the magnetic field and current are perpendicular to each other. The force on the current carrying wire shown above is therefore into the plane of the page and is determined by using the left-hand finger rule. ...
... to the plane formed by the field and the moving charge, and is greatest when the magnetic field and current are perpendicular to each other. The force on the current carrying wire shown above is therefore into the plane of the page and is determined by using the left-hand finger rule. ...
Section 15: Magnetic properties of materials
... atomic shells is what is responsible for their paramagnetic behavior. In all other materials equation (4) breaks down as temperature decreases. They all have a critical temperature below which the variation of susceptibility with temperature is very different from its variation above this temperatur ...
... atomic shells is what is responsible for their paramagnetic behavior. In all other materials equation (4) breaks down as temperature decreases. They all have a critical temperature below which the variation of susceptibility with temperature is very different from its variation above this temperatur ...
Name Section 18-1 “Magnets and Magnetism” pages 510
... _____16). Which of these is true when the poles of atoms line up? a. The atoms cancel each other out. c. The atoms make a weak magnetic field. b. The atoms are arranged in a domain. d. The atoms do not become magnetic. 17). Discuss three things that can cause the domains of a magnet’s atoms to lose ...
... _____16). Which of these is true when the poles of atoms line up? a. The atoms cancel each other out. c. The atoms make a weak magnetic field. b. The atoms are arranged in a domain. d. The atoms do not become magnetic. 17). Discuss three things that can cause the domains of a magnet’s atoms to lose ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... Word Bank: Magnetic poles, like, current, magnetic domains, magnetic field lines, magnetism, repel, permanent magnet, opposite, electromagnet, magnetic field, alternating current, direct current, galvanometer ...
... Word Bank: Magnetic poles, like, current, magnetic domains, magnetic field lines, magnetism, repel, permanent magnet, opposite, electromagnet, magnetic field, alternating current, direct current, galvanometer ...
Simulation(s) - Faraday`s Law
... 9. What happens to the magnetic field if the direction of current in the wire loop is reversed? What happens to the strength of the magnetic field as more electrons move (as current increases)? __________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______ ...
... 9. What happens to the magnetic field if the direction of current in the wire loop is reversed? What happens to the strength of the magnetic field as more electrons move (as current increases)? __________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______ ...
NAME: Block - The Oakwood School
... 8. When there is no voltage applied the electrons are still moving randomly. Since the number of electrons moving one direction is balanced by electrons moving the opposite direction then there is no net magnetic field. There is no magnetic field because there is no net flow of electrons. Predict w ...
... 8. When there is no voltage applied the electrons are still moving randomly. Since the number of electrons moving one direction is balanced by electrons moving the opposite direction then there is no net magnetic field. There is no magnetic field because there is no net flow of electrons. Predict w ...
Value Based Questions Magnetic effects of current and Magnetism
... During lightning, the electric current is in tens of thousands of amperes, while in the nervous system, it is only a few microamperes. She further discussed with her teacher about the magnitude of the magnetic field created by these currents. • What values did Shama have? • A galvanometer coil has a ...
... During lightning, the electric current is in tens of thousands of amperes, while in the nervous system, it is only a few microamperes. She further discussed with her teacher about the magnitude of the magnetic field created by these currents. • What values did Shama have? • A galvanometer coil has a ...
Technical Description of an MIR Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI
... wires are continually bathed in liquid helium at 452.4 degrees below zero Fahrenheit. This cold is insulated by a vacuum. While superconductive magnets are expensive, the strong magnetic field allows for the highestquality imaging, and superconductivity keeps the system economical to operate. ...
... wires are continually bathed in liquid helium at 452.4 degrees below zero Fahrenheit. This cold is insulated by a vacuum. While superconductive magnets are expensive, the strong magnetic field allows for the highestquality imaging, and superconductivity keeps the system economical to operate. ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.