Magnetism - TeacherWeb
... attract each other and like poles of magnets repel. • No Monopoles: If you cut a magnet in half, you get two poles on each ...
... attract each other and like poles of magnets repel. • No Monopoles: If you cut a magnet in half, you get two poles on each ...
Physics 1 notes 4-11-13 NOVA earth`s magnetic field
... the magnetic field seems to be fading and may disappear in about one thousand years. Magnetism seems like magic attraction or repulsion. Gravity is obvious and visible; magnetic force cannot be seen. The field protects earth from sun’s cosmic rays and radiation from other stellar sources. The ...
... the magnetic field seems to be fading and may disappear in about one thousand years. Magnetism seems like magic attraction or repulsion. Gravity is obvious and visible; magnetic force cannot be seen. The field protects earth from sun’s cosmic rays and radiation from other stellar sources. The ...
x - Angelfire
... • Randomly replace some of the Mn3+ with Ga3+ to give LaMn1-xGaxO3. • Ga3+ has a full d shell (10 electrons): → Ion is diamagnetic (no magnetic moment) → Not a Jahn-Teller ion; GaO6 octahedra, unlike MnO6, are not JT-distorted. How does such Gallium-doping affect the orbital ordering and hence the m ...
... • Randomly replace some of the Mn3+ with Ga3+ to give LaMn1-xGaxO3. • Ga3+ has a full d shell (10 electrons): → Ion is diamagnetic (no magnetic moment) → Not a Jahn-Teller ion; GaO6 octahedra, unlike MnO6, are not JT-distorted. How does such Gallium-doping affect the orbital ordering and hence the m ...
Electromagnetism - juan-roldan
... composed of small areas where the groups of atoms are aligned like the poles of a magnet. These regions are called domains. All of the domains of a magnetic substance tend to align themselves in the same direction when placed in a magnetic field. These domains are typically composed of billions of a ...
... composed of small areas where the groups of atoms are aligned like the poles of a magnet. These regions are called domains. All of the domains of a magnetic substance tend to align themselves in the same direction when placed in a magnetic field. These domains are typically composed of billions of a ...
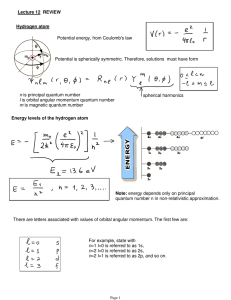
Lecture 12: Review.
... moments with the electromagnetic fields of the electrons. The level splitting caused by this interaction is even smaller than the fine structure, so it is called hyperfine structure. We consider magnetic-dipole hyperfine interaction, i.e. the interaction of the nuclear magnetic moment with the magne ...
... moments with the electromagnetic fields of the electrons. The level splitting caused by this interaction is even smaller than the fine structure, so it is called hyperfine structure. We consider magnetic-dipole hyperfine interaction, i.e. the interaction of the nuclear magnetic moment with the magne ...
01-01BasicMagnetism
... Magnetic north (MN) shows the direction a magnetic compass would point at the time the map was published. Grid north (GN) The difference between true north and grid north is an inherent effect of transforming the earth's spherical surface to a plane surface. ...
... Magnetic north (MN) shows the direction a magnetic compass would point at the time the map was published. Grid north (GN) The difference between true north and grid north is an inherent effect of transforming the earth's spherical surface to a plane surface. ...
File
... c. Strong electric current makes electromagnets d. Magnetic fields are made when the electric field changes 12. __b__ What can you make visible by sprinkling iron filings around a magnet? a. The areas called domains b. The magnetic field lines c. The magnetic forces d. The north and south poles 13. ...
... c. Strong electric current makes electromagnets d. Magnetic fields are made when the electric field changes 12. __b__ What can you make visible by sprinkling iron filings around a magnet? a. The areas called domains b. The magnetic field lines c. The magnetic forces d. The north and south poles 13. ...
Electron Spin Resonance
... Electrons have charge and spin (or more precisely angular momentum). The combination would lead you to expect that the electrons would also have a magnetic moment produced by the rotating charge. The electrons do indeed have a magnetic moment but it cannot be derived from a rotating charge, in fact ...
... Electrons have charge and spin (or more precisely angular momentum). The combination would lead you to expect that the electrons would also have a magnetic moment produced by the rotating charge. The electrons do indeed have a magnetic moment but it cannot be derived from a rotating charge, in fact ...
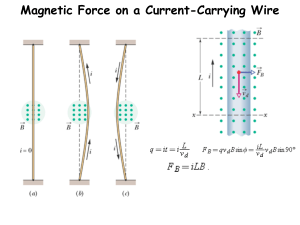
Magnetic Force on a Current-Carrying Wire - Easy Peasy All-in
... A positive charge moves along a circular path under the influence of a magnetic field. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the circle, as in Figure 21.12. If the velocity of the particle is reversed at some point along the path, will the particle retrace its path? If not, draw the ne ...
... A positive charge moves along a circular path under the influence of a magnetic field. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the circle, as in Figure 21.12. If the velocity of the particle is reversed at some point along the path, will the particle retrace its path? If not, draw the ne ...
A Magnet is an object with a magnetic force or field that attracts or
... A Maglev (Magnetic Levitation) train runs on electricity and uses magnetic force to float slightly above the rails or tracks because the magnets are repelling each other. These quiet trains are not slowed down by friction and travel superfast (up to 300 miles per hour). ...
... A Maglev (Magnetic Levitation) train runs on electricity and uses magnetic force to float slightly above the rails or tracks because the magnets are repelling each other. These quiet trains are not slowed down by friction and travel superfast (up to 300 miles per hour). ...
Chapter 19-3 and 20
... particles at rest are not affected by magnetic field (stationary) ► When moving, charged particles can be deflected by magnetic fields ► Used in TV tubes to create picture on screen ► Earth’s magnetic field deflects charged particles from outer space (cosmic rays) ...
... particles at rest are not affected by magnetic field (stationary) ► When moving, charged particles can be deflected by magnetic fields ► Used in TV tubes to create picture on screen ► Earth’s magnetic field deflects charged particles from outer space (cosmic rays) ...
Engineering Physics
... 3. Principles of Quantum Mechanics: Waves and Particles, de Broglie Hypothesis , Matter Waves, Davisson and Germer’s Experiment, Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle, Schrödinger’s Time Independent Wave Equation - Physical Significance of the Wave Function – Infinite square well potential extension to ...
... 3. Principles of Quantum Mechanics: Waves and Particles, de Broglie Hypothesis , Matter Waves, Davisson and Germer’s Experiment, Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle, Schrödinger’s Time Independent Wave Equation - Physical Significance of the Wave Function – Infinite square well potential extension to ...
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
... • In some inst., the freq. of the source is held constant while the strength of the field is scanned. • CW spectroscopy is inefficient in comparison to FT NMR, as it probes the NMR response at individual frequencies in succession. As the NMR signal is intrinsically weak, the observed spectra suffer ...
... • In some inst., the freq. of the source is held constant while the strength of the field is scanned. • CW spectroscopy is inefficient in comparison to FT NMR, as it probes the NMR response at individual frequencies in succession. As the NMR signal is intrinsically weak, the observed spectra suffer ...
Magnetism I - Galileo and Einstein
... • But it’s pretty rare: only 100 tons a year produced, all in China…and the Chinese are cutting back exports. • Meanwhile (from Wikipedia) • Neodymium-iron-boron magnets can have up to 6% of the neodymium substituted with dysprosium[20] to raise the coercivity for demanding applications such as driv ...
... • But it’s pretty rare: only 100 tons a year produced, all in China…and the Chinese are cutting back exports. • Meanwhile (from Wikipedia) • Neodymium-iron-boron magnets can have up to 6% of the neodymium substituted with dysprosium[20] to raise the coercivity for demanding applications such as driv ...
Magnetism - Physical Science
... – 2. Like poles repel. Unlike poles attract. – 3. Earth has magnetic poles. • A) A compass needle is a small bar magnet that can freely rotate. • B) A compass needle always points north. ...
... – 2. Like poles repel. Unlike poles attract. – 3. Earth has magnetic poles. • A) A compass needle is a small bar magnet that can freely rotate. • B) A compass needle always points north. ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.