4 Electromagnetism
... Magnetic force on a moving charge Hall voltage a Explanation of Hall effect b Derivation of Hall voltage c Characteristics of conductors revealed by Hall voltage Measuring magnetic fields by a Hall probe ...
... Magnetic force on a moving charge Hall voltage a Explanation of Hall effect b Derivation of Hall voltage c Characteristics of conductors revealed by Hall voltage Measuring magnetic fields by a Hall probe ...
Magnetic fraud
... notice a dynamic interaction with each other of parallel flowing streams of electrons. And as regards magnetic poles, they should be treated as some auxiliary images, that, when someone uses them incompetently, are misleading. In order not to mislead himself, one should understand what is the source ...
... notice a dynamic interaction with each other of parallel flowing streams of electrons. And as regards magnetic poles, they should be treated as some auxiliary images, that, when someone uses them incompetently, are misleading. In order not to mislead himself, one should understand what is the source ...
Constructive Interference
... Modern physics: understand in detail how nature works at distances 100,000,000,000,000 times smaller than we can see! ...
... Modern physics: understand in detail how nature works at distances 100,000,000,000,000 times smaller than we can see! ...
Coherent control of a single nuclear spin with an electric field
... with those electrons. In recent experiments at very low temperature (30 mK), we were able to show that the terbium’s nuclear spin can be manipulated purely by an oscillating electric field (the microwave field represented in Fig. 1). This is remarkable because the magnetic dipole associated with the ...
... with those electrons. In recent experiments at very low temperature (30 mK), we were able to show that the terbium’s nuclear spin can be manipulated purely by an oscillating electric field (the microwave field represented in Fig. 1). This is remarkable because the magnetic dipole associated with the ...
2·QUIZLET VOCABULARY: Quantum Numbers Study online at
... 4. Hunds rule: orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin 5. Magnetic (orbital) quantum Number: ml Indicates orientation of orbital in space S- 1 orbital P- 3 or ...
... 4. Hunds rule: orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin 5. Magnetic (orbital) quantum Number: ml Indicates orientation of orbital in space S- 1 orbital P- 3 or ...
Slide 1
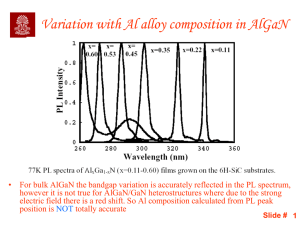
... • For bulk AlGaN the bandgap variation is accurately reflected in the PL spectrum, however it is not true for AlGaN/GaN heterostructures where due to the strong electric field there is a red shift. So Al composition calculated from PL peak position is NOT totally accurate ...
... • For bulk AlGaN the bandgap variation is accurately reflected in the PL spectrum, however it is not true for AlGaN/GaN heterostructures where due to the strong electric field there is a red shift. So Al composition calculated from PL peak position is NOT totally accurate ...
magnetic field
... cobalt, and certain alloys. They become strongly magnetized in the same direction as the magnetizing field, with high values of permeability. Paramagnetic materials include aluminum, platinum, manganese, and chromium. They become weakly magnetized in the same direction as the magnetizing field. Th ...
... cobalt, and certain alloys. They become strongly magnetized in the same direction as the magnetizing field, with high values of permeability. Paramagnetic materials include aluminum, platinum, manganese, and chromium. They become weakly magnetized in the same direction as the magnetizing field. Th ...
Even if the forces acting on a body are balanced in
... The direction of the force is reversed if either the direction of the current or the direction of the magnetic field is reversed – so you must switch the battery connections round or turn the magnet round A coil of wire current carrying wire placed between the poles of a fixed magnet rotates because ...
... The direction of the force is reversed if either the direction of the current or the direction of the magnetic field is reversed – so you must switch the battery connections round or turn the magnet round A coil of wire current carrying wire placed between the poles of a fixed magnet rotates because ...
BASIC CONCEPT OF SUPERCONDUCTIVITY: A PATH FOR HIGH
... framed coherently just in the BCS theory (1957). Badía-Majós (2006), aiming to understand stable levitation when a magnet is posed on a superconductor, proposed a treatment of superconductors of I and II type to give into account Meissner effect as well as pinning where “the main concepts involved a ...
... framed coherently just in the BCS theory (1957). Badía-Majós (2006), aiming to understand stable levitation when a magnet is posed on a superconductor, proposed a treatment of superconductors of I and II type to give into account Meissner effect as well as pinning where “the main concepts involved a ...
Permanent magnets - KCPE-KCSE
... understand that magnets repel and attract other magnets and attract magnetic substances describe the properties of magnetically hard and soft materials understand the term ‘magnetic field line’ understand that magnetism is induced in some materials when they are placed in a magnetic field describe e ...
... understand that magnets repel and attract other magnets and attract magnetic substances describe the properties of magnetically hard and soft materials understand the term ‘magnetic field line’ understand that magnetism is induced in some materials when they are placed in a magnetic field describe e ...
the magnetic field of the hot spectroscopic binary hd 5550
... also reported that the secondary has chemical peculiarities, but they could not distinguish more precisely the peculiar type of this component. We observed HD 5550 in the frame of the BinaMIcS (Binarity and Magnetic Interactions in various classes of Stars) project, with the goal to understand the i ...
... also reported that the secondary has chemical peculiarities, but they could not distinguish more precisely the peculiar type of this component. We observed HD 5550 in the frame of the BinaMIcS (Binarity and Magnetic Interactions in various classes of Stars) project, with the goal to understand the i ...
Single crystal growth of Heisenberg spin ladder and spin chain
... Low dimensional magnets have attracted great attention because of their simplicity in theoretical models, novel quantum phenomena and relation to high temperature superconductivity. Among them, quasi-1D systems such as spin ladders and spin chains have found their realization in several materials, e ...
... Low dimensional magnets have attracted great attention because of their simplicity in theoretical models, novel quantum phenomena and relation to high temperature superconductivity. Among them, quasi-1D systems such as spin ladders and spin chains have found their realization in several materials, e ...
Magnetism (Chap. 24) - Alejandro L. Garcia
... Magnetic Domains The magnetic field of an single iron atom is so strong that interactions among adjacent atoms cause large clusters of atoms, called magnetic domains, to line up with one another. A microscopic view of magnetic domains in a crystal of iron. Each domain consists of billions of aligne ...
... Magnetic Domains The magnetic field of an single iron atom is so strong that interactions among adjacent atoms cause large clusters of atoms, called magnetic domains, to line up with one another. A microscopic view of magnetic domains in a crystal of iron. Each domain consists of billions of aligne ...
What is magnetism?
... Magnetism is the force of attraction or repulsion in and around a material. Magnetism is present is all materials but at such low levels that it is not easily detected. Certain materials such as magnetite, iron, steel, nickel, cobalt and alloys of rare earth elements, exhibit magnetism at levels tha ...
... Magnetism is the force of attraction or repulsion in and around a material. Magnetism is present is all materials but at such low levels that it is not easily detected. Certain materials such as magnetite, iron, steel, nickel, cobalt and alloys of rare earth elements, exhibit magnetism at levels tha ...
9J Force Fields and Electromagnets
... When you rub two materials together, electrons may be transferred from one material to the other. If the objects are insulating materials, the object that gains electrons has a negative charge of static electricity. The object that loses electrons has a positive charge. A positively charged object w ...
... When you rub two materials together, electrons may be transferred from one material to the other. If the objects are insulating materials, the object that gains electrons has a negative charge of static electricity. The object that loses electrons has a positive charge. A positively charged object w ...
Electric and Magnetic Forces Study Guide for Content Test
... Uncharged vs. positively charged vs. negatively charged objects Electric Repel vs. Magnetic repel Electric attraction vs. magnetic attraction ...
... Uncharged vs. positively charged vs. negatively charged objects Electric Repel vs. Magnetic repel Electric attraction vs. magnetic attraction ...
... Given two systems of N1 ≈ N2 = 1022 spins with multiplicity functions g1(N1,s1) and g2(N2,s-s1), the product g1g2 as a function of s1 is relatively sharply peaked at s1 = ŝ1. For s1 = ŝ1 + 1012, the product g1g2 is reduced by 10-174 from its peak value. Use the Gaussian approximation of the multipli ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.