AY 105 Lab Experiment #3: Optical aberrations
... a particular rotation angle (or two) and specify the field angle(s) in Code V to produce a series of spot diagrams over the focus range. Qualitatively compare the appearance of the actual image to the spot diagrams. Estimate from the Code V results the size of the image at your off-axis angle, and c ...
... a particular rotation angle (or two) and specify the field angle(s) in Code V to produce a series of spot diagrams over the focus range. Qualitatively compare the appearance of the actual image to the spot diagrams. Estimate from the Code V results the size of the image at your off-axis angle, and c ...
File
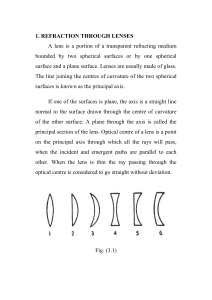
... spherical aberration, coma and astigmatism. Fig. 3.18 illustrates the presence of curvature' of the field in the image formed by a convex lens. A real image formed by a convex lens curves towards the lens [Fig, 3.18(a) and a virtual image curves away from the lens [Fig. 3.18 (b)]. Fig. 3.19 represen ...
... spherical aberration, coma and astigmatism. Fig. 3.18 illustrates the presence of curvature' of the field in the image formed by a convex lens. A real image formed by a convex lens curves towards the lens [Fig, 3.18(a) and a virtual image curves away from the lens [Fig. 3.18 (b)]. Fig. 3.19 represen ...
Chapter 3 Geometric Optics
... be projected onto a white card or piece of paper for easy viewing). In Section 3.3, you will perform a more quantitative study of a prism and its dispersed spectrum. ...
... be projected onto a white card or piece of paper for easy viewing). In Section 3.3, you will perform a more quantitative study of a prism and its dispersed spectrum. ...
Variable Focus Video: Reconstructing Depth and Video
... However, none of these methods can handle the DFD problem in the presence of scene or camera motion. In this paper, we present a framework to extend the DFD problem to scenarios with scene or camera motion. Active Range Sensors: These sensors use an active pulse (e.g., laser, ultrasound) and either ...
... However, none of these methods can handle the DFD problem in the presence of scene or camera motion. In this paper, we present a framework to extend the DFD problem to scenarios with scene or camera motion. Active Range Sensors: These sensors use an active pulse (e.g., laser, ultrasound) and either ...
High refractive index Fresnel lens on a fiber fabricated by
... Lensed fibers have been used for a long time in integrated optics to improve coupling efficiency to optical chips [1]. They are also used as probes in various applications such as optical trapping [2], endoscopic imaging [3], optical coherence tomography [4] and glucose sensing [5]. The major limita ...
... Lensed fibers have been used for a long time in integrated optics to improve coupling efficiency to optical chips [1]. They are also used as probes in various applications such as optical trapping [2], endoscopic imaging [3], optical coherence tomography [4] and glucose sensing [5]. The major limita ...
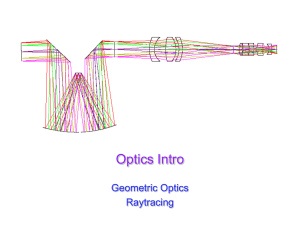
Lens Aberrations and Ray Tracing 1 Background
... Where would spherical aberrations be an issue? Many times an experiment will require a wellcollimated beam or focusing as much energy as possible into a point, situations that mandate minimal spherical aberrations. Which lens should be used? Bi-convex or plano convex — and in the latter case, which ...
... Where would spherical aberrations be an issue? Many times an experiment will require a wellcollimated beam or focusing as much energy as possible into a point, situations that mandate minimal spherical aberrations. Which lens should be used? Bi-convex or plano convex — and in the latter case, which ...
lenses - Van Buren Public Schools
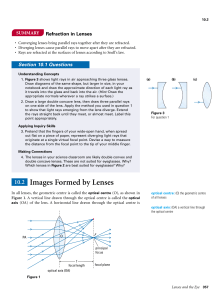
... The Three Principal Rays To locate the position of the image, you only have to know the paths of two rays from a point on the object, represented by the vertical arrow. Any point except for the point on the principal axis will work, but it is customary to choose a point at the tip of the arrow. The ...
... The Three Principal Rays To locate the position of the image, you only have to know the paths of two rays from a point on the object, represented by the vertical arrow. Any point except for the point on the principal axis will work, but it is customary to choose a point at the tip of the arrow. The ...
Chapter 2.1 - Focusing Fundamentals
... One of the difficult challenges in CCD imaging is making very small focus changes. Some focuser designs make this easy, but many do not. For example, refractors typically use rack-and-pinion focusers. These are effective for visual use, but they are often too coarse for CCD imaging. What works well ...
... One of the difficult challenges in CCD imaging is making very small focus changes. Some focuser designs make this easy, but many do not. For example, refractors typically use rack-and-pinion focusers. These are effective for visual use, but they are often too coarse for CCD imaging. What works well ...
Lecture 2
... Curvature of Field - When visible light is focused through a curved lens, the image plane produced by the lens will be curved The image appears sharp and crisp either in the center or on the edges of the viewfield but not both ...
... Curvature of Field - When visible light is focused through a curved lens, the image plane produced by the lens will be curved The image appears sharp and crisp either in the center or on the edges of the viewfield but not both ...
Intraframe Scene Capturing and Speed Measurement Based on
... caused by the leakage (until readout) is in the same order of magnitude (9). As a result, a bright trace will appear on the image, which represents the movement of the headlight during the readout. Technical details connected with the imager setup are described in Section 4.1. 3.3. Test Hardware. In ...
... caused by the leakage (until readout) is in the same order of magnitude (9). As a result, a bright trace will appear on the image, which represents the movement of the headlight during the readout. Technical details connected with the imager setup are described in Section 4.1. 3.3. Test Hardware. In ...
Porous Biomimetic Microlens Arrays as Multifunctional Optical
... on eyes as their photosensory organs for focusing, detection and imaging. Million of years of evolution have perfected the design of the lenses that are used for the image formation by organisms, and resulted in optical structures, whose multifunctional and hybrid characteristics are unparalleled in ...
... on eyes as their photosensory organs for focusing, detection and imaging. Million of years of evolution have perfected the design of the lenses that are used for the image formation by organisms, and resulted in optical structures, whose multifunctional and hybrid characteristics are unparalleled in ...
A Coaxial Optical Scanner for Synchronous Acquisition of 3D
... without a projector. Instead, we leverage the fact that we collect images from multiple viewpoints, and we introduce a technique for resolving the phase ambiguity through triangulation. A quantitative analysis of our results shows that this method provides depth with sub-millimeter precision (often ...
... without a projector. Instead, we leverage the fact that we collect images from multiple viewpoints, and we introduce a technique for resolving the phase ambiguity through triangulation. A quantitative analysis of our results shows that this method provides depth with sub-millimeter precision (often ...
Hwk Set #7 - Publisher`s solutions
... The figure shows the two lenses and a ray-tracing diagram. The ray tracing shows that the lens combination will produce a virtual, inverted image in front of the second lens. Solve: (a) From the ray-tracing diagram, we find that the image is 3.3 cm behind the second lens and the height of the final ...
... The figure shows the two lenses and a ray-tracing diagram. The ray tracing shows that the lens combination will produce a virtual, inverted image in front of the second lens. Solve: (a) From the ray-tracing diagram, we find that the image is 3.3 cm behind the second lens and the height of the final ...
PowerPoint Lecture - UCSD Department of Physics
... • Just as with mirrors, curved lenses follow same rules as flat interfaces, using local surface normal A lens, with front and back curved surfaces, bends light twice, each diverting incoming ray towards centerline. Follows laws of refraction at each surface. Parallel rays, coming, for instance from ...
... • Just as with mirrors, curved lenses follow same rules as flat interfaces, using local surface normal A lens, with front and back curved surfaces, bends light twice, each diverting incoming ray towards centerline. Follows laws of refraction at each surface. Parallel rays, coming, for instance from ...
Phys Chp 10
... called the principal axis (PA). If a lens is thin, a group of rays parallel to the principal axis is refracted through a point on the principal axis called the principal focus (F ). The focal length ( f ) is the distance between the principal focus and the optical centre, measured along the principa ...
... called the principal axis (PA). If a lens is thin, a group of rays parallel to the principal axis is refracted through a point on the principal axis called the principal focus (F ). The focal length ( f ) is the distance between the principal focus and the optical centre, measured along the principa ...
Overview
... Small disc source and small receiver (pt source solution) Large disc source and small receiver (non-pt source solution) Comparison of point source and non-point source solutions ...
... Small disc source and small receiver (pt source solution) Large disc source and small receiver (non-pt source solution) Comparison of point source and non-point source solutions ...
How Do Lenses and Mirrors Affect Light?
... or plastic. They are made to cause light rays to form certain kinds of images. What are some objects that use lenses? What are the lenses being used for in these objects? Why do lenses work the way they do? Recall what you learned about light in Lesson 1. • Light always travels in straight lines. • ...
... or plastic. They are made to cause light rays to form certain kinds of images. What are some objects that use lenses? What are the lenses being used for in these objects? Why do lenses work the way they do? Recall what you learned about light in Lesson 1. • Light always travels in straight lines. • ...
All-dielectric subwavelength metasurface focusing lens
... dielectric meta-surface lenses can be readily wafer-level integrated and manufactured using processes compatible with CMOS technology. These lenses can be designed to improve the effective array filling factor by being tightly mapped on a surface. Size, weight, and other packaging characteristics fo ...
... dielectric meta-surface lenses can be readily wafer-level integrated and manufactured using processes compatible with CMOS technology. These lenses can be designed to improve the effective array filling factor by being tightly mapped on a surface. Size, weight, and other packaging characteristics fo ...
Imaging the near field
... In the previous section we gave some qualitative arguments as to the properties of metal-dielectric multilayer stacks and is clear that for P-polarized light in the quasistatic limit this structure would behave as a near-perfect ‘fibre optic bundle’. In the electrostatic (magnetostatic) limit of larg ...
... In the previous section we gave some qualitative arguments as to the properties of metal-dielectric multilayer stacks and is clear that for P-polarized light in the quasistatic limit this structure would behave as a near-perfect ‘fibre optic bundle’. In the electrostatic (magnetostatic) limit of larg ...
Desert Island themed project - science
... ■ long sight, caused by the eyeball being too short, or the eye lens being unable to focus ■ short sight, caused by the eyeball being too long, or the eye lens being unable to focus. c) Range of vision. The eye can focus on objects between the near point and the far point. e) The power of a lens is ...
... ■ long sight, caused by the eyeball being too short, or the eye lens being unable to focus ■ short sight, caused by the eyeball being too long, or the eye lens being unable to focus. c) Range of vision. The eye can focus on objects between the near point and the far point. e) The power of a lens is ...
PPT
... • Just as with mirrors, curved lenses follow same rules as flat interfaces, using local surface normal A lens, with front and back curved surfaces, bends light twice, each diverting incoming ray towards centerline. Follows laws of refraction at each surface. Parallel rays, coming, for instance from ...
... • Just as with mirrors, curved lenses follow same rules as flat interfaces, using local surface normal A lens, with front and back curved surfaces, bends light twice, each diverting incoming ray towards centerline. Follows laws of refraction at each surface. Parallel rays, coming, for instance from ...
ptical Short Course International
... number of lenses. All of these losses are cumulative as the light progresses through the projection lens. Let’s take a walk through one optical element and see what happens to our starting 100% value of a light ray. We start out at 100% and hit the antireflection coating on the front surface of the ...
... number of lenses. All of these losses are cumulative as the light progresses through the projection lens. Let’s take a walk through one optical element and see what happens to our starting 100% value of a light ray. We start out at 100% and hit the antireflection coating on the front surface of the ...
The Truth About Base Curves - ABO-NCLE
... 4.99%. This much of a difference in magnification between the two eyes will induce aniseikonic symptoms that include: Asthenopia, Diplo!pia, Headaches, Nausea and Suppression of one eye20. By simply changing the base curve and thickness to (8 b.c., 5.9 ct.) in the right lens, which is the same as th ...
... 4.99%. This much of a difference in magnification between the two eyes will induce aniseikonic symptoms that include: Asthenopia, Diplo!pia, Headaches, Nausea and Suppression of one eye20. By simply changing the base curve and thickness to (8 b.c., 5.9 ct.) in the right lens, which is the same as th ...
1 CHAPTER 4 OPTICAL ABERRATIONS 4.1 Introduction We have
... The angle of incidence of the ray at R is 25.442 358 40 degrees to the normal, and the angle of refraction is 43.421 850 83 degrees. The net result of this is that there is a short linear “image” at T perpendicular to the tangential plane, and a short linear “image” at S perpendicular to the sagitta ...
... The angle of incidence of the ray at R is 25.442 358 40 degrees to the normal, and the angle of refraction is 43.421 850 83 degrees. The net result of this is that there is a short linear “image” at T perpendicular to the tangential plane, and a short linear “image” at S perpendicular to the sagitta ...
Camera

A camera is an optical instrument for recording images, which may be stored locally, transmitted to another location, or both. The images may be individual still photographs or sequences of images constituting videos or movies. The word camera comes from camera obscura, which means ""dark chamber"" and is the Latin name of the original device for projecting an image of external reality onto a flat surface. The modern photographic camera evolved from the camera obscura. The functioning of the camera is very similar to the functioning of the human eye.